Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Yuichiro Ohe
Author of
-
+
EP1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (ID 150)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: E-Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 08:00 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
EP1.01-51 - Efficacy Impact of Serum VEGF for Elderly or Poor PS Patients Receiving Anti-PD-1 Antibody with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 1691)
08:00 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
Background
Anti-programmed cell death (PD)-1 antibody therapies have shown durable clinical efficacy and manageable toxicity profiles, and have become a standard therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Because of manageable toxicity profiles, extensive interest in the potential benefits of anti-PD-1 antibody has expanded to high-risk patients such as the elderly or poor performance status (PS) patients. Here, we aimed to investigate predictive markers for the efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody in elderly patients and poor PS patients.
Method
The medical records of 75≥ years old or PS2 NSCLC patients treated with anti-PD-1 antibody (e.g., nivolumab and pembrolizumab) at the National Cancer Center Japan between December 1, 2015, and May 31, 2018, were reviewed retrospectively. We evaluated the association between efficacy for anti-PD-1 antibody and gender, smoking status, histology, PD-ligand 1(PD-L1) expression on tumor cells, white blood cell counts, lymphocyte counts, albumin, lactate dehydrogenase, c-reactive protein, and serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). We divided patients into two groups with the median values.
Result
A total of 235 patients with advanced NSCLC treated with anti-PD-1 antibody were reviewed. Of these patients, 31 patients were ≥ 75 years old, and 22 patients were PS2. The median PFS was 6.9 months in patients aged ≥ 75 years and 2.1 months in PS2 patients. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis showed that only the low-VEGF was significantly associated with longer PFS in patients aged ≥ 75 years (HR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.13-0.88; P = 0.025) and in PS2 patients (HR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.10-0.85; P = 0.023). The overall response rate of patients with low-VEGF was tend to be higher than that with high-VEGF among patients aged ≥ 75 years (43% vs. 20%; P = 0.18) and PS2 patients (20% vs. 0%; P = 0.084).
Conclusion
Low-VEGF in patients aged ≥ 75 years and PS2 patients was associated with longer PFS. Serum VEGF may thus be a biomarker for the efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody therapy.
-
+
MA11 - Immunotherapy in Special Populations and Predictive Markers (ID 135)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Immuno-oncology
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Frank Griesinger, Lecia Sequist
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 14:00 - 15:30, Hilton Head (1978)
-
+
MA11.07 - Efficacy of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors and EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC Patients with High PD-L1 Expression (Now Available) (ID 667)
14:00 - 15:30 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Recently, several studies have demonstrated that patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations show poor clinical outcomes in response to treatment with anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors. Conversely, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are not effective in NSCLC showing high programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression levels. In this study, we retrospectively investigated the relationship between high PD-L1 expression and the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors and EGFR-TKIs in patients with NSCLC.
Method
The subjects of this study were patients with NSCLC who had received treatment with PD-1 inhibitors at the National Cancer Center Hospital between March 2017 and December 2018. The PD-L1 expression in the tumor cells was divided into two groups based on the tumor proportion score (TPS): <50% (low) and ≥50% (high).
Result
Of the 414 patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors, the 263 patients in whom the PD-L1 expression levels could be evaluated were considered as being eligible for inclusion in this study. Among the 153 patients with high PD-L1 expression, we assessed the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors according to the EGFR mutation status. The objective response rate (ORR) was 29.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3 to 53.1) in the EGFR-mutated patients and 43.4% (95% CI, 35.4 to 51.8) in the EGFR wild-type patients. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.3 months (95% CI, 1.3 to 12.4) in the EGFR-mutated patients and 8.3 months (95% CI, 6.0 to 11.7) in the EGFR wild-type patients (hazard Ratio [HR] = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.62 to 1.14). A total of 33 patients received EGFR-TKI therapy. We assessed the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs according to the PD-L1 expression level. The ORR was 50.0% (95% CI, 28.0 to 72.0) in the high PD-L1 expression group and 52.9% (95% CI, 31.0 to 73.8) in the low PD-L1 expression group. The median PFS was 18.8 months (95% CI, 2.8 to 35.7) in the high PD-L1 expression group and 12.7 months (95% CI, 7.2 to 20.9) in the low PD-L1 expression group (HR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.38 to 1.81).
