Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Si Chen
Author of
-
+
P3.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 967)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.01-64 - Preliminary Data of Diverse Therapies in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harbouring RET-Rearrangement (ID 13677)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Si Chen
- Abstract
Background
Activating RET-rearrangement has been discovered to play a crucial role in NSCLC tumorigenesis. However, the lack of specificity narrowed efficacy of multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs) and the optimal treatment remains unknown. In this study, we compared chemotherapy, immunotherapy and MKIs in this group of patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively evaluated the efficacy of these three treatments in advanced, RET-rearranged NSCLC patients between January 2013 and April 2018 at our institution. RET-rearrangements were assessed by Next-generation sequencing (NGS) or any of FISH, IHC, RT-PCR. Treatment data were collected after the patients had been diagnosed with RET-rearranged advanced NSCLC. Progression-free survival (PFS) was measured from treatment start to disease progression, all-cause mortality or last follow up. Median follow-up time was 5.1months. NGS was performed to assess somatic mutation of available samples.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 30 patients with RET-rearrangement were investigated in this study. After the diagnosis, 15 patients, genetic profiles confirmed by NGS, received chemotherapy (n=10), checkpoint-inhibitors (n=7) and RET targeted MKI (n=6) with evaluable response. Several patients take any two of these three treatments as different line therapies. The disease control rate of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, MKI group was 70.0%, 71.43% and 50%, respectively. While the median PFS of three groups was 2.50 months, 2.70 months, 0.30 months, respectively, which of no significance. The NGS data of 10 patients showed that RET-rearrangement co-occurred with several other genes, including TP53, NTRK, CDK4, ERBB4. A low mutation burden (mean 4.5 mutations) was observed (Figure 1).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion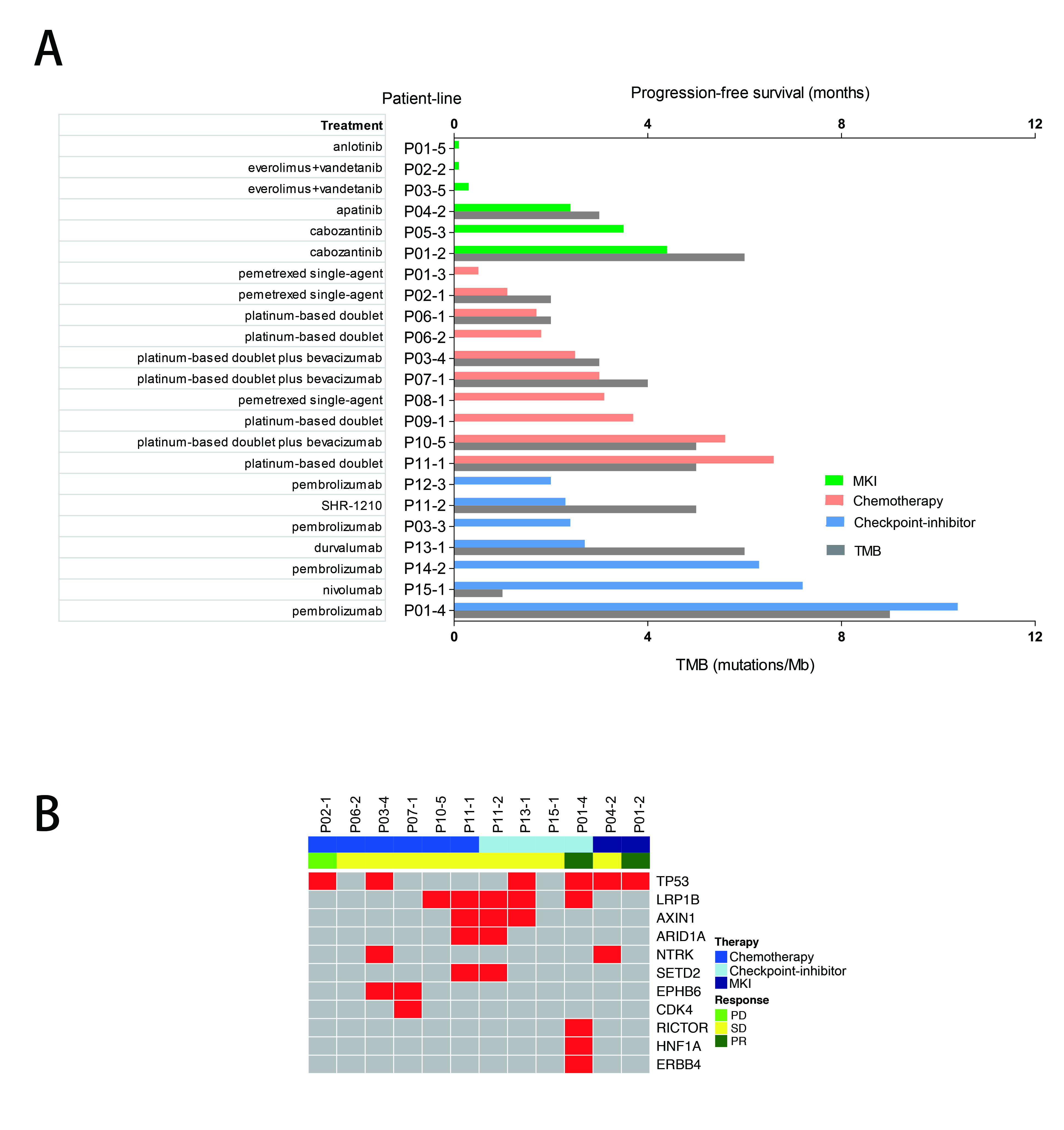
We confirmed relatively low PFS in advanced RET-rearranged NSCLC with MKIs reported in previous studies. But further investigation is warranted. Treatment with checkpoint-inhibitors seemed to encouragingly prolong PFS but a larger group of patients is needed to draw a definite conclusion.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


