Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Yuriko Terada
Author of
-
+
P3.16 - Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 982)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.16-43 - Is Sublobar Resection for Stage I Invasive Adenocarcinoma (≤2-cm) Feasible? (ID 13545)
12:00 - 13:30 | Presenting Author(s): Yuriko Terada
- Abstract
Background
Recent studies have reported that sublobar resection is not inferior to lobectomy for small-sized non-invasive adenocarcinoma (ADC); however, the adequacy for small-sized invasive ADC (IAD) remains unclear. The objective of this study was to identify prognostic factors and validate sublobar resection for small-sized IAD.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively reviewed patients with therapy-naïve, pathological stage I (≤2-cm) IAD, who had undergone complete resection from 1998-2015. Each tumor was evaluated by comprehensive histologic subtyping according to the 2015 World Health Organization classification. Overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
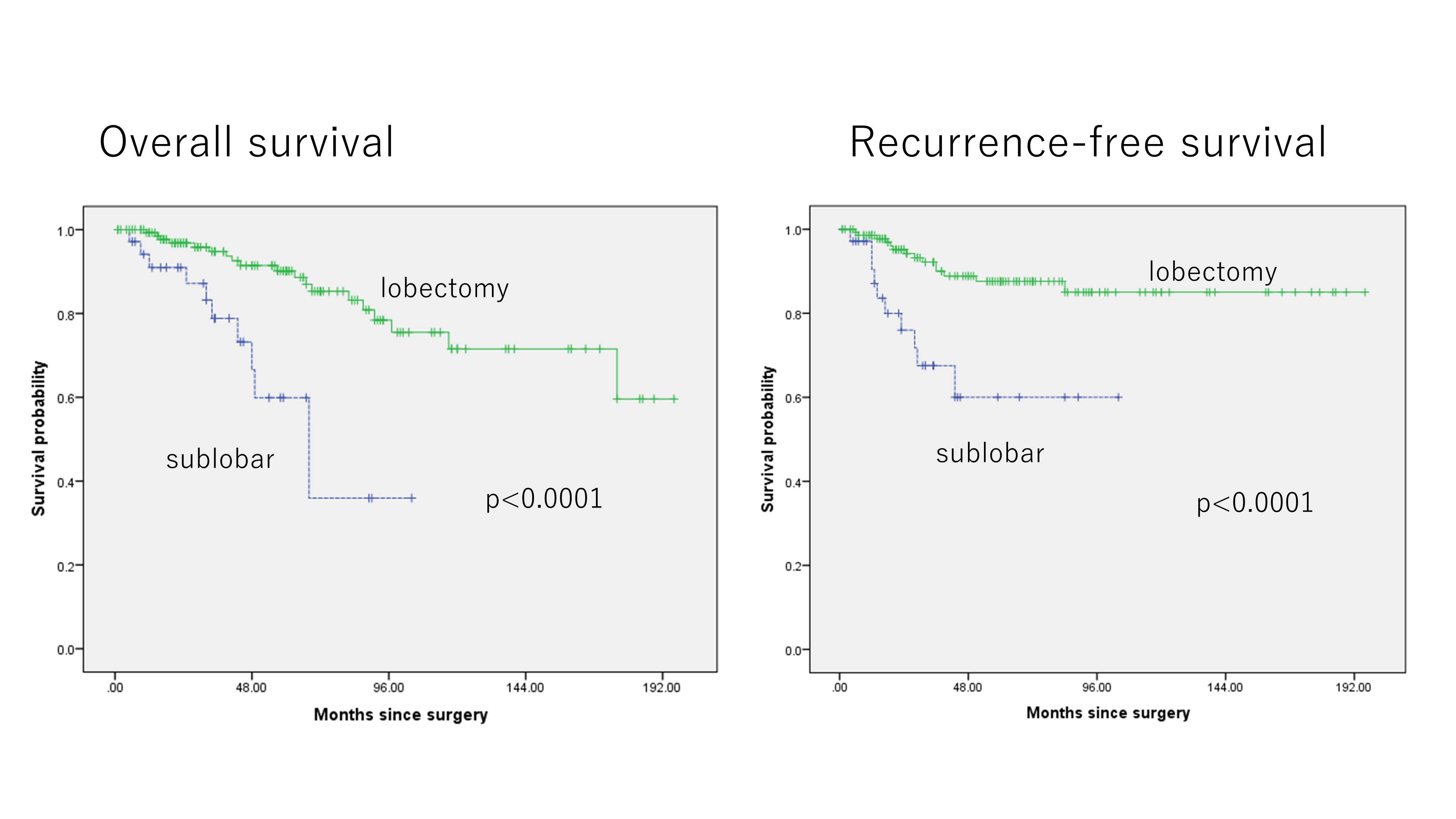 179 patients met inclusion criteria. 104 (58%) were male and 75 (42%) were female, with a median age of 68 years; sublobar resection was performed in 35 (20%), and lobectomy or pneumonectomy in 144 (80%). Median pathological tumor size was 1.5 cm, with a median invasive component size of 0.9 cm, and pleural, lymphatic, or vascular invasion in 27 (15%), 25 (14%), and 49 (23%) patients, respectively. In IAD, the elderly patients and ever smokers were likely to undergo sublobar resection (p=0.015, 0.011, respectively). Patients undergoing sublobar resection for IAD had significantly worse prognosis (5-year OS: 59.9%, 90.2%, p<0.0001) and increased risk of local recurrence (5-year RFS: 60.0%, 87.6%, p<0.0001). Multivariable analysis revealed that sublobar resection, age, and sex was an independent risk factor of overall survival and sublobar resection and vascular invasion was an independent risk factor of recurrence for IAD ≤2-cm.
179 patients met inclusion criteria. 104 (58%) were male and 75 (42%) were female, with a median age of 68 years; sublobar resection was performed in 35 (20%), and lobectomy or pneumonectomy in 144 (80%). Median pathological tumor size was 1.5 cm, with a median invasive component size of 0.9 cm, and pleural, lymphatic, or vascular invasion in 27 (15%), 25 (14%), and 49 (23%) patients, respectively. In IAD, the elderly patients and ever smokers were likely to undergo sublobar resection (p=0.015, 0.011, respectively). Patients undergoing sublobar resection for IAD had significantly worse prognosis (5-year OS: 59.9%, 90.2%, p<0.0001) and increased risk of local recurrence (5-year RFS: 60.0%, 87.6%, p<0.0001). Multivariable analysis revealed that sublobar resection, age, and sex was an independent risk factor of overall survival and sublobar resection and vascular invasion was an independent risk factor of recurrence for IAD ≤2-cm.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Sublobar resection in patients with IAD ≤2-cm was significantly associated with increased risk of recurrence and worse prognosis.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


