Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Shannon Chuai
Author of
-
+
MA15 - Colliding Approaches - EGFR and Immunotherapy (ID 916)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Targeted Therapy
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 107
-
+
MA15.06 - Circulating Tumor DNA Portrays the Resistance Landscape to a Novel Third Generation EGFR Inhibitor, AC0010 (ID 13641)
14:05 - 14:10 | Author(s): Shannon Chuai
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
In a Phase I/II dose-escalation and expansion study conducted at Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, AC0010 demonstrated promising efficacy and good tolerability in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR T790M-mediated resistance to previous EGFR TKIs, (NCT02330367). As disease progression (PD) with EGFR T790M-directed therapy also emerges over time, we investigated the resistance mechanisms to AC0010 in this study.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Serial ctDNA samples obtained from patients who developed PD with AC0010 were analyzed using ultra-deep sequencing capturing 295 cancer-related genes. Alterations that were absent before treatment and acquired at PD or that increased in abundance during treatment were identified as putative resistance mechanisms.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Longitudinal plasma samples were obtained from 23 patients who progressed on AC0010 (data cut-off October 14, 2016; figure1). Putative resistance mechanisms to AC0010 were identified in 19/23 patients (>1 putative resistance mechanism was detected in some patients). EGFR amplification was the predominant resistance mechanism (21.1% [4/19 patients]), followed by TP53 loss of heterozygosity (15.8% [3/19]). EGFR C797S mutation, Met amplification and mutations in the PI3KCA pathway each occurred in 10.5% of patients (2/19). SCLC transformation, ERBB2 amplification, CD79A_A32G mutation, CDKN2A_R80 mutation, CRLF2 amplification, MLH1 amplification, Rb1 loss, and concurrent rise in the allelic fraction of tumor suppressor gene TP53 and Rb1 were each detected in 5.3% of patients (1/19). In a patient with PD following single-agent AC0010 and EGFR amplification as the putative resistance mechanism to AC0010, subsequent treatment with AC0010 plus nimotuzumab (EGFR monoclonal antibody) successfully overcame resistance, resulting in a response that lasted for 7.7 months.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The resistance landscape to AC0010 appears to differ from that described previously with osimertinib. In this cohort of patients in China, EGFR amplification was the predominant resistance mechanism to AC0010 and could be potentially overcome by EGFR dual inhibition.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 935)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.03-34 - Combined Molecular and Radiological Evaluation Unveils Three Subtypes of Disease Progression to a Third Generation EGFR TKI (ID 12055)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Shannon Chuai
- Abstract
Background
The definition of disease progression (PD) to EGFR TKIs has evolved from RECIST to a combination of clinical and RECIST evaluation. Patients with dramatic, local or gradual progression to third generation EGFR TKIs have been tailored to different subsequent treatment strategies. However, little is known about progression to third generation EGFR TKIs from molecular perspective.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Longitudinal plasma samples were collected from T790M-positive patients who progressed on a third generation EGFR TKI AC0010 in a phase I/II study in Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute. A pre-defined and unified molecular and radiological evaluation of PD were performed. Ultra-deep sequencing capturing 295 cancer-related genes was performed to track the changes in ctDNA to depict molecular PD, which was defined by acquired SNV/SCNV, or ≥20% increase in allelic fraction/copy number of pre-existing SNV /SCNV or both. Radiological PD was defined by RECIST.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