ConclusionPD-L1 High
EGFR+
PD-L1 High
EGFR−
PD-L1 Low
EGFR+
PD-L1 Low
EGFR−
Total N
17
136
18
92
Median age, years (range)
62 (47–85)
62 (33–87)
64.5 (37–83)
62 (33–83)
Sex (n)
Female
Male
7
10
36
100
15
3
25
67
ECOG PS (n)
0, 1
2
14
3
125
11
16
2
81
11
Smoking history (n)
Never-smoker
Smoker
7
10
21
115
12
6
13
79
EGFR mutation status (n)
Ex 19 del
L858R
Others
7
6
4
13
2
3
ICI agent used (n)
Pembrolizumab
Nivolumab
11
6
105
31
4
14
21
71
Line of ICI therapy (n)
First-line
Second-line
Third-line or more
2
3
12
85
42
9
5
64
23
0
2
16
Efficasy
ORR (%)
PD-1 inhibitors
EGFR-TKIs
PFS (months)
PD-1 inhibitors
EGFR-TKIs
29.4
50.0
5.3
18.8
43.4
8.3
0
52.9
1.6
12.7
16.3
3.8
Even in a population of NSCLC patients showing high PD-L1 expression, the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors tended to be lower in the EGFR-mutated patients as compared to the EGFR wild-type patients. In regard to EGFR-mutated patients with a PD-L1 TPS of ≥50%, our findings suggested that high PD-L1 expression might not predict a poor efficacy of EGFR-TKIs.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA13 - Going Back to the Roots! (ID 139)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Maurice Perol, Kaoru Kubota
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 14:00 - 15:30, Vancouver (2003)
-
+
MA13.07 - Phase I/II Study of Carboplatin Plus Weekly Nab-Paclitaxel in Aged ≥75 Patients with Squamous-Cell Lung Cancer: TORG1322 (Now Available) (ID 1369)
14:00 - 15:30 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Combination chemotherapy of carboplatin (CBDCA) plus weekly nab-paclitaxel (nab-PTX) showed a favorable efficacy for elderly (70 year or older) patients with squamous non-small cell lung cancer (Sq-NSCLC) in a subgroup analysis of the CA031 study. We conducted a phase I/II study of CBDCA plus nab-PTX in chemo-naïve elderly patients with advanced Sq-NSCLC.
Method
Patients aged ≥75 years with untreated, measurable lesion, advanced Sq-NSCLC, performance status (PS) 0-1, and adequate organ function were eligible. In a phase I study, doses of carboplatin at an area under the curve (AUC) of 5 or 6 mg/mL min on day 1 (levels 1 and 2, respectively) were administered along with weekly nab-PTX (100 mg/m2) on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks up to 6 cycles using a modified 3 + 3 design. The primary endpoint for the phase II study was the 6-month progression-free survival (6m PFS) rate and hypothesis required 36 patients to be enrolled with expecting and threshold values for the primary endpoints of 40% and 25% (one-sided alpha = 0.05; beta = 0.2).
