Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Narumol Trachu
Author of
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-90 - PD-L1 Expression as a Predictive Biomarker in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with or without EGFR Mutation (ID 13528)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Narumol Trachu
- Abstract
Background
The prognostic value of PD-L1 expression and its clinical relevance of NSCLC is controversy. The impact of PD-L1 expression as the predictive biomarker for EGFR-TKIs treatment is needed to explore.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Medical records of metastatic NSCLC during September 2015-2016 had been reviewed. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining with Antibody clone 22C3 was used. The PD-L1 positive was defined by tumor proportion score (TPS) > 1%.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
204 patients were included. Patients with positive PD-L1 expression had significantly increased numbers of metastatic sites (P=0.009) and lung metastasis (P=0.045) compared to PD-L1 negative patients. Overall survival (OS) was longer in PD-L1 negative patients (22.7 months) compared to PD-L1 positive groups (13.6 months) (HR=1.48; P=0.03). Median OS were significantly different with the number of 7.2, 11.1, 25.7, 42.6 months in EGFR-/PD-L1+, EGFR-/PD-L1-, EGFR+/PD-L1+ and EGFR+/PD-L1- , respectively (P<0.001). Among EGFR positive patients, mOS of T790M-/PD-L1+, T790M-/PD-L1-, T790M+/PD-L1-, and T790M+/PD-L1+ were 22.1, 28, 42.6 and 48.4 months, respectively (P=0.03).
Patient characteristics categorized by PD-L1 expression (N = 204) Characteristics PD-L1 Negative
N=134 (65.69%)
PD-L1 Positive
N=70 (34.31%)
P value Age
- Median age (range)
- < 65 years
- > 65 years
65 (36-85)
64 (47.76)
70 (52.24)
65 (35-86)
33 (47.14
37 (52.86)
0.933 Sex
- Male
- Female
62 (46.27)
72 )53.73)
37 (52.86)
33 (47.14)
0.371 ECOG PS
- 0-1
- > 2
116 (86.57)
18 (13.43)
57 (82.61
12 (17.39)
0.452 Smoking status
- Never
- Ex-smoker
- Current smoker
82 (61.65)
36 (27.07)
15 (11.28)
36 (52.17)
18 (26.09)
15 (21.74)
0.131 Mean smoking pack-year (range) 29.72 (2-100) 25.68 (2-40) 0.873 Initial staging
- Recurrent
- Denovo metastasis
32 (23.88)
102 (76.12)
14 (20)
56 (80)
0.529 Histology
- Adenocarcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Others
117 (87.31)
1 (0.75)
2 (1.49)
14 (10.45)
58 (84.06)
3 (4.35)
2 (2.9)
6 (8.7)
0.288 EGFR mutation
- Negative
- Positive
47 (35.07)
87 (64.93)
32 (45.71)
38 (54.29)
0.092 Exon 19 deletion
- No
- Yes
87 (64.93)
47 (35.07)
50 (71.43)
20 (28.57)
0.348 L858R
- No
- Yes
100 (74.63)
34 (25.37)
53 (75.71)
17 (24.29)
0.865 ALK results
- Negative
- Positive
79 (92.94)
6 (7.06)
47 (97.92)
1 (2.08)
0.421 Number of site of metastasis
- 0-1
- > 2
88 (65.67)
46 (34.33)
37 (52.86)
33 (47.14)
0.009 Lung metastasis
- No
- Yes
92 (69.17)
41 (30.83)
38 (54.29)
32 (45.71)
0.045 Bone metastasis
- No
- Yes
101 (75.37)
33 (24.63)
53 (75.71)
17 (24.29)
0.957 Liver metastasis
- No
- Yes
122 (91.04)
12 (8.96)
