Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Vamsidhar Velcheti
Author of
-
+
MA15 - Usage of Computer and Molecular Analysis in Treatment Selection and Disease Prognostication (ID 141)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Pathology
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:John Le Quesne, Noriko Motoi
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 15:45 - 17:15, Tokyo (1982)
-
+
MA15.05 - Computerized Measurements of Cellular Diversity on H&E Tissue Are Prognostic of OS and Associated with Mutational Status in NSCLC (Now Available) (ID 1975)
15:45 - 17:15 | Presenting Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Tumor heterogeneity is known to be implicated in chemotherapeutic resistance and poor prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this study we sought to evaluate the role of computer extracted features reflecting the intrinsic cellular morphological diversity (ICMD) of tumors from digitized H&E stained images of early-stage NSCLC patients. Additionally, we sought to evaluate the association of these ICMD features in adenocarcinomas with the ALK and EGFR mutational status.
Method
Two cohorts, D1 and D2, of digitized H&E stained tissue microarray images (TMA) of NSCLC, n=395 and n=91, respectively, were used for modeling the ICMD predictor. A pretrained deep learning model was used for segmentation of nuclei, and clusters of proximally located nuclei were identified. The ICMD features were then extracted as the variations in shape, size, and texture measurements of nuclei within the clusters. A Cox proportional hazard model using the ICMD features was then trained for lung adenocarcinomas (LUAD, n=270), and squamous cell carcinomas (LUSC, n=216), separately, and was validated on independent cohort from (D3) The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (n=473) to predict Overall Survival (OS). Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed on (D3).
Result
In (D3), high risk patients predicted by the ICMD features had significantly poorer survival (HR (95% CI) = 1.48 (1.06-2.06), p=0.021 for LUSC, HR (95% CI) = 1.59 (1.11-2.29), p=0.006 for LUAD) in univariate analysis. In multivariate analysis, controlling for major clinical variables, ICMD was independently associated with 5-year OS (p<0.016). (See Table 1) We also found that ICMD features were associated with driver mutations ALK (p=0.0204) and EGFR (p=0.0017) in LUAD.
Table 1| Multivariate analysis for overall survival on the validation set D3.
ConclusionMultivariate Cox Proportional Hazard Model Analysis Controlling for Other Variables
TCGA-LUSC
TCGA-LUAD
Variable
HR (95% CI)
p value
HR (95% CI)
p value
Age (>65 vs <=65)
1.14(0.81-1.61)
0.451
0.89(0.63-1.28)
0.540
Smoking status
1.36(0.83-2.23)
0.221
1.14(0.64-2.01)
0.661
Overall Stage (Stage II vs I)
1.13(0.66-1.94)
0.651
1.86(1.04-3.32)
0.037
T-Stage (T2,3 vs T1)
1.26(0.85-1.87)
0.244
1.25(0.85-1.85)
0.263
N-Stage (N1 vs N0)
1.36(0.77-2.41)
0.292
3.11(1.55-6.23)
0.001
Developed Model
High risk vs. Low risk
1.52(1.08-2.13)
0.016
1.55(1.09-2.22)
0.015
CI = 95% confidence interval; HR = Mantel-Haenszel Hazard ratio. Values in bold are statistically significant, p<=0.05.
Computer extracted image features of cellular diversity were able to predict OS in NSCLC and were also associated with the ALK and EGFR mutational status. Future work will entail evaluating ICMD features in predicting added benefit of adjuvant therapy in early stage NSCLCs as well as correlating with gene expression data.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA25 - Precision Medicine in Advanced NSCLC (ID 352)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Sebastian Defranchi, Karen Kelly
- Coordinates: 9/10/2019, 14:30 - 16:00, Dublin (1997)
-
+
MA25.02 - Arrangement and Architecture of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte on H&E Slides Predict OS in Nivolumab Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Now Available) (ID 2911)
14:30 - 16:00 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are a promising and novel approach to treating chemotherapy refractory advanced NSCLC as well as first-line combination therapy in certain NSCLC. Nivolumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor is a promising ICI showing durable benefit with low toxicity in these patients. While PD-L1 positivity is an established tissue based biomarker for response to Nivolumab, studies have shown response rates ranging from 20-50%. Recent research has shown that TILs have been implicated in cancer aggressiveness as well as immune response. In this work, we go beyond simply counting TILs, and apply novel computer-extracted features characterizing the interaction and spatial co-localization of TILs and cancer nuclei (SpaTIL) in stratifying patients based on OS following nivolumab therapy.
Method
H&E tissue slides obtained from pre-treatment biopsies of 96 NSCLC patients treated with nivolumab were digitized and included for this study from 3 different institutions with the tumor region annotated by pathologists. Then 85 SpaTIL features related to TIL density, architecture and co-localization with tumor cells have been extracted to represent each patient. The most discriminative and uncorrelated features were selected by Elastic-Net regularized Cox-regression model to predict OS. The model was trained on D1 (n=25) and independently validated in D2 (n=32) and D3 (n=64). Multivariate analysis with clinico-pathologic factors was also performed.