Result
A total of 46 patients were enrolled in this study. The median age was 78 (range 75-85 years); male (n = 41); PS 0/1, (n = 15/31). Ten patients were enrolled in the phase I part. At dose level 1, 2/7 patients showed dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of grade 3 diarrhea and febrile neutropenia, and at dose level 2, 1/3 patient showed DLT of grade 3 anorexia. The recommended dose was determined to be level 2. Additional 36 patients were enrolled, and a total of 39 patients were evaluated in the phase II study. The median number of cycles was 4 (range 1-6), and the median follow-up time was 17.5 months (range 5.6-28.9). The 6m PFS rate was 59% (90% CI, 44.8-71.4), and the primary endpoint was met. The median overall survival time was 23.5 months (95% CI, 11.6-35.4), and the median PFS was 6.8 months (95% CI, 5.4-9.1). The response rate was 54% and disease control rate was 92%. Nineteen patients (49%) received post-study treatment and 14 out of 19 patients (74%) received immunotherapy. Common toxicities of grade 3 or 4 were neutropenia (61.5%), anemia (46.2%), thrombocytopenia (17.9%), and febrile neutropenia (15.4%). There was no treatment-related death.
Conclusion
Combination chemotherapy of CBDCA plus weekly nab-PTX had a promising efficacy and acceptable toxicities in elderly (aged ≥75) patients with advanced Sq-NSCLC. Clinical trial information: UMIN000011216.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA14 - The Adequate MTarget Is Still the Issue (ID 140)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Diego Signorelli, Juergen Wolf
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 15:45 - 17:15, Hilton Head (1978)
-
+
MA14.04 - Discussant - MA14.01, MA14.02, MA14.03 (Now Available) (ID 3777)
15:45 - 17:15 | Presenting Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Abstract not provided
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA15 - Usage of Computer and Molecular Analysis in Treatment Selection and Disease Prognostication (ID 141)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Pathology
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:John Le Quesne, Noriko Motoi
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 15:45 - 17:15, Tokyo (1982)
-
+
MA15.03 - Exploring Digital Pathology-Based Morphological Biomarkers for a Better Patients’ Selection to the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor of Lung Cancer (Now Available) (ID 1777)
15:45 - 17:15 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
For eligible patients’ selection for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy (ICI), it is important to establish more accurate predicting biomarkers, in addition to PD-L1 IHC and MSI-high. We hypothesized that morphological characteristics should reflect genetic alteration, thus could predict ICI responsiveness. In this study, we examined the predictive potential of morphological characteristics using digital whole-slide images as a new biomarker for ICI-treatment on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and their relationship to PD-L1 IHC and genetic alterations.
Method
71 NSCLC who received ICI therapy were recruited. Digital images of H&E and PD-L1 (22C3) IHC stained slides of pre-treatment biopsied or resected materials were examined by previously reported image analysis techniques using e-Pathologist ® (NEC, Japan). Morphological characteristics of cancer cells (three and six parameters of nuclear shape and chromatin texture) were extracted as MC-scores. Of 11 cases (pilot cohort), PD-L1 IHC (22C3) and tumor mutation burden (TMB) by the NGS-based target sequence (NCC oncopanel ®) were examined. Correlation between MC-score, PD-L1 IHC, TMB status, and clinical outcome was calculated. A p-value of less than 0.05 was defined as statistically significant.
Decision tree analysis for evaluating predicting ICI-responsiveness was built using statistically significant MC-scores. We also tested the predictive value of a deep learning analysis (AI model) with 5-fold cross-validation. AUC (area under the curve) of ROC analysis was calculated.
Result
Of the responders, the MC-score of cancer cell were statistically different from those of the non-responders; nuclear texture contour complexity (11.8 vs. 8.25, median value of responder vs. non-responders; p<0.01), homogeneity (0.396 vs. 0.421; p<0.01), angular second moment (ASM) (0.0203 vs. 0.0214; p=0.049) and nuclear circularity (0.878 vs. 0.885, p=0.026). Circularity (p=0.011) and texture homogeneity (p=0.048) correlated with TMB. ASM texture correlated with PD-L1 expression (p=0.018). The decision tree model for predictive and screening purposes resulted in 0.83 and 0.62 accuracies, respectively. AUC of AI-model for ICI responsiveness resulted in fair (0.74 on average, range 0.55-0.81).