As of October 2016, 102 serial plasma samples from 23 patients with clinical PD were included. Three subtypes of PD to AC0010 were revealed (Fig1). Molecular PD occurred prior to radiological PD in 43.5% of patients (10/23), with an average lead time of 3.0 months. Molecular PD occurred concurrently with radiological PD in 39.1% of patients (9/23). Interestingly, 17.4% of patients (4/23) experienced radiological PD prior to molecular PD, with molecular PD occurred during AC0010 continuation beyond progression (CBPD) in 3 patients. Of patients experienced clinical stable PD in extracranial lesions, radiological PD occurring prior to molecular PD group (n=2) demonstrated longer duration of AC0010 CBPD than molecular PD occurring prior to (n=3) or concurrently with radiological PD groups (n=4) (Median, 5.6 months vs. 1.9 months vs. 1.8 months).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion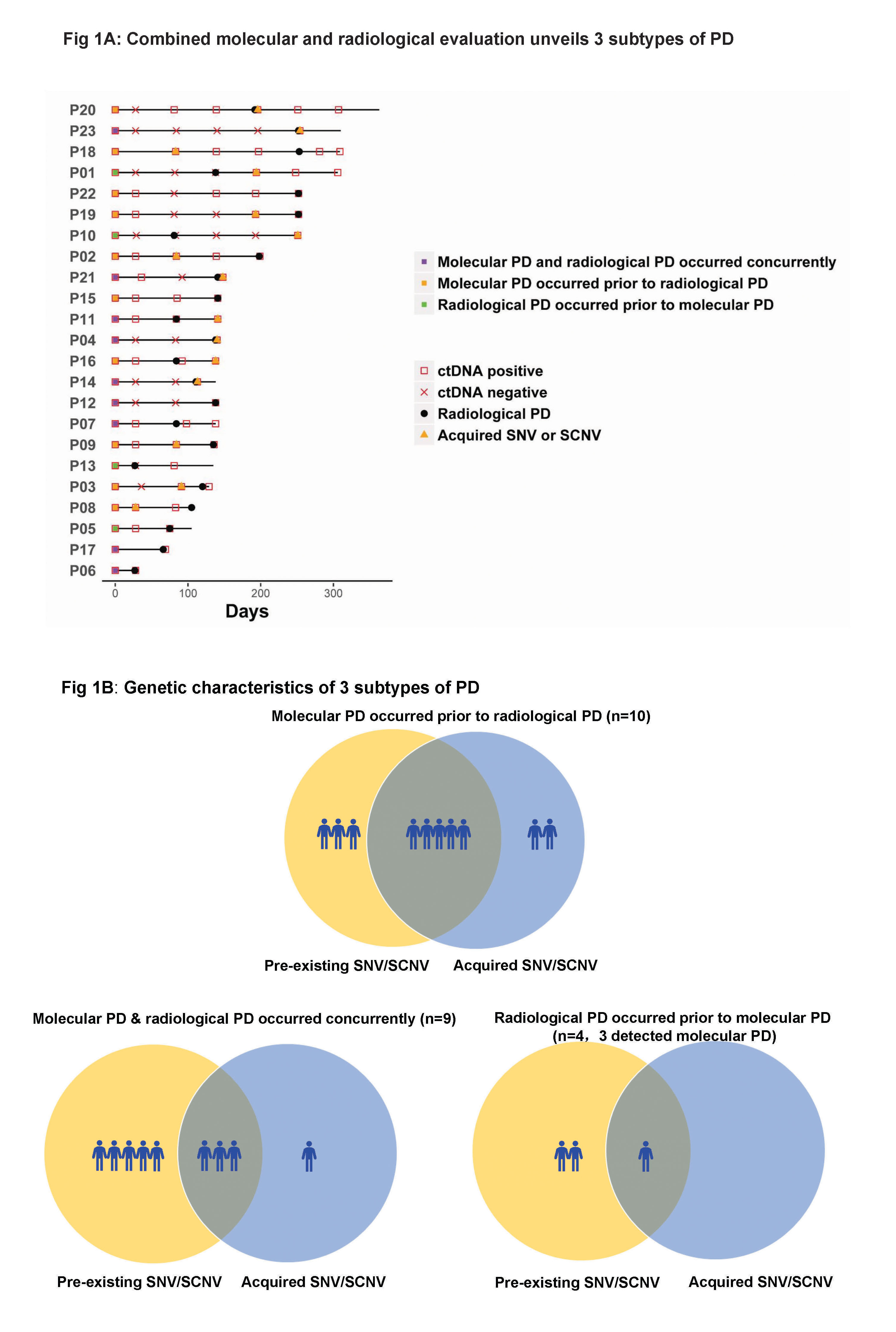
Our study revealed 3 distinct subtypes of PD to AC0010, providing insights into PD by combining molecular and radiological evaluation and might guide the optimal time for treatment switch and personalized subsequent treatments.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-16 - Dynamic ctDNA Monitoring Revealed Novel Resistance Mechanisms and Response Predictors of Osimertinib Treatment in East Asian NSCLC Patients (ID 13861)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Shannon Chuai
- Abstract
Background
Advanced NSCLC patients, harboring EGFR T790M, exhibit marked diversity in tumor behavior and response to AZD9291, yet a discriminable molecular profile remains elusive. In addition, although EGFRC797S was involved in 30% of AZD9291 resistance cases in Western patients, mechanisms for the rest patients remain unclear, especially for the East Asian population. We utilized circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) profiling to conduct dynamic monitoring in patients undergoing AZD9291, thus characterizing mutational heterogeneity and genomic evolution.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Longitudinal plasma samples were collected before, during and post of the AZD9291 treatment in Chinese NSCLC patients with acquired T790M mutation. A ctDNA panel, spanning 160KB of human genome, was used to perform capture-based targeted sequencing that comprises critical exons and introns of 168 genes. The EGFR mutation abundance and dynamic changes of allele fraction (AF) were analyzed with progression-free survival (PFS) after AZD9291 treatment.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 61 samples were collected longitudinally from 14 patients, of which 9 have experienced progressive disease (PD). Six patients exhibited a rebound of ctDNA prior to radiographic PD, suggesting the potential of ctDNA in early detection of PD. Several acquired mutations were detected with the AZD9291 resistance, including newly identified EGFR G796S, L792H/F/R/V, V802F, V843I mutations, expect for the previously reported RB1 and EGFR C797S, L718Q mutations. Patients with a higher ratio of T790M and EGFRactivating mutation at baseline had a significantly longer PFS (9.6m vs 4.5m, p=0.008). A lower ratio of EGFRactivating mutation AF compared to baseline at first follow-up was significantly correlated with a longer PFS (8.5m vs 5.0m, p=0.027). Furthermore, patients harboring other known driver mutations in addition to T790M at baseline had an inferior PFS (4.9m vs 7.8m, P=0.039).