Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Steven H Lin
Author of
-
+
OA01 - Improving Outcomes in Locoregional NSCLC I (ID 892)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 10:30 - 12:00, Room 107
-
+
OA01.06 - DETERRED: Phase II Trial Combining Atezolizumab Concurrently with Chemoradiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 12842)
11:25 - 11:35 | Presenting Author(s): Steven H Lin
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
While consolidation immunotherapy after chemoradiation (CRT) is the current standard of care for locally advanced NSCLC (LA-NSCLC), the effectiveness of immunotherapies may be enhanced when combined concurrently with CRT. We report on the safety and preliminary efficacy of combining PD-L1 blockade using atezolizumab (atezo) and concurrent CRT followed by consolidation full dose carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) with atezo and maintenance atezo up to 1 year for LA-NSCLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
This is a single institution phase II study in LA-NSCLC assessing the safety and feasibility of adding atezo to CRT in two parts: I) sequentially (N=10) with CP after completing CRT, or II) concurrently (N=30) with CRT followed by consolidation atezo with CP. Atezo was given at 1200 mg IV Q3 weeks for up to one year from the first dose. Radiation dose at 60-66 Gy in 30-33 fractions was combined with weekly low dose CP, followed by 2 cycles of full dose CP. Severe adverse events (AEs) ≥ grade 3 are defined within 15 weeks of start of therapy or any immune-related AEs during atezo treatment. Evaluable patients (pts) have received at least one dose of atezo.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
From February 2016 to April 2018, we accrued 40 evaluable pts. For part 1, any grade 3+ AEs was seen in 6 pts (60%), with most common being pneumonia (2 of 10, 20%). Three grade 3+ AEs (30%) were attributed to atezo, including dyspnea, arthralgia and a grade 5 TE fistula. Grade 2 radiation pneumonitis (RP) was seen in 3 pts. Four progressed with disease during atezo maintenance and have died, ranging from 0.93 to 1.86 years. Four pts completed atezo and are in follow up without recurrence. For part 2, 17 of 30 pts had any grade 3+ AEs (57%), with pneumonia being the most common (6 of 30, 20%). Three (10%) were attributed to atezo (dyspnea, fatigue and heart failure). RP was seen in 3 pts, with 2 grade 2 and 1 grade 3, which led to atezo discontinuation. So far, 4 pts have progressed and 4 have died, 2 due to disease and 2 due to treatment (neutropenic sepsis and gastric hemorrhage). All others have completed CRT and are on maintenance atezo, ranging from 5 to 19 doses. Updated efficacy results will be presented.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Concurrent atezo with CRT followed by consolidation and maintenance atezo appears safe without increased toxicities compared to CRT alone followed by consolidation and maintenance atezo.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
OA06 - Early Stage Lung Cancer: Outcomes and Interventions (ID 902)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 202 BD
-
+
OA06.08 - Discussant - OA 06.05, OA 06.06, OA 06.07 (ID 14557)
14:45 - 15:00 | Presenting Author(s): Steven H Lin
- Abstract
- Presentation
Abstract not provided
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.15 - Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 947)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.15-17 - Risk Factors of Local Recurrence in EGFR-Mutant Stage III-pN2 Adenocarcinoma After Complete Resection: A Multi-Center Real-World Cohort Study (ID 12740)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Steven H Lin
- Abstract
Background
Postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) of complete resected stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer with N2 nodal involvement remained contentious. Our previous study suggested low locoregional recurrences in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant patients. We sought to launch a multi-center large cohort study to evaluate the risk factors of locoregional recurrence in R0 resected EGFR mutant III-pN2 patients without PORT, producing evidence for the design of adjuvant regimens.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Three-hundred and fifty-nine consecutive patients with complete resected, pathological approved stage III-pN2 lung adenocarcinoma with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) have been investigated. Patients were excluded if they received induction therapy (7.5%) or PORT (9.6%). Three hundred cases have been analyzed. Clinicopathologic characteristics, pretreatment work-ups, EGFR mutant status and patterns of failure were documented. Patients were sub-staged by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)/ the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) 7th classification on N2 disease. Risk factors of locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRFS) were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analyses.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
According to IASLC/UICC 7th classification, there were 198 (66.0%) patients with unforeseen N2 (N2a), 36 (12.0%) with minimal/single station N2 (N2b), 41 (13.7%) with selectively centrally located N2 (N2c) and 25 (8.3%) with bulky and/or multilevel N2 (N2d). After surgery, 70 (23.3%) patients were treated with adjuvant tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs), while other 230 (76.7%) were free from adjuvant TKIs. With median follow-up of 28.5 (range:6-133) months, the 2-year LRFS, distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were 88.3%, 65.3%, 57.7% and 89.7%. Ultimately, 15.7% (47/300) patients developed locoregional recurrences. Distant metastasis was the predominant failure pattern. Multivariate analysis indicated that N2d disease (HR: 2.65, p=0.030) and extranodal extension (HR: 3.48, p<0.001) were risk factors of LRFS.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
R0 resected stage III-pN2 NSCLC patients with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) tended to present limited N2 disease and low locoregional recurrences. Patients without bulky N2, multilevel N2, and extranodal extension might be refrained from PORT. Further studies evaluating the optimal radiotherapy approach for completely resected N2-positive NSCLC are required for validation.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.16 - Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 948)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.16-40 - Evaluating the Tumor Heterogeneity in Lung Cancer by Constructing Tumor Heterogeneity Index (THI) from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ID 13134)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Steven H Lin
- Abstract
Background
To improve the evaluation of primary lung cancer heterogeneity using clinical routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), we proposed a method based on basic measurements from T1- and T2-weighted MRI.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
As a novel technique of magnetic resonance imaging analysis, we investigated a total of 203 patients with biopsy-proven primary lung cancer and with different T stages. All patients previously received positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan. Gross lesions were manually contoured on T1-weighted, T1-enhanced, T2-weighted and T2 fat suppression (T2fs) images. The ratios of standard deviation (SD) / mean tumor value from each sequence were calculated. Correlation analyses were performed between T stages and the ratios. P value <0.05 was defined as statistical significant. Then a linear regression was performed to determine the weight of each related ratio. A model was built to calculate Tumor Heterogeneous Index (THI). One hundred and one patients were analyzed as the training set and another 102 as validating set.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