Result
The top features consisted of the abundance of TILs around tumor cells and the distribution of the TILs. On the validation set, SpaTIL classifier yielded a HR=3.03 (95%CI=1.1 -8.35; p=0.042) on D2 and HR=4.12 (95%CI=1.87-9.09; p=0.02) on D3 by a log-rank test. On multivariate analysis with stage, smoking, histologic type, total lymphocyte count (See Table 1) SpaTIL was independently prognostic of OS (HR=7.88; 95%CI=1.66 – 37.216; p=0.009).

Table 1. Multivariate analysis for overall survival on the validation sets D2 and D3 Variables
HR(95% CI)
p value
Age (>65 vs <=65 yrs)
0.99(0.97-1.03)
0.67
Gender (Male vs Female)
1.05(0.75-2.79)
0.88
Smoking Status
(Former vs Never smoker)
3.19(0.92-11.061)
0.07
Histological Subtypes (Adeno vs Squamous)1
1.06(0.13-8.54)
0.95
EGFR status
1.32(0.49-3.52)
0.58
ALK status
0.63(0.36-1.10)
0.10
Total lymphocyte count
0.99(0.99-1.00)
0.33
SpaTIL Classifier
7.88(1.66-37.216)
0.009
CI = confidence interval; HR = Mantel-Haenszel Hazard ratio. Values in bold are statistically significant, p<=0.05.
Conclusion
Spatial interaction of TILs and cancer are independently prognostic of OS in nivolumab treated NSCLC. Further validation needs to be done to evaluate its utility.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (ID 158)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 09:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-86 - Occurrence of de Novo Dual HER2/HER3 or HER2/EGFR TMD Mutations: Extending the Spectrum of Targetable Mono-HER2 TMD in NSCLC? (ID 956)
09:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
HER2 (ERBB2) TMD mutations have recently been described as novel solo actionable drivers in NSCLC responsive to afatinib in small series. However, dual occurrence of de novo EGFR or HER3 (ERBB3) TMD mutations together with HER2 TMD mutations, which may have implications for dimerization patterns and treatment, has not been described.
Method
Hybrid-capture based comprehensive genomic profiling was performed on blood-based circulating tumor DNA (n=5,200) or FFPE tissue (n= 45,780) samples collected during clinical care from 50,980 unique NSCLC patients.
Result
HER2 TMD mutations were identified in 0.12% (60/50,980) of cases and included V659E (n=33), V659D (n=8), G660D (n=15), V659E+G660R, V659_I661>VVEGI, G660E>R, and S653C (1 each). Within this subset, the median age of patients was 61 years (range 33-91) and 62% were female. No co-occurring known NSCLC driver alterations were detected, except one case with EGFR exon 19 deletion and one case with EGFR L858R and lung co-primary tumors noted. However, co-occurring HER3 (I649R) or EGFR (G652R) TMD mutations were found in 18% (11/60) and 5.0% (3/60) of cases, respectively. Notably, these ERBB3 or EGFR TMD mutations only co-occurred with HER2 TMD V>D (8/9 cases) or G>D (7/15 cases), but not with V>E changes (0/34 cases; p=0.0002). HER2 amplification co-occurred with V659E in 15% (5/34) of cases, and G660D mutation was seen with the oncogenic extracellular domain S310F mutation in one case. Importantly, neither EGFR G652R nor ERBB3 I649R was found in the absence of a HER2 TMD mutation. Preliminary modelling studies suggest formation of a salt-bridge which would increase propensity for HER2/HER3 and HER2/EGFR heterodimerization favoring receptor activation. Two patients in this series with V659E were previously reported to have responded to afatinib and 1 patient with G660D+I649R did not respond to afatinib. Updated clinical data for these patients and others treated with HER2-tageted therapies will be presented.
Conclusion
HER2 TMD mutations (V659D/E or G660D/R) are uncommon but targetable driver alterations in NSCLC. In cases with HER2 TMD V>D or G>D, a de novo co-existing EGFR or HER3 TMD mutation was frequently observed (88% and 47%, respectively), which may explain differential dimerization preference and in turn response to ERBB inhibitors. We hypothesize that dual HER2/HER3 or HER2/EGFR TMD mutants may be more aggressive than single HER2 TMD mutants due to the arginine-aspartic acid interaction, and these dual mutants may require combined kinase inhibitor + antibody therapy to block dimerization. Studies utilizing models to further characterization these co-alterations are in progress.
