Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Jin-Yu Guo
Author of
-
+
P1.15 - Treatment in the Real World - Support, Survivorship, Systems Research (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 947)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.15-17 - Risk Factors of Local Recurrence in EGFR-Mutant Stage III-pN2 Adenocarcinoma After Complete Resection: A Multi-Center Real-World Cohort Study (ID 12740)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Jin-Yu Guo
- Abstract
Background
Postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) of complete resected stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer with N2 nodal involvement remained contentious. Our previous study suggested low locoregional recurrences in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant patients. We sought to launch a multi-center large cohort study to evaluate the risk factors of locoregional recurrence in R0 resected EGFR mutant III-pN2 patients without PORT, producing evidence for the design of adjuvant regimens.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Three-hundred and fifty-nine consecutive patients with complete resected, pathological approved stage III-pN2 lung adenocarcinoma with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) have been investigated. Patients were excluded if they received induction therapy (7.5%) or PORT (9.6%). Three hundred cases have been analyzed. Clinicopathologic characteristics, pretreatment work-ups, EGFR mutant status and patterns of failure were documented. Patients were sub-staged by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)/ the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) 7th classification on N2 disease. Risk factors of locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRFS) were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analyses.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
According to IASLC/UICC 7th classification, there were 198 (66.0%) patients with unforeseen N2 (N2a), 36 (12.0%) with minimal/single station N2 (N2b), 41 (13.7%) with selectively centrally located N2 (N2c) and 25 (8.3%) with bulky and/or multilevel N2 (N2d). After surgery, 70 (23.3%) patients were treated with adjuvant tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs), while other 230 (76.7%) were free from adjuvant TKIs. With median follow-up of 28.5 (range:6-133) months, the 2-year LRFS, distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were 88.3%, 65.3%, 57.7% and 89.7%. Ultimately, 15.7% (47/300) patients developed locoregional recurrences. Distant metastasis was the predominant failure pattern. Multivariate analysis indicated that N2d disease (HR: 2.65, p=0.030) and extranodal extension (HR: 3.48, p<0.001) were risk factors of LRFS.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
