Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Alexia Zagouras
Author of
-
+
P2.04 - Immuno-oncology (ID 167)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track: Immuno-oncology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/09/2019, 10:15 - 18:15, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.04-16 - Novel CT Based Radiomic Features are Prognostic and Predictive of Benefit of Chemoimmunotherapy in Advanced Non-Squamous NSCLC (ID 2769)
10:15 - 18:15 | Author(s): Alexia Zagouras
- Abstract
Background
Carboplatin, pemetrexed and pembrolizumab (C/P/P) is currently approved for patients with advanced non-squamous carcinoma of the lung (NS-NSCLC) based on superior survival outcomes noted in KEYNOTE-189. Since clinical benefit was observed across all PD-L1 expression categories, there are currently no robust predictive biomarkers that can identify subsets of patients likely to derive benefit from this regimen. We sought to evaluate whether radiomic features extracted from within and outside the nodule on pre-therapy CT scans could predict response to C/P/P.
Method
We retrospectively identified 52 patients with stage IV NS-NSCLC who received C/P/P. Of these, 6 were excluded because of non-evaluable thoracic lesions. Lung tumors were contoured on 3D SLICER software by an expert reader. Textural and shape radiomic features were extracted from intra/peritumoral regions using MATLAB® 2018b platform (Mathworks, Natick, MA). The primary endpoint of our study was RECIST response and secondary end point was overall survival (OS). A linear discriminant analysis classifier (LDA) was used to predict response across 100 iterations of threefold cross validation in the dataset. Performance of classifier on response was measured by area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). To build the multivariate radiomic signature for OS, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression model was used and a risk score was computed according to a linear combination of selected features. Patients were divided into high-risk or low-risk groups based on median risk score.
Result
The top five radiomic features (intra/peritumoral textural patterns) predictive of response to C/P/P were identified by mRMR feature selection method. LDA classifier using these features could discriminate responders from non-responders with an AUC of 0.77 ± 0.05.
The radiomic risk score was calculated using a linear combination of top six selected features from LASSO with corresponding coefficients. In a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model using a combination of clinicopathologic and radiomic features, the radiomics signature was found to be significantly associated with OS (averaged on 100 iteration of CV) (HR 10.42; 95% CI: 4.18-26; P = 4.92e-07). Kaplan-Meier survival analyses according to the radiomics signature risk-score showed significantly worse survival in the high risk category.
Conclusion
Textural features within and outside the nodule on pre-treatment CT images of patients with NS-NSCLC treated with C/P/P were predictive of responses and OS. Additional validation of these quantitative image-based biomarkers in independent cohorts is warranted.
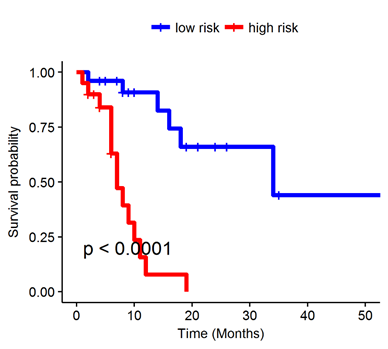
Figure: Kaplan-Meier survival analyses of patients (N = 46) with NS-NSCLC treated with C/P/P using the radiomics signature risk-score.