Conclusion
Our results indicate the substantial value of the morphological feature as a biomarker for ICI therapy. Morphological characteristics are eligible from archived FFPE samples, showed good correlation to the underlying genetic alteration. Digital pathology can serve useful predictive morphological biomarkers for precision medicine of lung cancer patients, and promising the power of AI-assisted pathology.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
OA07 - Precision Medicine Involves Biology and Patients (ID 132)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Oral Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Silvia Novello, Fabrice Barlesi
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 11:00 - 12:30, Copenhagen (1980)
-
+
OA07.03 - Clinical Outcome of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR/HER2 Exon 20 Insertions Identified in the LC-SCRUM-Japan (Now Available) (ID 629)
11:00 - 12:30 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
In-frame insertions in exon 20 (Ex20ins) of EGFR/HER2 occur in 2-5 % of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). There is no approved targeted therapy for patients with these mutations. Historical control data would be valuable for the development of novel targeted therapies for these rare cancers.
Method
A nationwide genome screening project in Japan (LC-SCRUM-Japan) has been established for the development of molecular-targeted therapies for lung cancers. In this project, 161 cancer-related genes have been analyzed by a next-generation sequencing (NGS) system, Oncomine™ Comprehensive Assay. The therapeutic efficacy and survival of the patients with non-squamous (non-sq) NSCLC harboring EGFR/HER2 Ex20ins were evaluated using a large-scale clinico-genomic database in the LC-SCRUM-Japan.
Result
A total of 3441 advanced non-sq NSCLC patients were successfully analyzed from 2015 to 2018. EGFR Ex20ins were detected in 73 patients (2%; M766_A767insASV/A767_S768insSVD/H773_V774insH/D770_N771insNPH/N771_P772insPH/others=22/17/5/4/4/21) and HER2 Ex20ins were detected in 128 patients (4%; A775_G776insYVMA/G776delinsVC/P780_Y781insGSP/others=95/16/10/7). The median age of the patients was 62 (range, 33-90) years. Eighty-one patients (40%) were male and 114 (57%) were never smoker. Two-hundred patients (99%) were diagnosed as adenocarcinoma and 1 as adenosquamous-cell carcinoma. Based on our database, the median overall survivals in patients with EGFR Ex20ins were 22.4 (95%CI, 15.3-36.8) months, and those with HER2 Ex20ins were 18.8 (13.6-30.3) months. In the patients with EGFR/HER2 Ex20ins, the objective response rate (ORR) and median progression-free survivals (mPFS) of 1st-line platinum-containing chemotherapies were 32% and 6.0 (5.7-7.0) months, respectively. The ORR and mPFS of docetaxel with or without ramucirumab were 26% and 5.1 (3.8-5.9) months, respectively. The ORR and mPFS of PD-1 inhibitor were 0% and 2.0 (1.6-2.6) months, respectively. No significant difference in the therapeutic efficacy of these drugs was observed between the patients with EGFR Ex20ins and HER2 Ex20ins. In 19 patients with EGFR Ex20ins treated with 1st/2nd generation EGFR-TKIs, the ORR was 5% (a M766_A767insASV-positive tumor responded to afatinib) and the mPFS was 2.1 (1.3-4.2) months.