-
+
P1.04 - Immuno-oncology (ID 164)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Immuno-oncology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 09:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.04-25 - CT Based Vessel Tortuosity Features Are Prognostic of Overall Survival and Predictive of Immunotherapy Response in NSCLC Patients (ID 826)
09:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Recently majority of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) without targetable mutations are treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). Since there are currently no validated biomarkers for predicting benefit of immunotherapy (IO), there is an unmet clinical need for development of such biomarkers. The tumor vasculature is a key component of the tumor micro-environment that can influence its behavior and therapeutic refractoriness. We aimed to evaluate the prognostic and predictive potential of quantitative vessel trotuosity (QVT), in the NSCLC patients treated with ICI drugs. Two hypotheses were established: first, the QVT on pre-treatment CT scans of NSCLC patients are associated with overall survival (OS). Second, the prognostic QVT features can lead to identify the patients who will benefit from IO.
Method
This study include 128 patients with advanced NSCLC. All patients underwent a baseline contrast CT imaging. Patients who did not receive IO drugs after 2 cycles due to a lack of response or progression as per RECIST were classified as non-responders. The dataset was splitted into a discovery (N=64) and validation sets (N=64). A set of 74 QVT features pertaining to tortuosity and curvature of tumor vasculature was extracted in CT scans. The initial set of QVT features were reduced to 8 features using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) in conjunction with OS data of the patients. Then, cox proportional hazard model was used to determine the contribution of each feature for categorizing survival groups. The weighted sum of selected 8 features gave a risk score (QRS) per patient. Patients in validation set were stratified based on QRS using the cutoff and feature weights learned in the discovery set. Prognostic features in conjunction with a linear discriminant machine learning model and OS were used to build a model to predict the response to IO. The prognostic features were also used for unsupervised clustering of the patients.
Result
The QRS risk score was able to stratify patients into two survival groups in validation set (Fig1. a-b) with p-value=0.022, Hazard ratio (HR)=0.47 and concordance index (CI)=0.61. The response prediction model yielded an AUC of 0.64±0.03 (Fig1.c). The agreement between patients with high OS and positive response to therapy was found to be 0.62 on unsupervised clustering method (Fig1. d).
Conclusion
The CT extracted QVT features was found to be prognostic of OS and also showed predictive value that could be used to identify patients who will benefit from IO.
-
+
P1.16 - Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research (ID 186)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 09:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.16-15 - Rates of Systemic Anticancer Therapy (SACT) for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (aNSCLC) in the US, 2011–2018 (ID 2704)
09:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
The SACT options for aNSCLC continue to increase each year with approvals of more effective therapies that improve long-term outcomes, such as immunotherapies (IO). Our aim was to examine trends in SACT rates from 2011-2018 for patients with aNSCLC and no known EGFR/ALK aberrations at US community oncology practices.
Method
We used the nationwide Flatiron Health EHR-derived database (data cutoff: 31Jan2019), which incorporates oncologist-defined, rule-based lines of therapy. Adults with aNSCLC diagnosis date from Jan2011-Jun2018, inclusive, with recorded EHR activity ≤90 days after diagnosis, were eligible. Patients with known EGFR/ALK-positive tumors, or nonsquamous histology (NSQ) with unknown or untested EGFR/ALK status, were excluded. We summarized no-treatment and first-line (1L) SACT rates as a proportion of aNSCLC diagnosed from 2011-2018, while limiting 2L and 3L SACT rates to aNSCLC diagnoses from 2011-2016 in order to have sufficient follow-up. Results were stratified by NSQ and squamous (SQ) histology, as well as by pre-IO and post-IO years of aNSCLC diagnosis, defined broadly as 2011-2014 and 2015+, respectively, based on the earliest IO approval for 2L therapy in Mar2015.
Result
The figure depicts 1L, 2L, and 3L SACT rates by year of aNSCLC diagnosis for EGFR/ALK-negative NSQ and for SQ. For NSQ, the pre-IO and post-IO no-treatment rates were 28% (2286/8246) and 22% (2520/11,639), respectively. For SQ, the pre-IO and post-IO no-treatment rates were 34% (1781/5200) and 26% (1549/6040).
Conclusion
For both EGFR/ALK-negative NSQ and SQ aNSCLC, 1L SACT rates are trending upward, with no-treatment rates showing substantial drops in the post-IO (versus pre-IO) period. The 2L and 3L SACT rates are variable for both NSQ and SQ; and SACT rates for NSQ tend to be substantially greater than for SQ across all lines of therapy and years of diagnosis.
-
+
P1.16-42 - Real-World Trends in Systemic Anticancer Therapy (SACT) for Squamous Advanced NSCLC (aNSCLC) in the US, 2011–2018 (ID 2768)
09:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
The SACT options for aNSCLC continue to increase each year with approvals of more effective therapies that improve long-term outcomes, as seen with immunotherapies (IO). Our aim was to examine real-world trends in SACT distribution and sequence from first- to second-line (1L-2L) for squamous aNSCLC from 2011-2018 at US community oncology practices.
