Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Hui Liu
Author of
-
+
P1.15 - Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 947)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.15-17 - Risk Factors of Local Recurrence in EGFR-Mutant Stage III-pN2 Adenocarcinoma After Complete Resection: A Multi-Center Real-World Cohort Study (ID 12740)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Hui Liu
- Abstract
Background
Postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) of complete resected stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer with N2 nodal involvement remained contentious. Our previous study suggested low locoregional recurrences in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant patients. We sought to launch a multi-center large cohort study to evaluate the risk factors of locoregional recurrence in R0 resected EGFR mutant III-pN2 patients without PORT, producing evidence for the design of adjuvant regimens.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Three-hundred and fifty-nine consecutive patients with complete resected, pathological approved stage III-pN2 lung adenocarcinoma with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) have been investigated. Patients were excluded if they received induction therapy (7.5%) or PORT (9.6%). Three hundred cases have been analyzed. Clinicopathologic characteristics, pretreatment work-ups, EGFR mutant status and patterns of failure were documented. Patients were sub-staged by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)/ the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) 7th classification on N2 disease. Risk factors of locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRFS) were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analyses.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
According to IASLC/UICC 7th classification, there were 198 (66.0%) patients with unforeseen N2 (N2a), 36 (12.0%) with minimal/single station N2 (N2b), 41 (13.7%) with selectively centrally located N2 (N2c) and 25 (8.3%) with bulky and/or multilevel N2 (N2d). After surgery, 70 (23.3%) patients were treated with adjuvant tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs), while other 230 (76.7%) were free from adjuvant TKIs. With median follow-up of 28.5 (range:6-133) months, the 2-year LRFS, distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were 88.3%, 65.3%, 57.7% and 89.7%. Ultimately, 15.7% (47/300) patients developed locoregional recurrences. Distant metastasis was the predominant failure pattern. Multivariate analysis indicated that N2d disease (HR: 2.65, p=0.030) and extranodal extension (HR: 3.48, p<0.001) were risk factors of LRFS.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
R0 resected stage III-pN2 NSCLC patients with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) tended to present limited N2 disease and low locoregional recurrences. Patients without bulky N2, multilevel N2, and extranodal extension might be refrained from PORT. Further studies evaluating the optimal radiotherapy approach for completely resected N2-positive NSCLC are required for validation.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.16 - Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 948)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.16-40 - Evaluating the Tumor Heterogeneity in Lung Cancer by Constructing Tumor Heterogeneity Index (THI) from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ID 13134)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Hui Liu
- Abstract
Background
To improve the evaluation of primary lung cancer heterogeneity using clinical routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), we proposed a method based on basic measurements from T1- and T2-weighted MRI.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