Conclusion
The patients with EGFR/HER2 Ex20ins-positive NSCLC showed poor responses to PD-1 inhibitors and 1st/2nd generation EGFR-TKIs. These historical data are highly informative in evaluating the efficacy of novel targeted therapies for EGFR/HER2 Ex20ins-positive NSCLC.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
OA12 - Profiling the Multidisciplinary Management of Stage III NSCLC (ID 144)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Oral Session
- Track: Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Dirk De Ruysscher, Bartomeu Massuti
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 15:45 - 17:15, Seoul (2007)
-
+
OA12.02 - Randomized Phase II Study of CDDP+S-1 vs CDDP+PEM Combined with Thoracic RT for Locally Advanced Non-Sq NSCLC: SPECTRA Study (Now Available) (ID 428)
15:45 - 17:15 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
SPECTRA, a multicenter, randomized phase II study of CDDP+S-1 versus CDDP+pemetrexed (PEM) combined with thoracic radiotherapy (TRT) for locally advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), previously reported that toxicities were tolerable and manageable in both arms; however, febrile neutropenia was more frequently observed in the CDDP+S-1 arm (9.6%/2%). Completion rate of TRT (60Gy) and chemotherapy (4 cycles) was 92%/98% and 73%/86%, respectively. Response rate was 60%/64% (WCLC 2017, MA17.06). Here, we present primary analysis of 2-year survival data.
Method
Patients were randomly assigned to receive CDDP+S-1 (CDDP 60mg/m2, d1, and S-1 80mg/m2, d1-14, q4w, up to 4 cycles) or CDDP+PEM (CDDP 75mg/m2, d1, and PEM 500mg/m2, d1, q3w, up to 4 cycles) combined with TRT 60Gy in 30 fractions. The primary endpoint was 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) rate. The sample size was set at 100 patients.
Result
Between Jan 2013 and Oct 2016, 102 patients were enrolled in this study from 9 institutions in Japan. All 102 patients were eligible and assessable, of whom 52 were assigned to CDDP+S-1 and 50 to CDDP+PEM. Baseline characteristics were similar (CDDP+S-1/CDDP+PEM): median age (range) 64.5 (39-73)/63.5 (32-74) years; women, n=17 (33%)/n=17 (34%); stage IIIB, n=21 (40%)/n=20 (40%); ECOG PS of 1, n=14 (27%)/n=14 (28%); never smoker, n=12 (23%)/n=12 (24%); and adenocarcinoma, n=47(90%)/n=45(90%); activating EGFR mutation, n=9 (17%)/n=4 (8%); ALK fusion, n=2 (4%)/n=3 (6%). A total of 72 PFS events were observed at the data cut-off (28 November 2018). After a median follow-up of 32.1 months, median PFS was 12.7/13.8 months (HR=1.16, 95% CI, 0.73-1.84, p=0.538), and 2-year PFS rate was 36.5% (95% CI, 23.5-49.6)/32.1% (95%CI, 18.9-45.4). Disease progression was observed in 33 and 36 patients. Distant metastases were the first site of failure in 24 and 31 patients. Local relapse as the first site of failure was observed in 14 and 13 patients. After a median follow-up of 34.6 months, 44 OS events were observed. Median OS was 48.3/59.1 months (HR=1.05, 95%CI, 0.58-1.90, p=0.883), and 2-year OS rate was 69.2% (95%CI, 56.7-81.8)/66.4% (95%CI, 53.0-79.9). 27 patients in each arm received post-study chemotherapy including EGFR-TKIs (n=7/n=5), ALK-TKIs (n=0/n=3), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n=6/n=10).
Conclusion
2-year PFS rate in the CDDP+S-1 arm was better than that in the CDDP+PEM arm. We will select the CDDP+S-1 arm as the investigational arm in a future phase III study. UMIN000009914 (release date: 31/Jan/2013)
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (ID 158)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 2
- Now Available
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 09:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-102 - Actionable Gene Aberration and the Response of Matched Therapy Among Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma (Now Available) (ID 1177)
09:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
Background
Tumor genotyping using multiplex gene panel is now standard for precision medicine in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). We sought to assess the prevalence of actionable genomic alterations among NSCLC patients using our next-generation sequencing panel (NCC Oncopanel) and the response of matched therapy.
Method
This is a post-hoc analysis of prospective study in which patients with advanced solid cancer were prospectively enrolled to undergo the comprehensive genomic profiling panel (NCC Oncopanel) conducted between July 2013 and March 2018 in National Cancer Center Hospital. The NCC Oncopanel assay, a multiplexed next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay of 114 cancer-associated genes, was performed in a CLIA-compliant laboratory in National Cancer Center. Subjects were primarily patients without any known actionable alteration such as EGFR or ALK. Patients with NSCLC were extracted into this analysis. Clinical data and treatment outcomes were retrospectively collected.