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Several novel resistance mechanisms were identified by ctDNA monitoring in the East Asian patients treated with AZD9291. Relative AF of T790M, changes of AF after treatment and the presence of concurrent driver mutations at baseline could predict clinical benefit of AZD9291 treatment.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 952)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.03-36 - DNA Methylation: A More Sensitive Marker for Treatment Monitoring? (ID 12916)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Shannon Chuai
- Abstract
Background
Detection of genomic aberrations in cell-free DNA (cfDNA), requiring ultra-deep sequencing due to the low allelic frequencies (AF) of mutation, has been utilized to monitor treatment response. However, 20%-30% of patients yield no mutation from plasma genotyping despite deep sequencing depth, thus necessitating alternative monitoring method. The role of aberrant DNA methylation in the process of tumorigenesis both at individual genes and a genome-wide scale has been well elucidated. We investigated the potential of DNA methylation as a biomarker for treatment monitoring.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We investigated the performance of mutation and DNA methylation as biomarkers to evaluate response to osimertinib using a DNA methylation panel consisting of 100,000 CpG sites and a targeted panel for mutation detection consisting of 168 lung cancer related genes with an average sequencing depth of 1,000x and 10,000x, respectively. Longitudinal plasma samples from 6 patients undergoing osimertinib were collected prior to treatment and at regular interval until disease progression, ranged from 6 to 9 times. Methylation level of a given sample was reflected by the percentage of significantly methylated blocks, which were significantly hypermethylated blocks comparing to healthy individuals.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
All patients had EGFR sensitizing mutation and T790M at baseline. Four patients had additional concurrent mutations, including TP53, RB1, OR6F1 and BRCA2. At PD, all patients had detectable mutations except for one and 3 developed EFGR C797S. Four patients had at least two times of no detectable mutation during treatment. Among them, P05 and P06 had 5 and 6 times of no detectable mutation, respectively. In contrast, all patients had significantly methylated blocks detected at every point. In general, the trend of changes in mutation AF corresponds to the changes in the percentage of significantly methylated blocks in all patients except for one, who only had mutations detected at baseline and had consistently detectable DNA methylation at every point. Collectively, DNA methylation reached nadir at best response and gradually increased thereafter. An elevation of mutation AF or the emergence of new mutation(s) (molecular PD) was observed in 4 patients prior to PD assessed by imaging. In all patients, an elevation of DNA methylation was observed prior to PD assessed by imaging; among them, 3 had changes in DNA methylation prior to molecular PD, suggesting DNA methylation may be a more sensitive biomarker.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Collectively, our study demonstrates DNA methylation, continuously increasing from the nadir (best response), can be utilized as a biomarker for treatment monitoring.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