R0 resected stage III-pN2 NSCLC patients with sensitive EGFR mutation (exon 19 or exon 21) tended to present limited N2 disease and low locoregional recurrences. Patients without bulky N2, multilevel N2, and extranodal extension might be refrained from PORT. Further studies evaluating the optimal radiotherapy approach for completely resected N2-positive NSCLC are required for validation.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.16 - Treatment of Early Stage/Localized Disease (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 948)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.16-40 - Evaluating the Tumor Heterogeneity in Lung Cancer by Constructing Tumor Heterogeneity Index (THI) from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ID 13134)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Jin-Yu Guo
- Abstract
Background
To improve the evaluation of primary lung cancer heterogeneity using clinical routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), we proposed a method based on basic measurements from T1- and T2-weighted MRI.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
As a novel technique of magnetic resonance imaging analysis, we investigated a total of 203 patients with biopsy-proven primary lung cancer and with different T stages. All patients previously received positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan. Gross lesions were manually contoured on T1-weighted, T1-enhanced, T2-weighted and T2 fat suppression (T2fs) images. The ratios of standard deviation (SD) / mean tumor value from each sequence were calculated. Correlation analyses were performed between T stages and the ratios. P value <0.05 was defined as statistical significant. Then a linear regression was performed to determine the weight of each related ratio. A model was built to calculate Tumor Heterogeneous Index (THI). One hundred and one patients were analyzed as the training set and another 102 as validating set.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
There were 56 patients diagnosed with T1 disease, 60 with T2 disease, 51 with T3 disease and 36 with T4 disease. Pair matching was performed between training set and validating set. As a result of the correlation analyses, SD/mean ratio showed significantly correlations with T stages in T1-enhanced (p=0.003), T2-weighted (p<0.0001) and T2fs sequences (p=0.002). Based on a linear regression model, THI was established for assessing the heterogeneity of lung tumor, consisting the three ratio measurements. Correlation analysis demonstrated that Higher THI was significantly related to more advanced T stages (p<0.0001).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion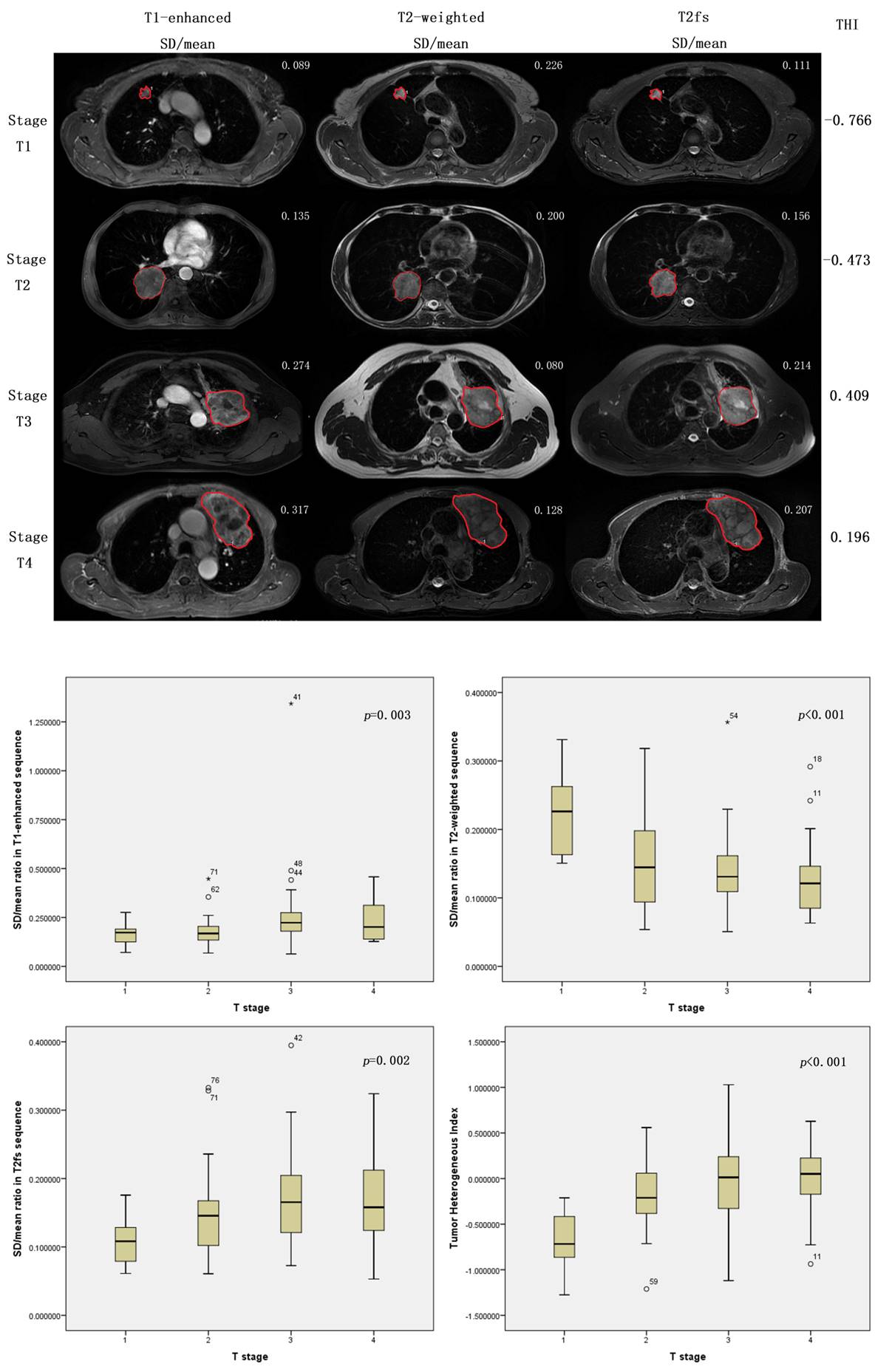
The proposed SD/mean ratio measurements and the calculation of THI according to clinical routine MR images could be clinical biomarkers that correlated with T stages, and were capable of evaluating heterogeneity of lung cancers.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