Result
In total, 100 patients were extracted. Sufficient tumor tissue for NGS analysis were available in 91 patients; median age was 57 (range 30‒77); 74 (81.3%) adenocarcinoma; 44 (48.4%) female; 42 (46.2%) never smoker. According to the OncoKB and CIViC database, and the Clinical Practice Guidelines for NGS in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment issued by three major Japanese cancer-related societies, 85 patients (93.4%) had at least one potential pathogenic alteration. Actionable gene aberrations were identified in 49 (53.9%). Evidence levels were ranked as follows: 24 (26%) harbored level 1 aberrations (ALK, EGFR, ROS1, BRAF); 15 (16%) harbored level 2 (RET, DDR2, MET, ATM, BRCA2, CDK4, CTNNB1, EZH2, JAK2, NRAS, TSC1); 10 (11%) harbored level 3A (CDKN2A, ERBB2, HRAS, PTEN, SMARCA4, STK11). Matched therapy was administered into 29 (31.9%) leading to the objective response rate of 58.6% and the disease control rate of 79.3% with the median progression-free survival of 10.5 months (95%CI; 5.1‒15.8).
Conclusion
Multiplex gene panel is feasible and useful in screening candidates for matched therapy among NSCLC patients. NSCLC patients without any known actionable mutations should be considered to undergo comprehensive genomic profiling.
-
+
P1.01-103 - Preliminary Results of Brigatinib in Japanese Patients (Pts) Who Previously Received Alectinib: Brigatinib-2001 Study (ID 1180)
09:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
Background
Brigatinib is a next-generation ALK inhibitor with broad preclinical activity against ALK resistance mutations. To evaluate efficacy and safety of brigatinib in Japanese pts, a single-arm, multicenter, phase 2 study of brigatinib in pts with ALK-positive NSCLC (NCT03410108) in Japan is ongoing, with the primary endpoint of objective response rate (ORR) by independent review. This study has a safety evaluation lead-in phase to confirm the tolerability and pharmacokinetics of brigatinib with a small number of Japanese pts prior to the expansion phase. Here we report the preliminary results from pts in the safety lead-in phase who had been heavily pre-treated with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), including alectinib and ceritinib.
Method
Stage IIIB, IIIC, or IV NSCLC with documented ALK rearrangements were enrolled. Up to 4 ALK TKIs (alectinib, ceritinib, crizotinib and lorlatinib) and 3 lines of prior other systemic anti-cancer treatment were allowed only for the safety evaluation lead-in phase. Brigatinib of 180 mg QD with 90 mg QD lead-in for the first 7 days (90→180mg QD) was administered and efficacy was evaluated every 8 weeks.
Result
All 9 pts previously received prior alectinib, of whom 6 received 2 or more prior ALK TKIs. The standard dose of 90→180mg QD was well tolerated among Japanese pts. Only 1 dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) was observed: grade 3 lipase increase without clinical evidence of pancreatitis. The most common AEs were increased blood creatine phosphokinase (n=7), increased aspartate aminotransferase (n=6), and hypertension (n=5). By investigator assessment, 5 of 9 pts (56%) had confirmed partial response by the end of cycle 6. Tumor samples from 5 pts were collected prior to the start of brigatinib treatment, and 2 cases had secondary mutation, including one pt with a G1202R mutation who had a confirmed partial response to brigatinib by investigator assessment. Intensive PK sampling data in Japanese pts are comparable with those in non-Japanese pts.
Conclusion
Standard dose of brigatinib 90→180mg is tolerable in Japanese pts and show promising preliminary anti-tumor activity in the post-alectinib setting.
