Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Deepak Koppaka
Author of
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-125 - EGFR Mutations by NGS in Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancer (ID 13230)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Deepak Koppaka
- Abstract
Background
Targets for Squamous cell lung cancer are none as against adenocarcinomas.Also there is limited data available from ct DNA in these patients
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
This prospective observational study looked at patients with squamous cell carcinoma lung, either newly diagnosed or having a progressive disease on prior therapy were enrolled. cf-DNA was extracted from peripheral blood and analyzed for EGFR, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF mutations using NGS.20 ml of the blood sample was collected from the patient prior to the initiation of therapy or at progression.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Sixteen patients of squamous cell carcinoma lung were enrolled into the study. The mean circulating cell-free tumour DNA extracted from the plasma was 96.6 ng (Range, 15-200 ng). Genomic analysis by NGS on the extracted DNA revealed mutations in the EGFR pathway among 8 (50%) patients. The commonest mutation was Exon 21 Leu858Arg (4 patients). One patient had Exon 20 Thr790Met mutation. One patient had complex mutations with coexisting Exon 21 Leu858Arg and Exon18 Gly719Arg in the same sample. Two patients had KRAS Exon2 Gly12Cys mutation.
Among the patients with Exon 21 mutation, two patients were treatment naïve and two patients were having a progressive disease (one post Gemcitabine/Carboplatin-based chemotherapy and another post Gemcitabine/Carboplatin and Docetaxel chemotherapy). Patient with complex mutations had progressive disease post Gemcitabine/Carboplatin. Patient with Exon 20 T790M mutation had a hyper-progressive disease post-Nivolumab based regimen. While one patient with KRAS mutation one patient was treatment naive while another had progressive disease post Gemcitabine/Carboplatin-based regimen (Table 2).
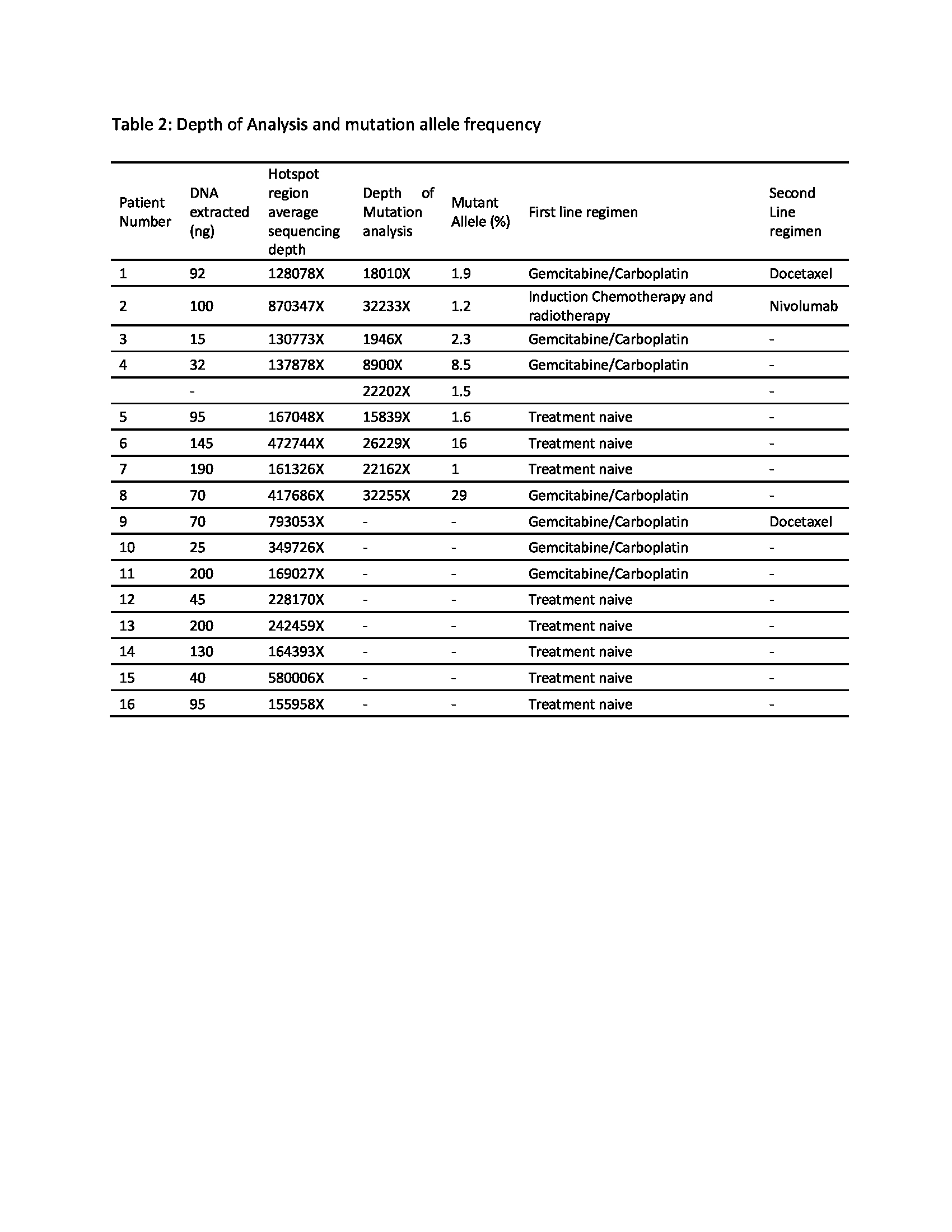
Two patients with Exon 21 mutations who progressed on earlier lines of treatment received Gefitinib. One patient had progressive disease at 3 months while the other patient succumbed to the disease two months after starting Gefitinib. Treatment Naïve patients with EGFR Exon 21 mutations (N=2) upfront received Gemcitabine and Carboplatin-based chemotherapy. Of this 1 patient is currently progression-free and another patient progressed 6 months post chemotherapy and at progression was started on Gefitinib. Patient has a stable disease after 3 months of treatment and still on gefitinib. Patient with Exon 20 T790M mutation was stated on nab-paclitaxel and succumbed to the illness 6 months later. Patient with complex mutations received Docetaxel as second-line chemotherapy and had a progressive disease 4 months after the initiation of therapy and died.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma lung detection of EGFR mutations helps increase the treatment armamentarium for management of these patients. cf-DNA is a good technique for detecting relevant mutations
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