There were 56 patients diagnosed with T1 disease, 60 with T2 disease, 51 with T3 disease and 36 with T4 disease. Pair matching was performed between training set and validating set. As a result of the correlation analyses, SD/mean ratio showed significantly correlations with T stages in T1-enhanced (p=0.003), T2-weighted (p<0.0001) and T2fs sequences (p=0.002). Based on a linear regression model, THI was established for assessing the heterogeneity of lung tumor, consisting the three ratio measurements. Correlation analysis demonstrated that Higher THI was significantly related to more advanced T stages (p<0.0001).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion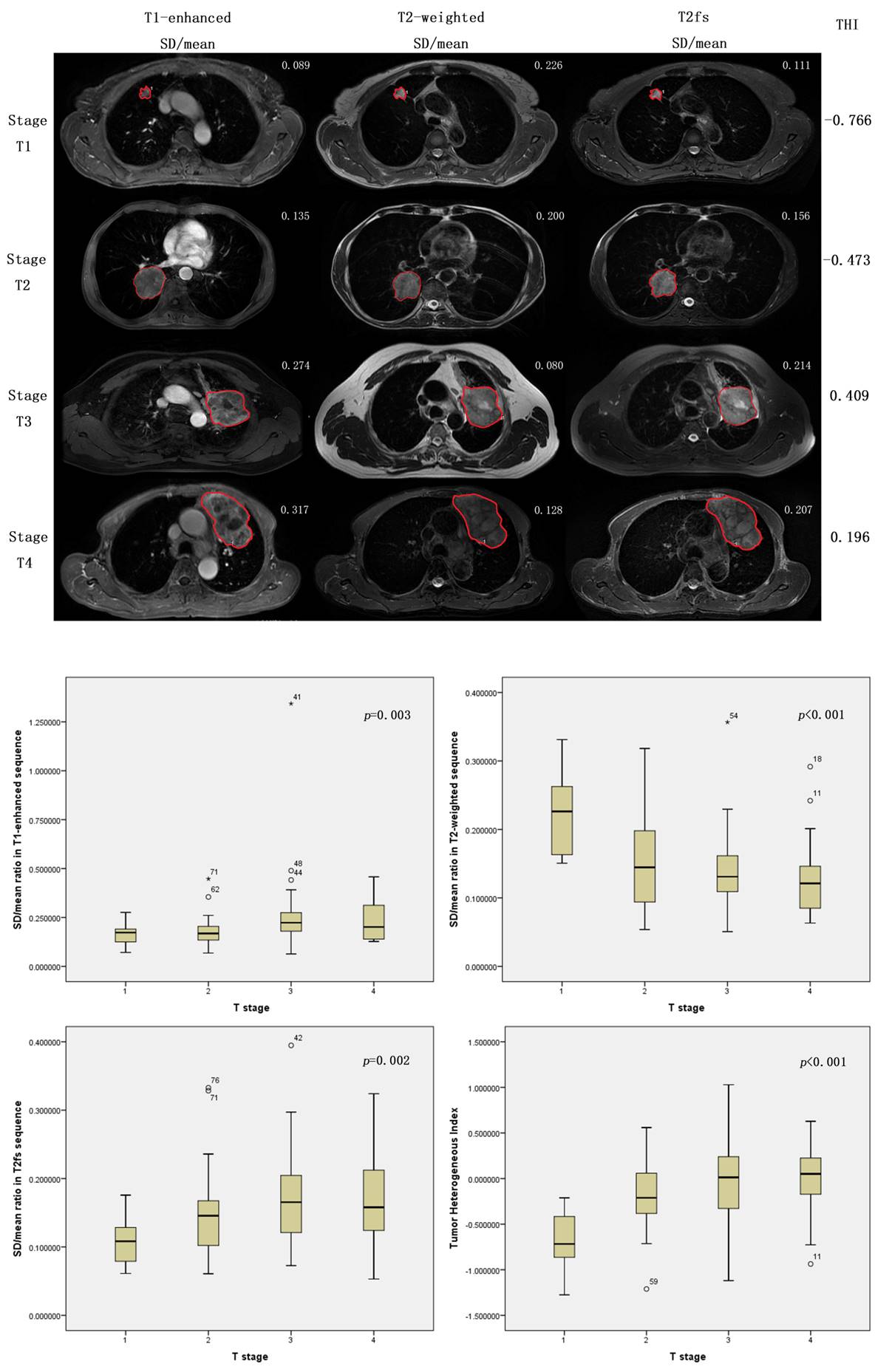
The proposed SD/mean ratio measurements and the calculation of THI according to clinical routine MR images could be clinical biomarkers that correlated with T stages, and were capable of evaluating heterogeneity of lung cancers.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.04 - Immunooncology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 953)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.04-25 - Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Immunotherapy Plus SABR (I-SABR) Versus SABR Alone for Early Stage NSCLC (ID 12620)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Steven H Lin
- Abstract
Background
Section not applicable
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR), which delivers high biologically effective radiation doses, can kill cancer cells, release tumor-associated antigens, and activate tumor-specific T cells, thereby functioning as a cancer-specific vaccine in situ. The combination of the immune-triggering effects of ionizing radiation with immune check point PD-1inhibitor may leverage the effects of radiotherapy, transforming what was once considered a local therapy to a novel systemic treatment. Further, the combined effects of local tumor control plus systemic control may improve cure rate in early stage NSCLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Section not applicable
This is a randomized phase II trial (NCT03110978) designed to study SABR (biological effective dose >100 Gy) with or without concurrent and adjuvant Nivolumab for total of 7 doses in early stage or isolated recurrent NSCLC. Inclusion criteria: stage I disease (tumor size ≤5 cm, N0M0) OR selected cases of stage IIa disease (tumor size >5 cm but ≤7 cm, N0M0), including multiple primary tumors, OR isolated lung-parenchymal recurrent or persistent NSCLC suitable for SABR. Tumor tissue /blood/stool samples will be collected before/during/after treatment and at the time of recurrence. Primary endpoints: Event-free survival (EFS), defined as local recurrence, regional recurrence, distant metastasis, secondary malignancy and death; secondary endpoints: overall survival; toxicity; exploratory analyses of potential predictive markers and immunologic mechanisms of action.
Statistical design: It is considered clinically significant with a decrease of the 4-year cumulative event rate from 46% to 23%. Assuming a one-sided type I error rate of 0.05, an accrual rate of 3.5 patients per month, and an additional 20 months of follow-up, a study with 70 patients in each arm will have 85% power to detect an improvement of 23% in 4-year EFS rate. One interim analysis will be done to allow early termination of the trial should evidence at that time reveal that I-SABR is superior to SABR-only or that no difference is found between the two treatment arms.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Section not applicable
Up to April 30, 2018, 36 of planned 140 patients have been enrolled.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Section not applicable
Phase II randomized clinical trial comparing immunotherapy plus Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (I-SABR) versus SABR Alone for stage I, selected stage IIa or isolated lung parenchymal recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is ongoing and met with anticipated enrolment rate.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