-
+
P1.09 - Pathology (ID 173)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Pathology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 09:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.09-11 - Influences of Sampling Method to Morphological Feature Measurement of Lung Cancer Cell (ID 886)
09:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
Background
Progress of imaging technologies in the field of histopathology enables us to exploit artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to detect cancer based on digital images for screening or quality assurance of diagnosis process. Nowadays, reports on the application of AI to cancer detection which claim 99-percent detection accuracy are found in every proceedings or journal of digital pathology. However, little attention has been paid to the influences of sampling method to AI-based histological diagnosis.
Method
Whole slide images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained slides collected from 94 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases were captured by a virtual slide scanner (NanoZoomer, Hamamatsu Photonics, Japan). Sampling methods were needle biopsy (59 cases), operation (12 cases) and endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) (29 cases). Regions of interest (ROI) were selected by an experienced pathologist. After selecting tumor cells only by AI-based tumor cell detecter (Figure.1), following morphological features were calculated: nuclear area, perimeter (Peri), circularity (Circ) and five texture features, i.e., angular secondary moment (ASM), contrast(Cont), homogeneity (Hom) and entropy (Ent) of gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), and contour complexity (CC).
Result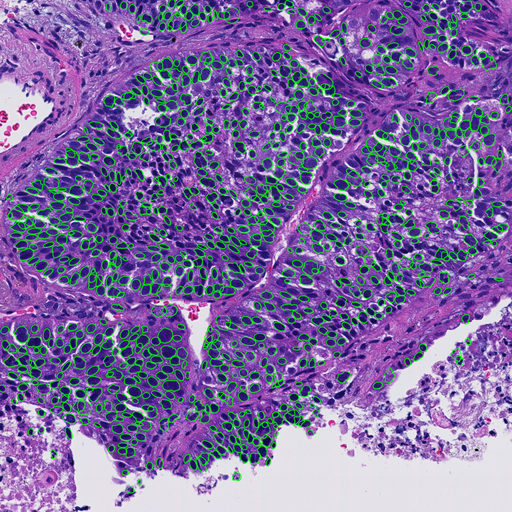
We found significant differences (p<0.05) in most of feature values except nuclear area and perimeter.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that methods of sampling significantly affect morphological feature values of nucleus and this fact must be taken into consideration when applying AI-based techniques to tissue image classification.
-
+
P2.14 - Targeted Therapy (ID 183)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Targeted Therapy
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.14-55 - Real-World Safety and Efficacy Data of Osimertinib in Patients from Japan with EGFR T790M-Positive NSCLC (ID 1601)
10:15 - 18:15 | Presenting Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
Background
Osimertinib, a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), was approved in Japan on 28 March 2016 as second- or later-line treatment for patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have progressed on EGFR-TKIs. Post-marketing activities included the Japan-local All-patient Clinical Experience Investigation, reporting Japanese real-world safety and efficacy of osimertinib in the approved indication.
Method
Overall, 3629 patients investigated at 718 hospitals between 28 March 2016 and 31 August 2018 were included. Adverse events were assessed by attending physicians to determine whether they were possibly causally-related to osimertinib. Osimertinib antitumour activity was evaluated by attending physicians using RECIST version 1.1. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were also analysed. The planned observation period was 12 months.
Result
The median observation period for patients in the safety analysis set (n=3578) was 343 days (range: 1–764). Adverse drug reactions occurred in 58.1% (2079/3578) of patients. Adverse drug reactions (as per Japanese Prescribing Information) of interstitial lung disease, prolonged QT interval, liver disorder, and haematotoxicity were reported in 6.8% (245/3578) (Gr≥3, 2.9% [104/3578]), 1.3% (45/3578) (Gr≥3, 0.1% [5/3578]), 5.9% (212/3578) (Gr≥3, 1.0% [35/3578]), and 11.4% (409/3578) (Gr≥3, 2.9% [104/3578]) of patients, respectively. The objective response rate and disease control rates for patients in the efficacy analysis set (n=3563) were 69.9% (2492/3563; 95% confidence interval [CI] 68.4, 71.4) and 86.7% (3090/3563; 95% CI 85.6, 87.8). PFS rates at 6 months and 12 months were 77.4% (95% CI 75.9, 78.9) and 53.2% (95% CI 51.3, 55.1). OS rates at 6 months and 12 months were 88.3% (95% CI 87.2, 89.4) and 75.4% (95% CI 73.8, 77.0). Selected subgroup analyses of efficacy are presented in Table 1.