Method
This study used the nationwide Flatiron Health de-identified, EHR-derived database (cutoff: 31Jan2019). Eligible patients were adults who initiated 1L SACT from Jan2011-Jun2018 for aNSCLC with squamous histology, excluding patients with known EGFR/ALK-positive tumors. Descriptive analyses included patients receiving ≥1 SACT dose, assigning all SACT regimens to mutually exclusive classes in hierarchical order (combination regimens assigned by highest component), from highest to lowest: (1) PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor (anti-PD1/L1)-based, (2) EGFR/ALK TKI-based, (3) platinum-based chemotherapy combination with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (PBC+VEGF), (4) PBC only, (5) single agent chemotherapy, (6) others. The 2L regimens were examined for patients with 1L SACT initiation only through 2017 to enable sufficient follow-up. Results were stratified by years and by pre-IO and post-IO years of 1L initiation, defined as 2011-2014 and 2015-2018, respectively, based on the earliest IO approval for 2L therapy in Mar2015.
Result
For 1L therapy, in the pre-IO period, most patients were prescribed PBC (80%), and post-IO, most patients were prescribed PBC (68%) or anti-PD1/L1 (21%). Among patients prescribed 1L therapy, the percentages who received 2L therapy were 44%-53% following 1L PBC and 25%-37% following 1L anti-PD1/L1, with 19% of 2017 1L anti-PD1/L1 starts still on 1L therapy (table).
Conclusion
PBC remain the most common 1L SACT prescribed through mid-2018 for patients with squamous aNSCLC at US community oncology practices. Prescribing of PD1/PD-L1 inhibitors as 1L has gradually increased since regulatory approval starting in 2015. Approximately one-half of patients with squamous aNSCLC prescribed 1L PBC are treated with 2L therapy.
-
+
P2.04 - Immuno-oncology (ID 167)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Immuno-oncology
- Presentations: 2
- Now Available
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.04-16 - Novel CT Based Radiomic Features are Prognostic and Predictive of Benefit of Chemoimmunotherapy in Advanced Non-Squamous NSCLC (ID 2769)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Carboplatin, pemetrexed and pembrolizumab (C/P/P) is currently approved for patients with advanced non-squamous carcinoma of the lung (NS-NSCLC) based on superior survival outcomes noted in KEYNOTE-189. Since clinical benefit was observed across all PD-L1 expression categories, there are currently no robust predictive biomarkers that can identify subsets of patients likely to derive benefit from this regimen. We sought to evaluate whether radiomic features extracted from within and outside the nodule on pre-therapy CT scans could predict response to C/P/P.
Method
We retrospectively identified 52 patients with stage IV NS-NSCLC who received C/P/P. Of these, 6 were excluded because of non-evaluable thoracic lesions. Lung tumors were contoured on 3D SLICER software by an expert reader. Textural and shape radiomic features were extracted from intra/peritumoral regions using MATLAB® 2018b platform (Mathworks, Natick, MA). The primary endpoint of our study was RECIST response and secondary end point was overall survival (OS). A linear discriminant analysis classifier (LDA) was used to predict response across 100 iterations of threefold cross validation in the dataset. Performance of classifier on response was measured by area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). To build the multivariate radiomic signature for OS, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression model was used and a risk score was computed according to a linear combination of selected features. Patients were divided into high-risk or low-risk groups based on median risk score.
Result
The top five radiomic features (intra/peritumoral textural patterns) predictive of response to C/P/P were identified by mRMR feature selection method. LDA classifier using these features could discriminate responders from non-responders with an AUC of 0.77 ± 0.05.
The radiomic risk score was calculated using a linear combination of top six selected features from LASSO with corresponding coefficients. In a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model using a combination of clinicopathologic and radiomic features, the radiomics signature was found to be significantly associated with OS (averaged on 100 iteration of CV) (HR 10.42; 95% CI: 4.18-26; P = 4.92e-07). Kaplan-Meier survival analyses according to the radiomics signature risk-score showed significantly worse survival in the high risk category.
Conclusion
Textural features within and outside the nodule on pre-treatment CT images of patients with NS-NSCLC treated with C/P/P were predictive of responses and OS. Additional validation of these quantitative image-based biomarkers in independent cohorts is warranted.
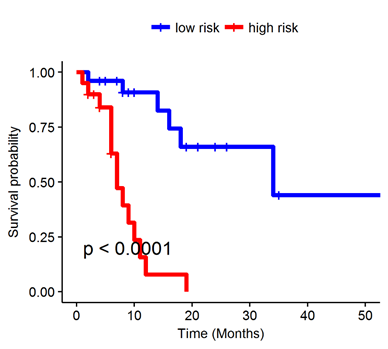
Figure: Kaplan-Meier survival analyses of patients (N = 46) with NS-NSCLC treated with C/P/P using the radiomics signature risk-score.