62 (88.57)
8 (11.43)
0.573 Pleural metastasis
- No
- Yes
91 (67.91)
43 (32.09)
62 (88.57)
20 (28.57)
0.606 Brain metastasis
- No
- Yes
117 (87.31)
17 (12.69)
58 (82.86)
12 (17.14)
0.387 Adrenal metastasis
- No
- Yes
122 (91.04)
12 (8.96)
62 (88.57)
8 (11.43)
0.573
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion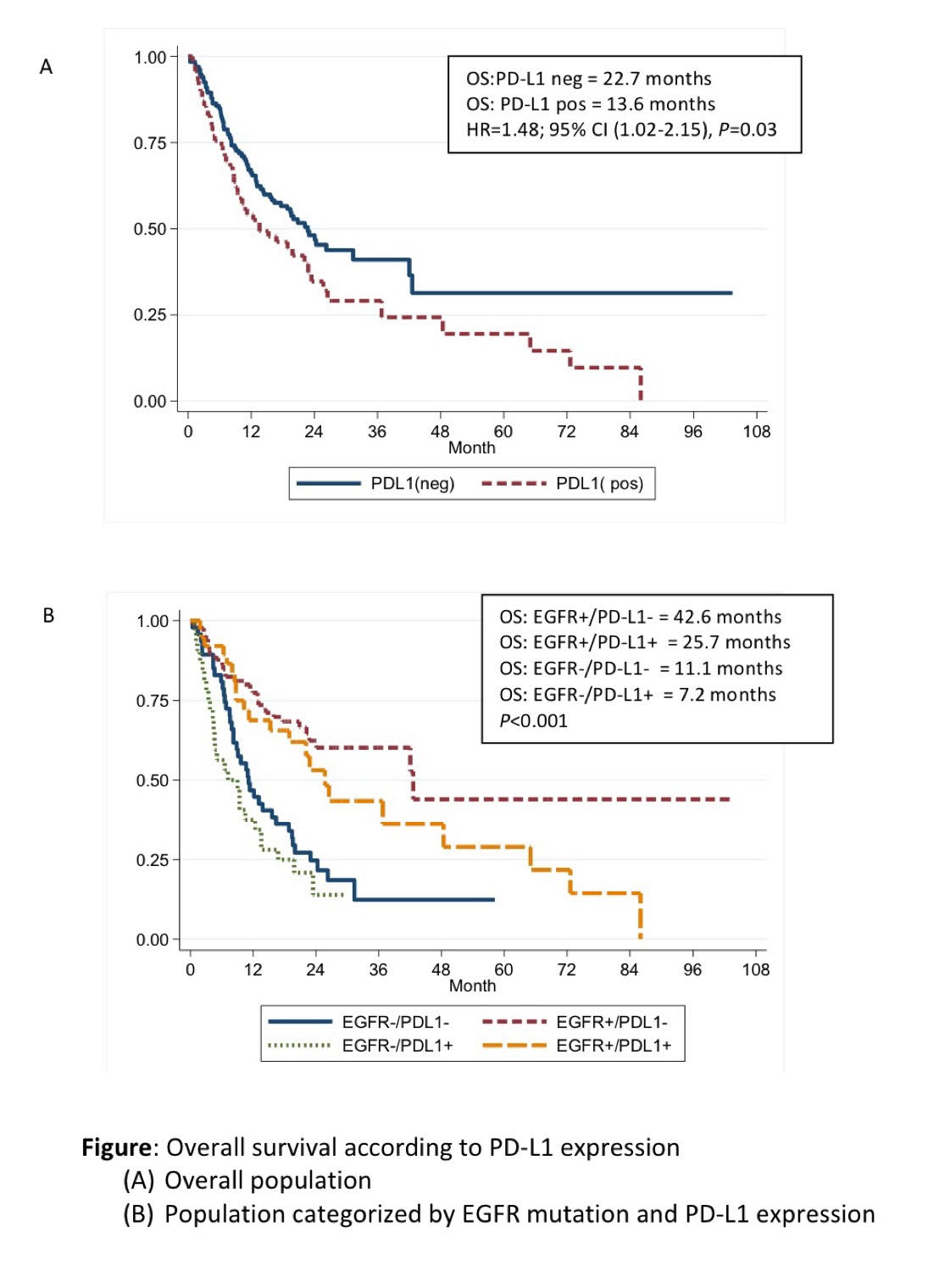
PD-L1 expression was associated with poorer survival outcomes among advanced NSCLC patients regardless of EGFR mutation status. PD-L1 expression is also the potential of predictive biomarker for EGFR TKIs treatment. The larger studies are needed to identify the prognostic and predictive values in T790M mutation population.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.09 - Pathology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 975)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.09-10 - Circulating Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) Molecular Profile of Thai NSCLC Patients Using Difference Variant Frequency of NGS (ID 13744)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Narumol Trachu
- Abstract
Background
Detecting cfDNA in the liquid biopsy has become a promising method to explore the genetic landscape of tumor heterogeneity. We developed a pilot-study to find the suitable cutoff of variant frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by NGS to track tumor-associated mutations in NSCLC patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Ninety-four samples (24 early-stage NSCLC, 70 late-stage NSCLC) were collected from Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand. Profiling cfDNA using Ion Proton NGS platform. Overall average base coverage depth from NGS was 10,000x, all variants selected have read depths >10x in order to reach 0.1% sensitivity. Each of selected variants has threshold variant quality (QUAL) >20. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) was performed for EGFR-mutation testing to determine the appropriated cutoff variant frequency from NGS.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In early-stage NSCLC, a minimum-threshold variant frequencies at 0.1% could detect EGFR exon19 deletion in all samples (24,100%), with BRAF (12,50%), KRAS (21,87.5%) and other mutations in AKT1, MET, PIK3CA, PTEN, ROS1 (14,58%). None of these mutations identified when using conventional level cutoff at 3% (Table1). ddPCR observed EGFR-mutations in 2 early-stage cases only (8.3%). In late-stage NSCLC, 64 (91.4%) cases were observed multiple mutations, suggesting tumor heterogeneity. At 0.1% cutoff in NGS, Thirty-six (52.9%) cases of EGFR-mutations in NGS and ddPCR were identical. Thirteen (18.6%) samples shown partial discrepancies in the mutations. Interestingly, NGS found EGFR-mutations in 20 (28.6%) samples which ddPCR failed to detect, 12 of them contained T790M. Only one sample (1.4%) using 0.1% cutoff was unable to detect EGFR-mutation. Higher variant allele frequencies were found in EGFR-positive detected by ddPCR compared to not-detected by ddPCR.