Conclusion
These data support the currently established benefit–risk assessment of osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M positive NSCLC.
-
+
PL02 - Presidential Symposium including Top 7 Rated Abstracts (ID 89)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Plenary Session
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Giorgio Vittorio Scagliotti, Ramon Rami-Porta
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 08:00 - 10:15, Barcelona (2005)
-
+
PL02.08 - Registrational Results of LIBRETTO-001: A Phase 1/2 Trial of LOXO-292 in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Cancers (Now Available) (ID 964)
08:00 - 10:15 | Author(s): Yuichiro Ohe
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
No targeted therapy is currently approved for patients with RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). LOXO-292 is a highly selective RET inhibitor with activity against diverse RET fusions, activating RET mutations and brain metastases. Based on initial data from LIBRETTO-001, LOXO-292 received FDA Breakthrough Designation for the treatment of RET fusion-positive NSCLC in August 2018.
Method
This global phase 1/2 study (87 sites, 16 countries) enrolled patients with advanced RET-altered solid tumors including RET fusion-positive NSCLC (NCT03157128). LOXO-292 was dosed orally in 28-day cycles. The phase 1 portion established the MTD/RP2D (160 mg BID). The phase 2 portion enrolled patients to one of six cohorts based on tumor type, RET alteration, and prior therapies. The primary endpoint was ORR (RECIST 1.1). Secondary endpoints included DoR, CNS ORR, CNS DoR, PFS, OS, safety and PK.
Result
As of 17-June 2019, 253 RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients were treated. The primary analysis set (PAS) for LOXO-292 registration, as defined with the US FDA, consists of the first 105 consecutively enrolled RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients who received prior platinum-based chemotherapy; 58 patients (55%) also received prior anti PD-1/PD-L1 agents. The majority of PAS responders have been followed for ≥6 months from first response. Of the remaining 148 patients, 79 had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy, 55 did not receive prior platinum-based chemotherapy and 14 did not have measurable disease at baseline.
Conclusion
Among PAS patients, the investigator-assessed ORR was 68% (95% CI 58-76%, n=71/105, 2 PRs pending confirmation). Responses did not differ by fusion partner or the type or number of prior therapies, including chemotherapy, anti PD-1/PD-L1 agents and multikinase inhibitors with anti-RET activity. The median DoR was 20.3 months (95% CI 13.8-24.0) with a median follow-up of 8 months; as evidenced by the wide confidence interval, this DoR estimate is not statistically stable due to a low number of events (16 of 69 confirmed responders). The intracranial ORR was 91% (n=10/11: 2 confirmed CRs, 8 confirmed PRs) for patients with measurable brain metastases at baseline.
The ORR in efficacy evaluable treatment naïve RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients was 85% (95% CI 69-95%, n=29/34, 7 PRs pending confirmation). In the safety data set of all 531 patients, 5 treatment-related AEs occurred in ≥15% of patients: dry mouth, diarrhea, hypertension, increased AST and increased ALT. Most AEs were grade 1-2. Only 9 of 531 (1.7%) patients discontinued LOXO-292 for treatment-related AEs.
LOXO-292 had marked antitumor activity in RET fusion-positive NSCLC patients and was well tolerated. These data will form the basis of an FDA NDA submission later this year.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.