-
+
P2.04-48 - Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer and Pre-Existing Autoimmune Diseases (Now Available) (ID 1450)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
The prevalence of autoimmune diseases (AIDs) in patients with lung cancer is approximately 14%. However, patients with pre-existing AIDs have been excluded from trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) known to cause immune activation and lead to immune related adverse events (irAEs) limiting the data on safety and efficacy of these agents. Oncologists are therefore wary to use them in this at-risk population.
Method
We conducted a single institution IRB-approved retrospective study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of combination and single agent ICI therapy in patients with pre-existing AIDs and concomitant advanced lung cancer that were treated with ICI from 2011 to 2018. Primary endpoints were incidence of irAEs and AID flares. The secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
Result
We evaluated records from 29 patients with lung cancer of which 17 (59%) had adenocarcinoma, 10 (34%) had squamous cell carcinoma, two (7%) had small cell cancer, and one (3%) had undifferentiated non-small cell lung cancer. AIDs included rheumatic (72%), gastrointestinal (10%), endocrine (10%) and neurologic (7%). 34% of patients experienced an irAE, though only 7% were severe (grade 3-4 colitis and hepatitis). 66% of patients reported no irAEs at all. The most common irAEs were dermatitis (14%) and colitis (10%). 10% of patients had to permanently discontinue ICIs due to an irAE while 17% temporarily held their ICI. 96% of patients with AIDs were either stable or in remission. AID flares were observed in 28% of patients with 24% requiring treatment. None of the AID flares resulted in permanent discontinuation of ICI therapy. 21% of patients were on immunomodulatory therapies at start of ICI treatment. The use of immunomodulatory medications was not associated with an increased incidence of either irAEs or AID flares. Median OS from ICI initiation was 8.5 months and median PFS was 6 months. There was no statistically significant difference for OS or PFS by presence of irAE or presence of immunomodulatory therapy at start of ICI use.
Conclusion
In this cohort, patients with pre-existing AIDs and advanced lung cancer reported fewer AID flares (28%) than has been cited in the literature (approximately 50%). IrAEs were seen at an incidence similar to that observed in patients without AIDs. In our cohort, the majority of adverse reactions were manageable and did not require permanent discontinuation of ICI therapy. Furthermore, the presence of irAEs did not detrimentally affect patients’ OS or PFS. Based on these findings, we would consider ICI therapy as an option in select patients with pre-existing autoimmunity.
-
+
P2.14 - Targeted Therapy (ID 183)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Targeted Therapy
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.14-24 - An Open-Label Randomized Phase II Study of Combining Osimertinib With and Without Ramucirumab in TKI-Naïve EGFR-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC (ID 851)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, has become the first-line therapy for patients with metastatic EGFR-mutant NSCLCs since 2018. Osimertinib is well-tolerated, therefore, it opens opportunities to be combined with other therapeutic agents to enhance the treatment outcome. In preclinical models, it has been shown that upregulated VEGF signaling mediates acquired resistance to EGFR therapies. In xenograft models, combination of anti-VEGF medications with EGFR inhibitors were significantly more effective than erlotinib or gefitinib alone. Ramucirumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting VEGF receptor 2, is approved with docetaxel in as second line treatment for NSCLCs. In clinical trial evaluations, the phase 3 RELAY trial (NCT02411448) studying ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with metastatic untreated EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients showed a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival in the combination group compared to erlotinib alone. A phase I study of osimertinib with ramucirumab (NCT02789345) demonstrated safety and feasibility of this combination. With strong preclinical and clinical evidence showing dual inhibition of VEGF/EGFR signaling prolongs progression-free survival for EGFR-mutant lung cancers, and demonstrated safety, we are conducting a phase 2 trial to evaluate the osimertinib ramucirumab combination’s efficacy in treatment-naïve EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
Method
The OSI+RAM trial is a randomized phase 2 study with the primary endpoint being progression-free survival in osi+ram group as compared to osimertinib monotherapy group. The major inclusion criteria include patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations (L858R/Exon 19 del). The major exclusion criteria include prior anti-EGFR or anti-VEGF treatments. Patients with stable CNS metastasis are allowed. Based on the results from erlotinib bevacizumab (NEJ026) study, we expect an improvement of PFS from 18.9 months to 29.7 months, corresponding to a hazard ratio of 0.65. The trial plans to enroll total of 150 patients, with 100 allocating to osi+ram arm and 50 to osimertinib monotherapy. Total of 9 study sites in the USA are planned. Hoosier Cancer Research Network will facilitate the execution of the trial. The trial protocol has received IND exemption from US FDA and has been approved by IRB at MD Anderson Cancer Center. The first subject is expected to be enrolled in May 2019. A planned interim analysis will be performed after the first 75 subjects are enrolled. NCT03909334.
