Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Evrim Tunç
Author of
-
+
P3.08 - Oligometastatic NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 974)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.08-01 - Treatment Outcomes in Oligometastatic Disease of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single Center Experience (ID 12795)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Evrim Tunç
- Abstract
Background
Even if oligometastatic disease is staged as 4, survival rates are higher when curative approaches are performed for both primary tumour and metastasis. We analysed our institution data of oligometastatic disease.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
52 NSCLC patients with limited metastasis were retrospectively analysed. All treatment modalities (surgery, CRT, supportive-care, palliative chemotherapy) were compared in terms of survival. Curative treatment was defined as surgery or CRT (concurrent or sequential).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion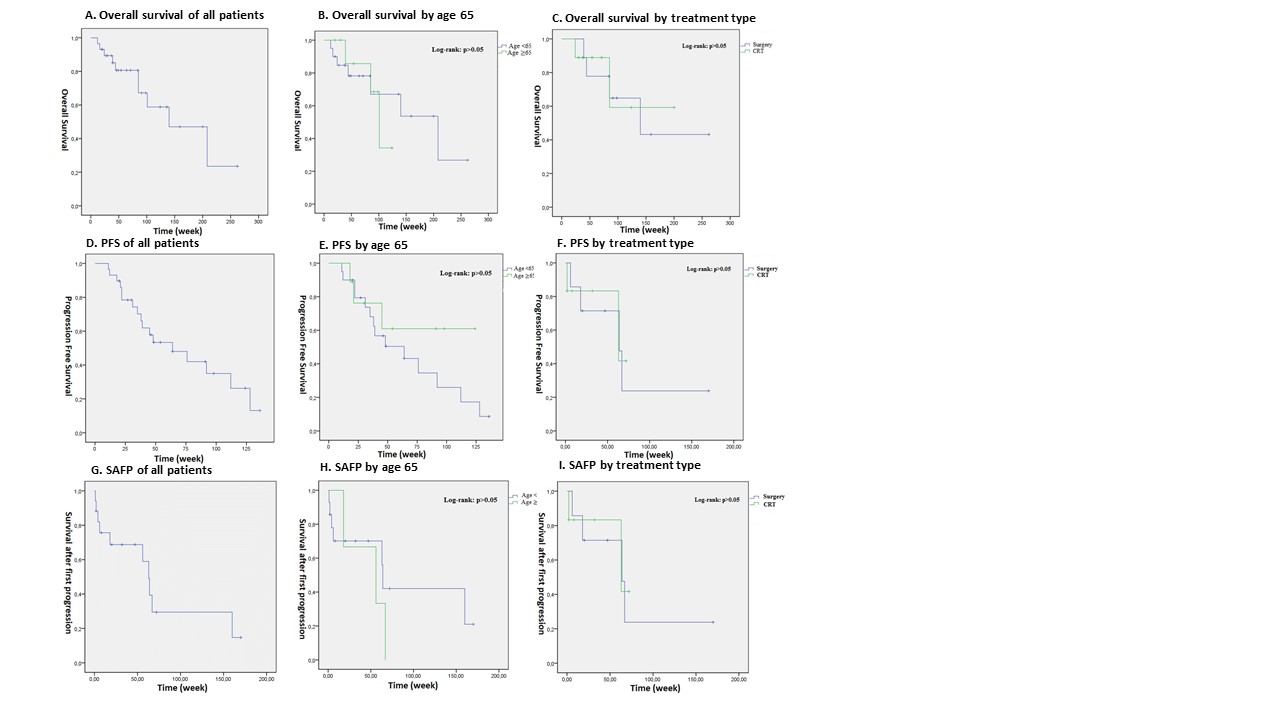 Results: Median overall survival (OS) was 35.2±4.1 months. Surgery was superior to CRT in terms of OS (36.7 months vs. 27.4 months, p>0.05). Progression free survival (PFS) was 29.4±3.9, survival after first progression (SAFP) was 15.6±2.8 months. Patients performed metastasectomy had higher SAFP rates than others with significance (20.07±3.8 months vs. 7.9±1.7 months p=0.046). Adenocarcinoma was related better SFAP than non-adenocarcinoma group (23±4.1 vs 6.4±1.5, p=0.002). The 1- and 2-year OS were, 67% and 50.4%, respectively. Among curative treatment group, while patients under age 65 (n=25) had 31 months OS, patients above 65 (n=13) had 22 months (p=0.88).
Results: Median overall survival (OS) was 35.2±4.1 months. Surgery was superior to CRT in terms of OS (36.7 months vs. 27.4 months, p>0.05). Progression free survival (PFS) was 29.4±3.9, survival after first progression (SAFP) was 15.6±2.8 months. Patients performed metastasectomy had higher SAFP rates than others with significance (20.07±3.8 months vs. 7.9±1.7 months p=0.046). Adenocarcinoma was related better SFAP than non-adenocarcinoma group (23±4.1 vs 6.4±1.5, p=0.002). The 1- and 2-year OS were, 67% and 50.4%, respectively. Among curative treatment group, while patients under age 65 (n=25) had 31 months OS, patients above 65 (n=13) had 22 months (p=0.88).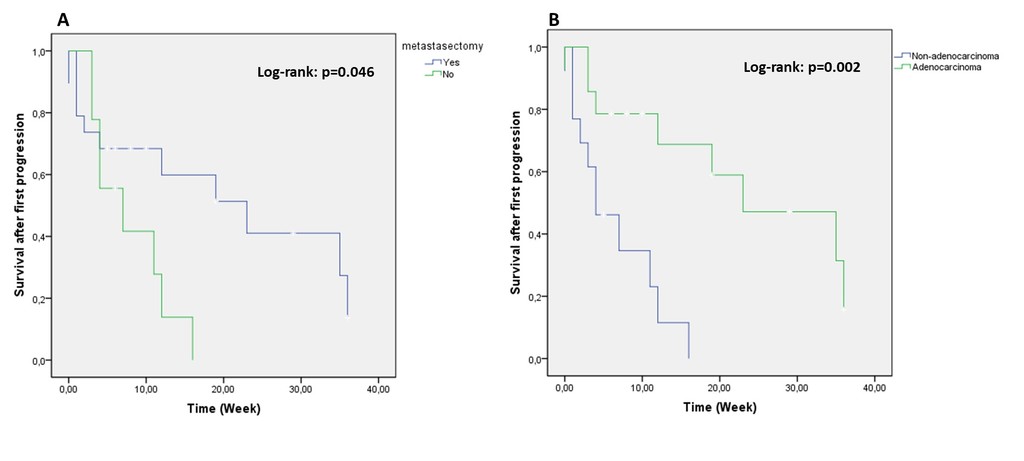
Conclusion: Our study revealed that in well-selected NSCLC patients with limited metastasis survival rates can reach up to 3 years even in geriatric population. And clinical N staging and co-morbidity are well known prognostic factors.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


