Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Yan Zhang
Author of
-
+
P2.13 - Targeted Therapy (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 962)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.13-30 - High-Dose Icotinib in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR 21 L858R Mutation: The Randomized, Open-Label INCREASE Study (ID 13184)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yan Zhang
- Abstract
Background
NSCLC patients with 21 L858R mutation are less responsive to EGFR TKI treatment. This study aims to determine if high-dose icotinib can improve tumor response and progression-free survival (PFS) in this patient population.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
In this randomized, open-label, multicenter phase II trial (INCREASE), patients with treatment-naïve, EGFR-mutant (19 deletion or 21 L858R at 1:2 ratio) lung adenocarcinoma were enrolled. Patients with 21 L858R were randomized to receive either routine-dose (125mg tid, 21 L858R-RD) or high-dose icotinib (250mg tid, 21 L858R-HD), whereas patients with 19 del receive icotinib 125mg tid until progression. The primary endpoint is PFS.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Between May 22, 2015 and November 15, 2017, 253 patients were enrolled (21 L858R-RD group, n=86; 21 L858R-HD group, n=90; 19 del group, n=77). Baseline characteristics were similar among groups with the exception of age. The median PFS (by IRC) were 9.20 months (95%CI 8.31, 10.74), 12.85 (10.09, 15.84), and 12.48 (9.23, 13.93) for 21 L858R-RD, 21 L858R-HD, and 19 del group, respectively, for modified intent-to-treat population (p=0.0848); and 8.84 months (8.21, 10.55), 12.62 (9.59, 14.26), and 12.22 (9.17, 13.60) for per-protocol set (p=0.0445). The ORR were 47.7%, 73.3%, and 75.3% for 21 L858R-RD, 21 L858R-HD, and 19 del group, respectively (p=0.0007). Patients in high-dose group experienced significantly higher incidence of AEs than routine-dose groups (21 L858R-RD vs 21 L858R-HD vs 19 del: 54.7% vs 81.1% vs 66.2%, p=0.0007), but the incidences of grade 3/4 AE were similar among the groups (4.7% vs 5.6% vs 5.2%, p=0.9632).
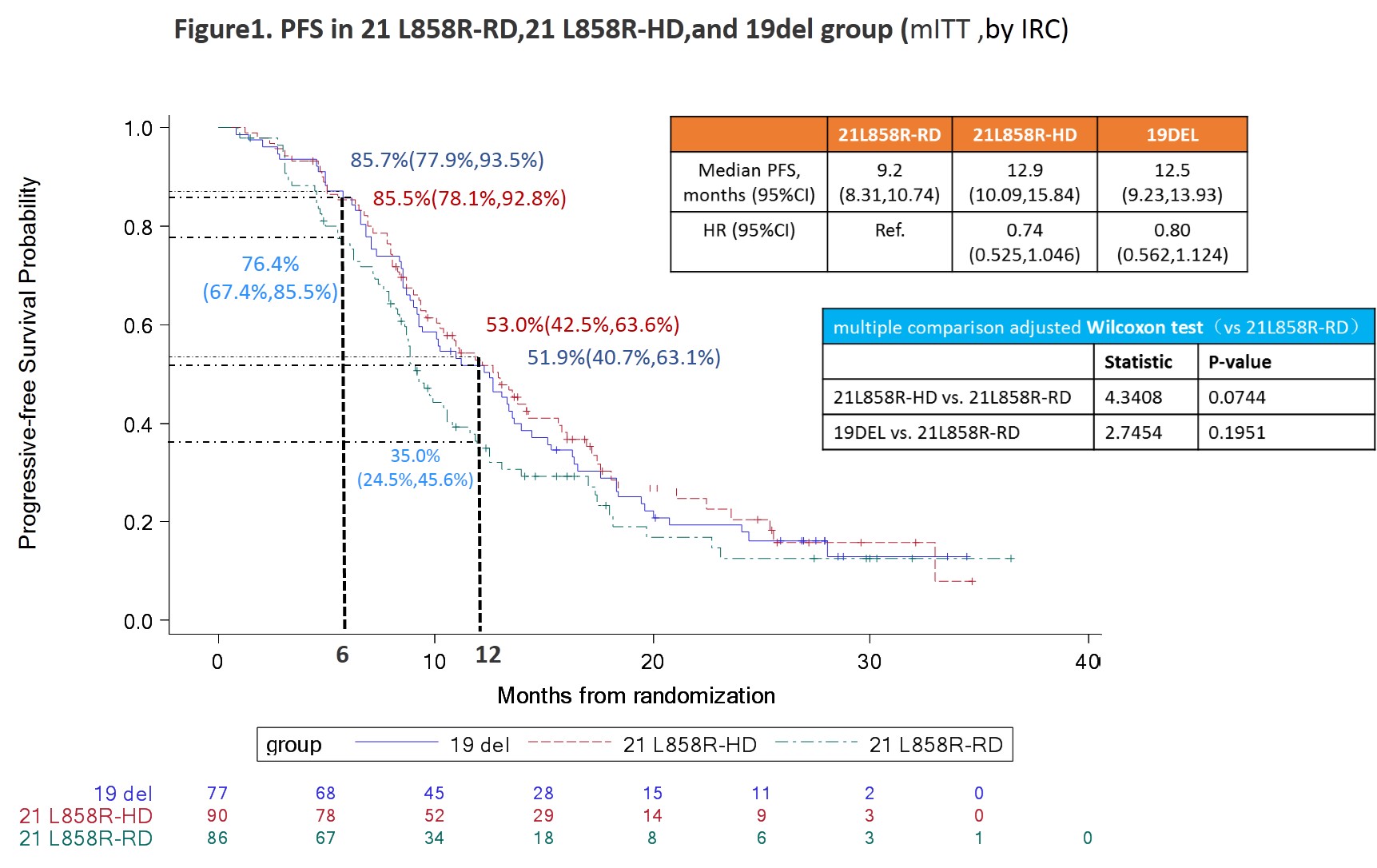
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
A prolonged PFS and improved ORR were observed in patients treated with high-dose icotinib in NSCLC patients harboring 21 L858R mutation with tolerable toxicity.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.13 - Targeted Therapy (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 979)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.13-21 - Apatinib Plus Icotinib as First-Line Therapy For EGFR Co-Mutations NSCLC in Chinese Patients: An Exploratory Study (ID 11987)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Yan Zhang