Table1 Mutations detected variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by NGS at minimum threshold cut-off 0.1% variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by NGS at minimum threshold cut-off 0.1% variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by NGS at conventional level detection of somatic variants cut-off 3% variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by NGS at conventional level detection of somatic variants cut-off 3% variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by ddPCR (EGFR only) variant allele frequencies detected from liquid biopsy by ddPCR (EGFR only) N (%) median (range) N (%) median (range) N (%) median (range) BRAF (V600E) early stage total N=24 12 (50%) 0.8 (0.3-2.5) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA BRAF (V600E) late stage total N=70 11 (15.7%) 0.6 (0.1-1.1) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA KRAS early stage 21 (87.5%) 0.1 (0.1-0.5) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA KRAS late stage 50 (71.4%) 0.2
(0.1-13.6)
3 (4.3%) 11.1 (5.8-14.3) NA NA AKT1 (E17K) early stage 7 (29.2%) 0.1 (0.1-0.7) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA AKT1 (E17K) late stage 12 (17.1%) 0.1 (0.1-0.7) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA MET exon 14 splicing early stage 4 (16.7%)
0.1 (0.1-0.1) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA MET exon 14 splicing late stage 3 (4.3%) 0.2 (0.2-0.2) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA PIK3CA early stage 9 (37.5%) 0.2 (0.1-0.8) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA PIK3CA late stage 19 (27.1%) 0.3 (0.1-0.7) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA PTEN (R233*) early stage 6 (25.0%) 0.1 (0.1-0.4) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA PTEN (R233*) late stage 11 (15.7%) 0.1 (0.1-0.2) 0 (0%) 0 NA NA ROS1
early stage 0 (0%) 0 0 (0%) 0 NA NA ROS1
late stage 4 (5.7%) 0.55
(0.1-0.7)
0 (0%) 0 NA NA EGFR
Exon 19 Deletion
early stage 24 (100%) 0.35
(0.1-2.1)
0 (0%) 0 1 (4.2%) 0.5 (0.5-0.5) EGFR
Exon 19 Deletion
late stage 25 (35.7%) 0.6
(0.1-49.0)
6 (8.6%) 9.4 (4.5-49.5) 20 (28.6%) 0.65 (0-49.0) EGFR L858R early stage 5 (20.8%) 0.2 (0.1-0.5) 0 (0%) 0 0 (0%) 0 EGFR L858R late stage 21 (30%) 1.4 (0.1-9.7) 4 (5.7%) 4.6 (4.4-6.4) 14 (20%) 1.8 (0.3-9.7) EGFR T790M early stage 8 (33.3%) 0.1 (0.1-0.2) 0 (0%) 0 0 (0%) 0 EGFR T790M late stage 30 (42.9%) 0.1 (0.1-4.6) 2 (2.9%) 7.5 (5.3-9.7) 16 (22.9%) 0.15 (0-4.1) EGFR Exon18 (G719X) early stage 6 (25%) 0.2 (0.1-0.4) 0 (0%) 0 1 (4.2%) 0.4 (0.4-0.4) EGFR Exon18 (G719X) late stage 4 (5.7%) 4.5
(0.1-49.2)
2 (2.9%) 27.9
(6.7-49.2)
2 (2.9%) 25.6 (2-49.2) EGFR Exon 20 Insertion early stage 0 (0%) 0 0 (0%) 0 0 (0%) 0 EGFR Exon 20 Insertion late stage 1 (1.4%) 73.8
(73.8-73.8)
1 (1.4%) 91.7
(91.7-91.7)
0 (0%) 0
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Detecting variant frequencies at 0.1% could reveal more hidden tumor-associated mutations compared to variant frequency cutoff at 3%. With a careful validation, profiling cfDNA using NGS can be a crucial method to accurately select treatment for NSCLC patients in the future.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