As a novel technique of magnetic resonance imaging analysis, we investigated a total of 203 patients with biopsy-proven primary lung cancer and with different T stages. All patients previously received positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan. Gross lesions were manually contoured on T1-weighted, T1-enhanced, T2-weighted and T2 fat suppression (T2fs) images. The ratios of standard deviation (SD) / mean tumor value from each sequence were calculated. Correlation analyses were performed between T stages and the ratios. P value <0.05 was defined as statistical significant. Then a linear regression was performed to determine the weight of each related ratio. A model was built to calculate Tumor Heterogeneous Index (THI). One hundred and one patients were analyzed as the training set and another 102 as validating set.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
There were 56 patients diagnosed with T1 disease, 60 with T2 disease, 51 with T3 disease and 36 with T4 disease. Pair matching was performed between training set and validating set. As a result of the correlation analyses, SD/mean ratio showed significantly correlations with T stages in T1-enhanced (p=0.003), T2-weighted (p<0.0001) and T2fs sequences (p=0.002). Based on a linear regression model, THI was established for assessing the heterogeneity of lung tumor, consisting the three ratio measurements. Correlation analysis demonstrated that Higher THI was significantly related to more advanced T stages (p<0.0001).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion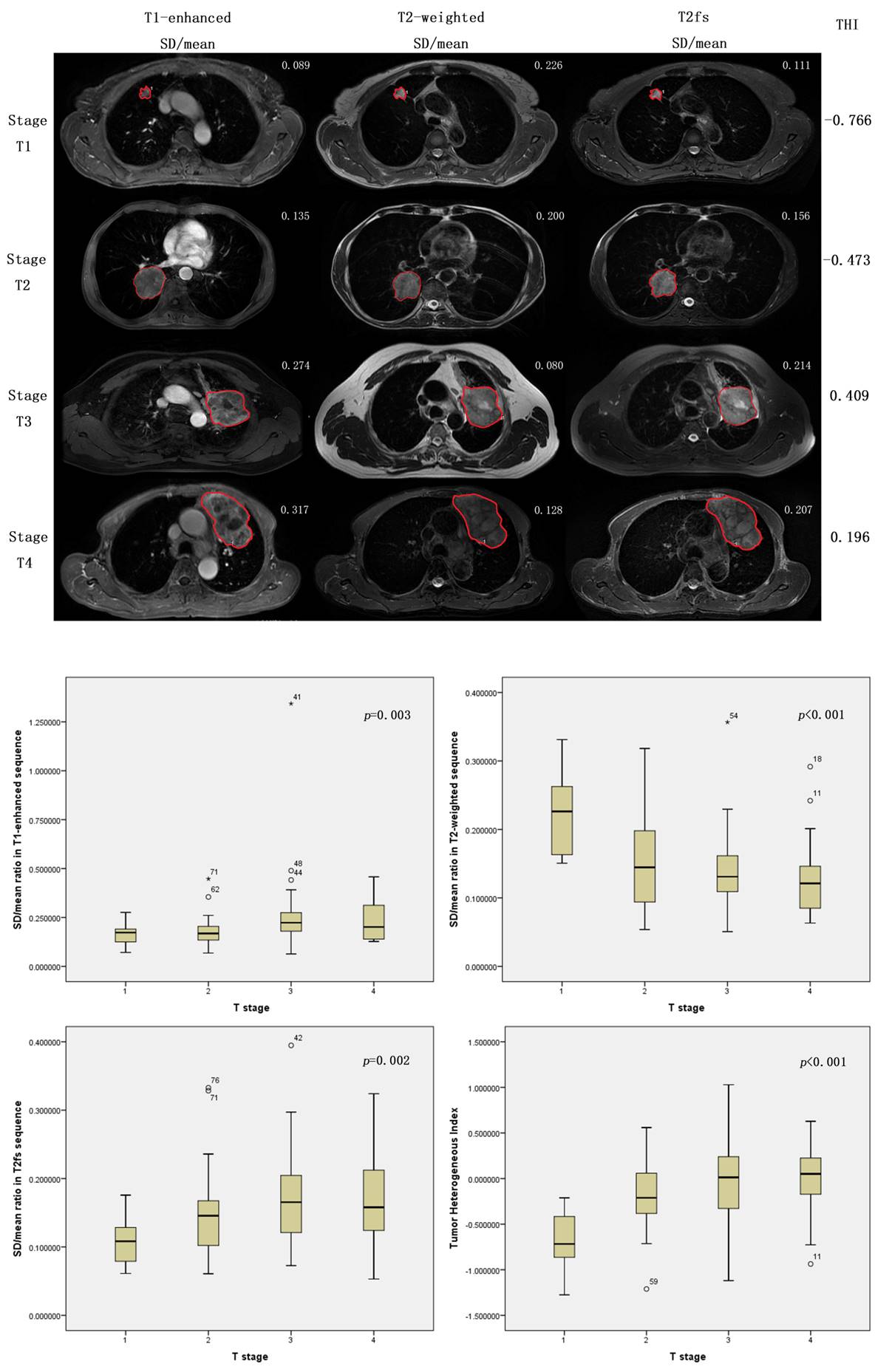
The proposed SD/mean ratio measurements and the calculation of THI according to clinical routine MR images could be clinical biomarkers that correlated with T stages, and were capable of evaluating heterogeneity of lung cancers.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.17 - Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 966)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.17-26 - Quantifying the Interfractional Motion of the Esophagus During Radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 12964)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Hui Liu
- Abstract
Background
To quantify the interfractional motion of the esophagus during radiation therapy for locally advanced non small cell lung cancer using daily cone beam CT.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
The analysis of interfractional esophagus motion was performed on treatment planning 4DCT scans and daily CBCT acquired from 35 patients with stage IIIA/B NSCLC. The simulation CT and CBCT were fused using bone registries and adjusted to the carina. Interfractional motion of the esophagus in the right-left (RL) and anterior-posterior (AP) directions at levels of sternal notch (A), carina (B), 2.5 cm below the carina (C) and the left lower pulmonary vein (D) was recorded and analyzed respectively.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 612 CBCT image sets were obtained. The mean interfractional RL motion at level A, B, C and D was 0.5±2.9mm, -0.2±3.7mm, -0.5±3.9mm and -1.3±4.8mm, with the mean absolute value of 2.1±2.0mm, 2.7±2.6mm, 2.9±2.6mm and 3.4±3.6mm, respectively. The mean AP motion at level A, B, C and D was -0.3±2.0mm, 1.0±2.0mm, 1.3±2.2mm and 2.2±2.4mm, with the mean absolute value of 1.6±1.3mm, 1.7±1.6mm, 2.6±1.9mm and 3.4±3.6mm, respectively. Coverage of 95% of esophageal mobility requires 4.9 mm left, 4.4mm right, 3.1mm posterior and 3.7mm anterior margins at level A; 5.3 mm left, 6.5mm right, 4.5mm posterior and 1.9mm anterior margins at level B; 5.5 mm left, 7.2mm right, 4.8mm posterior, and 2.0mm anterior margins at level C; and 4.9 mm left, 7.9mm right, 6.3mm posterior, and 1.6mm anterior margins at level D.