Result
Section not applicable
Conclusion
Section not applicable
-
+
P2.16 - Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research (ID 187)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.16-17 - Real-World Trends in Systemic Therapy for Nonsquamous EGFR/ALK-Negative Advanced NSCLC (aNSCLC) in the US, 2011–2018 (ID 2744)
10:15 - 18:15 | Presenting Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Systemic anticancer therapy (SACT) options for aNSCLC continue to increase each year with approvals of more effective therapies that improve long-term outcomes, as seen with immunotherapies (IO). We aimed to examine real-world trends in SACT distribution and sequence from first- to second-line (1L-2L) for EGFR/ALK-negative nonsquamous aNSCLC from 2011-2018 at US community oncology practices.
Method
This study used the nationwide Flatiron Health de-identified, EHR-derived database (cutoff: 31Jan2019). Eligible patients were adults with aNSCLC, nonsquamous histology with known EGFR/ALK-negative status, who initiated 1L SACT from Jan2011-Jun2018. SACT regimens were assigned to mutually exclusive classes in hierarchical order, from highest to lowest: (1) PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor (anti-PD1/L1)-based, (2) EGFR/ALK TKI-based, (3) platinum-based chemotherapy (PBC) combination with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (PBC+VEGF), (4) PBC only, (5) single agent chemotherapy, (6) others. 2L regimens were examined for patients initiating 1L SACT only through 2017 to enable sufficient follow-up. Results were stratified by year and by pre-IO/post-IO years of 1L initiation, defined as 2011-2014/2015-2018, respectively, based on earliest IO approval for 2L therapy in Mar2015.
Result
For 1L, in the pre-IO period, most patients were prescribed PBC (53%) or PBC+VEGF (30%), and post-IO, most were prescribed PBC (43%), anti-PD1/L1 (25%), or PBC+VEGF (23%). Among patients prescribed 1L therapy, the percentages who received 2L therapy were 50%-62% post-1L PBC; 56%-62% post-1L PBC+VEGF; and 28%-38% post-1L anti-PD1/L1 (table). A substantial percentage (25%) of those initiating 1L anti-PD1/L1 in 2017 were still on therapy at cutoff.
Conclusion
Changing trends in real-world prescribing of 1L-2L SACT for EGFR/ALK-negative nonsquamous aNSCLC from Jan2011-Jun2018 include decreasing use of PBC in 1L and 2L, decreasing use of PBC+VEGF in 1L, and, increasing use of PD1/PD-L1 inhibitors in 1L and 2L. Slightly more than one-half of patients with nonsquamous aNSCLC prescribed 1L PBC are subsequently treated with 2L therapy.
-
+
P2.16-41 - Pembrolizumab for Previously Treated, PD-L1–Expressing Advanced NSCLC: Real-World Time on Treatment and Overall Survival (ID 2364)
10:15 - 18:15 | Presenting Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Information from real-world clinical settings remains limited regarding outcomes of pembrolizumab therapy for advanced NSCLC. Our aim was to examine real-world time on treatment (rwToT) and overall survival (OS) for patients prescribed pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously treated, PD-L1–expressing advanced NSCLC, thus clinically similar to patients in the KEYNOTE-10 (KN010) trial.
Method
This retrospective study used Flatiron Health’s nationally representative EHR-derived database to identify adult patients with histologically confirmed advanced NSCLC and PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥1% previously treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy (and appropriate TKI if nonsquamous NSCLC with EGFR/ALK aberration). Eligible patients initiated pembrolizumab monotherapy from January 1, 2016, to May 31, 2018; those with <6 months of follow-up were excluded. Kaplan-Meier (KM) rwToT and OS were calculated.
Result
Median follow-up was 15.6 months (range 6.0–32.8 months). Of 281 eligible patients (56% male), median age was 68 years; 36% had squamous NSCLC; 10% brain metastases; and 57%, 18%, and 25% ECOG performance status 0–1, ≥2, and unknown, respectively. Baseline characteristics were similar across PD-L1 TPS distributions. The table summarizes rwTOT and OS by PD-L1 TPS categories.
Conclusion
Real-world patients treated with pembrolizumab monotherapy after platinum-containing chemotherapy for PD-L1–expressing advanced NSCLC experienced rwToT and OS benefits similar to findings in a clinical trial setting, validating KN010 findings and approved indication in second line.
