Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Lei Tang
Author of
-
+
MA10 - Emerging Technologies for Lung Cancer Detection (ID 129)
- Event: WCLC 2019
- Type: Mini Oral Session
- Track: Screening and Early Detection
- Presentations: 1
- Now Available
- Moderators:Fabrizio Bianchi, Marcelo Sanchez
- Coordinates: 9/08/2019, 15:15 - 16:45, Dublin (1997)
-
+
MA10.02 - Deep Learning with Radiomics May Predict High-Grade Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Histological Patterns in Ground Glass Opacity Lesions (Now Available) (ID 128)
15:15 - 16:45 | Author(s): Lei Tang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Adenocarcinoma (ADC) is the most common histological subtype of lung cancers in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in which ground glass opacifications (GGOs) found on computed tomography (CT) scans are the most common lesions. These lesions are usually treated with limited lung resection. However, the presence of a micropapillary or solid component is identified as an independent predictor of prognosis, indicating a more extensive resection. The accurate classification of subtypes still remains difficult in radiology or in frozen pathological analysis, even with the help of classical radiomics. The purpose of our study is to explore imaging phenotyping using a novel method combining radiomics with deep learning (RDL) to predict high-grade patterns within lung ADC.
Method
Included in this study were 111 patients differentiated as having GGOs and pathologically confirmed ADC. Four different methods were compared to classify the GGOs for the prediction of the pathological subtypes of high-grade lung ADCs, including classic machine learning, radiomics, deep learning method, and a proposed novel method referred as RDL. A four-fold cross-validation approach was used to evaluate the performance of such methods.
Result
We analyzed 32 patients with high-grade patterns and 79 without such patterns. The proposed RDL has achieved an overall accuracy of 0.888, which significantly outperforms classic machine learning, radiomics, and deep learning alone (p< 0.001, paired t-test).
Conclusion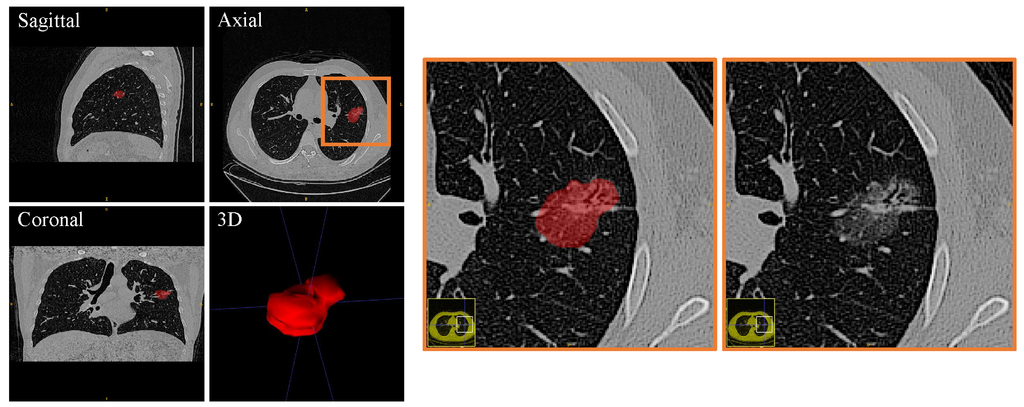
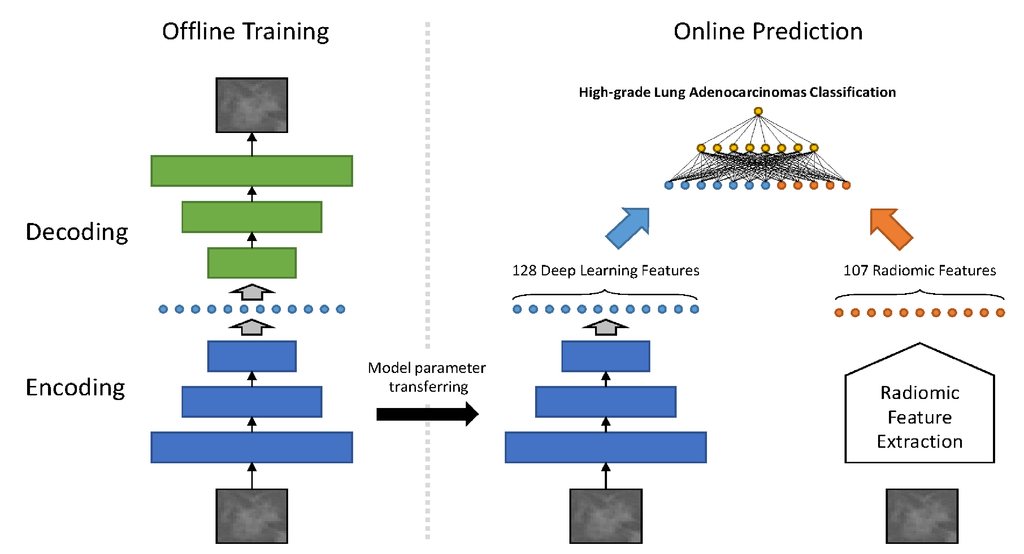
High-grade lung ADC based on histologic pattern spectrum in GGO lesions might be predicted by a novel framework combining radiomics with deep learning, which reveals a significant advantage over traditional methods.
Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.