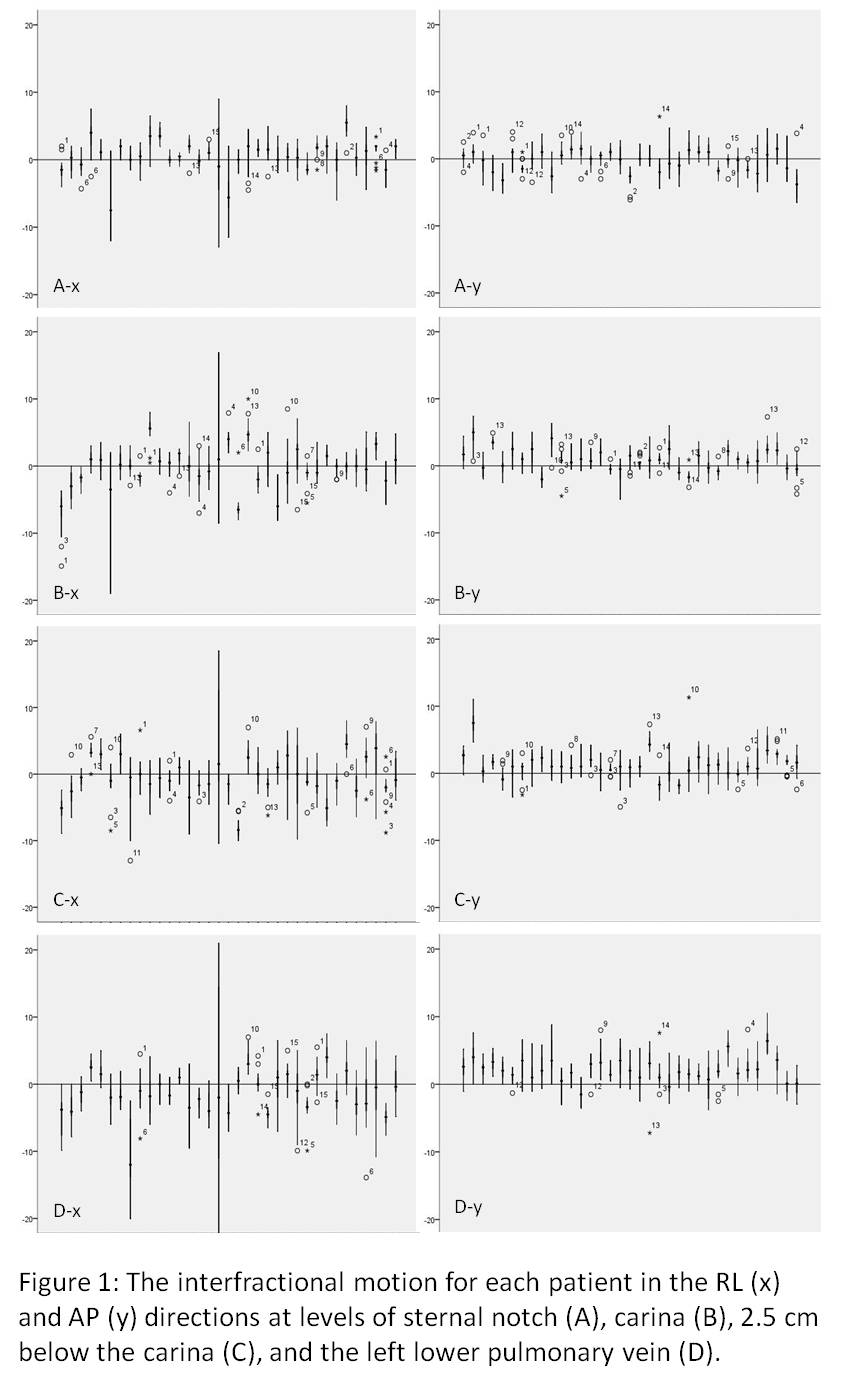
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In RL and AP directions, the average of the absolute interfractional motion of the esophagus was 3.4mm or less at all the four levels. The interfractional motion was greatest at the level of left lower pulmonary vein. The absolute RL motion was greater than AP motion. These data helps to set margin for ITV for future IMRT trials to account for esophageal motion.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 967)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.01-60 - A Novel MET D1246H Mutation After Progression of EGFR-TKI/MET Inhibitor Combined Therapy in a NSCLC Patient with Acquired MET Amplification (ID 13625)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Hui Liu
- Abstract
Background
MET amplification was the second common acquired resistance mechanism to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It may be benefited by combinations of EGFR TKIs and the MET inhibitor. However, the acquired resistance mechanism to this combination therapy remains to be identified.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
A patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma harboring both EGFR L858R mutation and acquired MET amplification, progressed after the combination of MET inhibitor gefitinib and EGFR-TKI crizotinib. The next generation sequencing (NGS) based circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) assay was performed. Results were applied to discover a novel mutation after resistance to target therapy.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A 52-year-old Chinese never-smoking woman with EGFR L858R mutant adenocarcinoma had systemic progression after gefitinib, pemetrexed/platinum-pemetrexed maintenance, and SBRT local progressed lung metastasis. The NGS-based ctDNA analysis revealed that the MET amplification was found besides continually present EGFR L858R mutation. The patient started treatment with crizotinib (250mg Bid) and gefitinib (250mg/d). The NGS was performed after progression of this combined therapy. It revealed two novel mutations of MET D1246H (MAF 0.9%) and EGFR T790M mutation (MAF 0.2%), in addition to the initial presence of EGFR L858R mutation (MAF 9.8%) and MET amplification (LR 6.7). The patient started to receive osimertinib (80mg/d) and cabozantinib (20mg/d and later increased to 40mg/d). The patient tolerated this combination well while the symptoms did not relief. After 8 weeks, the re-scan CT showed pulmonary lesions progressed. The NGS-based ctDNA assay performed again and it showed that L858R mutation (MAF 11.4%) and MET amplification (LR 4.9) presented while the EGFR T790 mutation and MET D1246H disappeared. Then the patient received osimertinib (80mg/d) and crizotinib (250mg Bid). The patient felt symptoms improved greatly after 1 week’s administration and CT scan after 2 months showed good response. However,one more month later, the patient felt deteriorative symptoms of dyspnea and chest X-ray showed increasing pleural effusion , progressing pulmonary lesions. The NGS-based ctDNA assay at that time revealed that MET D1246H (MAF 14.4%) appeared again, in addition to the initial presence of EGFR L858R mutation (MAF 22.4%) and MET amplification (LR 8.2) while the EGFR T790 mutation was not existed. However, the patient died because of respiratory failure.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