-
+
P2.17 - Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease (ID 189)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.17-34 - Integrated Clinico-Radiomic Nomogram for Predicting Disease-Free Survival (DFS) in Stage I and II Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 2886)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Early stage non-small cell lung cancer (ES-NSCLC) comprises about 45% of all NSCLC patients, with 5-year survival ranging between 30-49%. Surgical resection is the standard of care curative modality in these patients but about 30-55% of patients often recur following surgery within the first 3 years. There is currently no validated method to stratify patients based on their risk of recurrence following surgery in these patients. In this project, we develop and validate a nomogram using a combination of CT-derived radiomic textural features and clinco-pathologic factors, in order to predict DFS in ES-NSCLC.
Method
This study comprised 350 ES-NSCLC patients from two different institutions who underwent surgery (75 patients relapsed). Radiomic textural features were extracted from tumor region (Intratumoral - IT) as well as from the annular ring shaped peritumoral region (PT) with 3mm as a ring thickness and extending 9 mm outside the nodule. A total of 124 features from Gabor, Laws, Laplace, Haralick and Collage feature families were extracted from IT and each PT ring for all patients. The most stable, significant and uncorrelated features were selected from D1 (N=221) and used to build a Lasso-regularized multivariate Cox-regression model to generate a Radiomic Risk Score (RRS) derived from weighted Lasso coefficients. Further, RRS was integrated with clinic-pathologic variables (Lympho-vascular invasion LVI and AJCC stage) which were independently predictive on DFS in multivariate analysis to build a clinical-radiomics score (CRS). A nomogram was constructed to visually assess the CRS and RRS on DFS. Performances were evaluated using hazard ratios (HR), concordance index (C-Index) along with decision and calibration curves to show the differences between the individual and integrated risk scores.
Result
Top 14 radiomic features included 6 from IT and 8 from 0-9 mm PT distance. The constructed RRS could predict DFS (n=221, C-index=0.69, HR = 3.8; 95% CI- 2.7-5.6, p<0.05) on training (D1) and (n=129, C-index=0.69, HR – 2.5; 95% CI – 1.8-4.7; p<0.05) on a blinded validation cohort (D2), Addition of LVI and pN to build the CRS, increased C-index to 0.74, (p<0.05). Decision and calibration curve analysis shows improved performance of CRS over RRS or clinco-pathologic factors alone.
Conclusion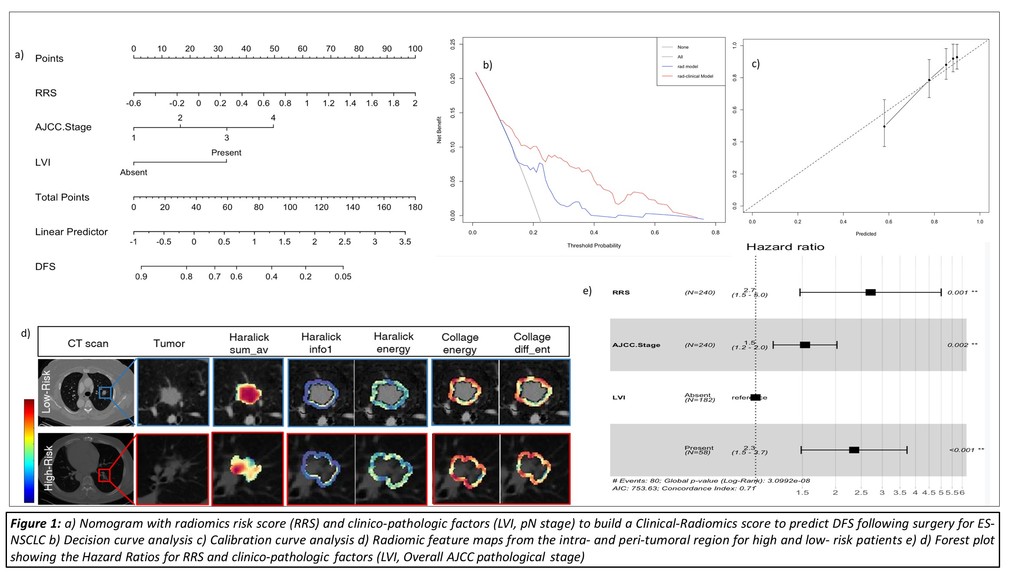
Addition of prognostic clinical factors (LVI, AJCC stage) improved the performance of the Radiomic Risk Score model in order to accurately predict DFS in ES-NSCLC patients undergoing surgery.
-
+
P2.17-35 - Integrating CT Radiomic & Quantitative Histomorphometric Whole Slide Image Features Predicts Disease Free Survival in ES-NSCLC (ID 2910)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
Background
Early-Stage non-small cell lung cancer (ES-NSCLC) accounts for approximately 40% of NSCLC cases, with 5-year survival rates varying between 31-49%. Radiomic textural features from pre-treatment CT scans and QH features from H&E stained WSIs have been shown to be independently prognostic of outcome. With diagnostic CT scans and surgical resection, the standard of care in ES-NSCLC, in this work we seek to take a multimodality approach using routine imaging to improve the predictive performance in determining DFS following resection.