- Abstract
Background
To date, the phenomenon of EGFR co-mutated with other genes in untreated NSCLC patients was common, which might be the reason of EGFR-TKI primary resistance. In our previous research, samples from 81 NSCLC Chinese patients were tested with next-generation sequencing (NGS) based targeted panel assay, 49% (40/81) patients had EGFR co-mutations,the top-ranked co-mutant genes were TP53 (35%, 28/81) and cell cycle pathway related genes (19%, 15/81). Clinical data indicated that antiangiogenic drug combination with EGFR-TKI might reverse EGFR-TKI acquired resistance. Apatinib is a new antiangiogenic drug targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and Icotinib is a potent and specific EGFR-TKI, which were both made in China. In this study, we aim to assess the efficacy and safety of Apatinib plus Icotinib as first-line therapy for EGFR co-mutations NSCLC in Chinese patients, and compare the differences of curative effect among EGFR co-mutant subgroups.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
This single-arm, open-label exploratory study will recruit 50 Chinese patients with stage IIIB/IV NSCLC who have never received any anti-tumor treatment previously. Tumor tissue and matched blood of each patient will be collected for NGS-based 450 cancer related genes panel assay, designed to comprehensively assess EGFR mutation and co-mutations. Meanwhile, ctDNA extracted from blood samples will be collected for NGS-based 329 cancer related gene before treatment as baseline, and every 2 months after enrollment until disease progression, to evaluate the evolution of genomic variation and effects of drug efficacy. The analysis of genomic alterations including single base substitution, short and long insertions/deletions, copy number variations, gene rearrangement in selected genes and also tumor mutation burden (TMB) calculated as total somatic substitutions and indels per megabase. Patients with EGFR-sensitizing mutations accompanied with other genomic alterations will receive Apatinib 250mg, qd, po and Icotinib 150mg, tid, po until disease progression, or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint of this study is progression free survival (PFS), and the secondary endpoints include objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS), quality of life (QOL) and drug-safety.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Not applicable
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Not applicable
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