MET mutations might be a potential acquired resistance mechanism after progression during EGFR-TKI /MET inhibitor combined therapy in advanced NSCLC patient with primary EGFR mutation and secondary acquired MET amplification.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.17 - Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 983)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.17-08 - Assessing Primary Lung Cancer Lesion Using Ratio Metrics of T1 and T2-Weighted Images in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ID 13151)
12:00 - 13:30 | Presenting Author(s): Hui Liu
- Abstract
Background
To assess if ratio metrics of T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) images in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could serve as a sensitive marker to improve the diagnostic efficacies of primary pulmonary lesions with reference to T stages in lung cancer patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Based on the ratio of T1- and T2-weighted signal intensities, we studied a large cohort of NSCLC patients with different T stages using a novel magnetic resonance imaging analysis technique. A total of 101 patients with PET/CT scan and biopsy-proven primary lung lesions were investigated. Gross pulmonary lesions were manually contoured, and corresponding tumor SUVmax, tumor T1-weighted (T1w)/T2-weighted (T2w) intensity ratio, tumor T1-enhanced (T1C)/T2w intensity ratio, muscle T1w/T2w intensity ratio and muscleT1C/T2w intensity ratio had been measured and correlated with T stages.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
There were 25 patients with T1 disease, 29 with T2 disease, 27 with T3 disease and 20 with T4 disease. All the 101 lung lesions were SUV avid, MRI imaging and (18)F-FDG PET/CT agreed on T stages in all patients (100%). Median SUVmax were 12.4 in T1, 12.4 in T2, 12.9 in T3 and 13.0 in T4 patients, respectively. Patients showed lower T1/T2w ratio values in tumor while higher T1/T2w ratio in muscle area (median tumorT1/T2w ratio: 0.69, median muscleT1/T2w ratio: 2.45, P=0.000). In contrast enhanced MRI, a higher T1C/T2w ratio was observed in tumor as compared to T1/T2w ratio (median tumorT1/T2w ratio: 0.69, median tumorT1C/T2w ratio: 2.45, P=0.000). However, tumor T1Cw/T2w ratio was still lower than muscle T1C/T2w ratio (median tumorT1C/T2w ratio: 2.45, median muscleT1C/T2w ratio: 3.25, P=0.000).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The T1/T2-weighted ratio can improve diagnostic efficacies of primary pulmonary lesions that match hypermetabolic tissues in PET/CT and enables more detailed tissue characterization of lung cancers.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