Method
A retrospective chart review of Stage I and II (ES-NSCLC) pts undergoing surgical resection between 2005-14 with available CT and resected tissue yielded 70 pts. A total of 248 radiomic CT textural features from inside the tumor (Intratumoral –IT) and outside the tumor (Peritumoral – PT) and 242 QH features related to the nuclear shape, texture and spatial orientation and architecture from H&E WSI were extracted. We developed two risk models, Radiomic and QH using the most stable, discriminative and uncorrelated features from CT and WSI respectively determined by Lasso-regularized Cox regression to predict Disease free survival (DFS). Model performances were analyzed using Hazard Ratios (HR), Concordance Index (C-index) and Decision curve analysis. We built a nomogram to calculate the DFS based around the individual models as well as an integration of the QH and Radiomic models.
Result
Top 6 Radiomic features included 2 IT and 4 PT features from the Haralick and Collage families. The QH model comprised 6 nuclear shape and graph features. In predicting DFS, While the Radiomic model had a HR of 2.4 (p <0.01) with C-index – 0.67, the QH model had HR – 3.1 (p <0.01) with C-index – 0.74. Integration of the Radiomic and QH model yielded a C-index of 0.78 (p< 0.01). After addition of prognostic clinical factors (LVI, AJCC stage) to the model, the C-index was 0.80, almost doubling either modalities alone. The constructed nomogram visualized the apparent benefits of the three models while a decision curve clearly demonstrated the increased benefit of combined integrated model.
Conclusion
Integration of CT-derived radiomic and tissue-derived QH features was found to show improved performance in predicting RFS when compared to either radiomics or QH alone.

-
+
PL02 - Presidential Symposium including Top 7 Rated Abstracts (ID 89)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Plenary Session
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Giorgio Vittorio Scagliotti, Ramon Rami-Porta
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 08:00 - 10:15, Barcelona (2005)
-
+
PL02.08 - Registrational Results of LIBRETTO-001: A Phase 1/2 Trial of LOXO-292 in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Cancers (Now Available) (ID 964)
08:00 - 10:15 | Author(s): Vamsidhar Velcheti
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
No targeted therapy is currently approved for patients with RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). LOXO-292 is a highly selective RET inhibitor with activity against diverse RET fusions, activating RET mutations and brain metastases. Based on initial data from LIBRETTO-001, LOXO-292 received FDA Breakthrough Designation for the treatment of RET fusion-positive NSCLC in August 2018.
Method
This global phase 1/2 study (87 sites, 16 countries) enrolled patients with advanced RET-altered solid tumors including RET fusion-positive NSCLC (NCT03157128). LOXO-292 was dosed orally in 28-day cycles. The phase 1 portion established the MTD/RP2D (160 mg BID). The phase 2 portion enrolled patients to one of six cohorts based on tumor type, RET alteration, and prior therapies. The primary endpoint was ORR (RECIST 1.1). Secondary endpoints included DoR, CNS ORR, CNS DoR, PFS, OS, safety and PK.
Result
As of 17-June 2019, 253 RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients were treated. The primary analysis set (PAS) for LOXO-292 registration, as defined with the US FDA, consists of the first 105 consecutively enrolled RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients who received prior platinum-based chemotherapy; 58 patients (55%) also received prior anti PD-1/PD-L1 agents. The majority of PAS responders have been followed for ≥6 months from first response. Of the remaining 148 patients, 79 had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy, 55 did not receive prior platinum-based chemotherapy and 14 did not have measurable disease at baseline.
Conclusion
Among PAS patients, the investigator-assessed ORR was 68% (95% CI 58-76%, n=71/105, 2 PRs pending confirmation). Responses did not differ by fusion partner or the type or number of prior therapies, including chemotherapy, anti PD-1/PD-L1 agents and multikinase inhibitors with anti-RET activity. The median DoR was 20.3 months (95% CI 13.8-24.0) with a median follow-up of 8 months; as evidenced by the wide confidence interval, this DoR estimate is not statistically stable due to a low number of events (16 of 69 confirmed responders). The intracranial ORR was 91% (n=10/11: 2 confirmed CRs, 8 confirmed PRs) for patients with measurable brain metastases at baseline.
The ORR in efficacy evaluable treatment naïve RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients was 85% (95% CI 69-95%, n=29/34, 7 PRs pending confirmation). In the safety data set of all 531 patients, 5 treatment-related AEs occurred in ≥15% of patients: dry mouth, diarrhea, hypertension, increased AST and increased ALT. Most AEs were grade 1-2. Only 9 of 531 (1.7%) patients discontinued LOXO-292 for treatment-related AEs.
LOXO-292 had marked antitumor activity in RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients and was well tolerated. These data will form the basis of an FDA NDA submission later this year.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.


