Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Xiguang Liu
Author of
-
+
P1.05 - Interventional Diagnostics/Pulmonology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 937)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.05-09 - Dielectric Property Test for the Rapid Differential Diagnosis of Lung Nodules/Mass (ID 13075)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xiguang Liu
- Abstract
Background
Developing new methods for rapid diagnosis for lung nodules/mass has always been one of the most attractive topics. And it has been found that the dielectric property, including permittivity and conductivity, varies from benign tissues to malignancies. However, no studies comparing the dielectric property between lung benign tumors to malignancies has been reported and whether dielectric property test could be used for differential diagnosis remains uncertain.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Patients with lung nodules/mass who received surgical resection were included for permittivity and conductivity test right after the occupying lesions were removed and before sent for pathological examination. The informed consents were obtained before surgery. Independent-samples T Test and multiple variables for ROC curve analysis were used.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
More than 250 lesions were expected to be tested for calculating the differential diagnosing cutoff value. For each lesion, 4000 datasets of permittivity and conductivity at different frequencies from 1MHz to 4000MHz were collected. By far, 73 patients with 74 lung occupying lesions were enrolled for dielectric property test, including 19 lung benign tumors and 55 malignancies. Though the differences of mean permittivity and conductivity between the 2 groups were not statistically significant (p>0.05), there might be a tendency to distinguish the 2 groups. And the mean values of permittivity and conductivity and their independent values at frequency 1MHz, 500MHz, 1000MHz, 1500MHz, 2000MHz, 2500MHz, 3000MHz, 3500MHz, 4000MHz were chosen as multiple variables for ROC curve analysis. With the false positive rate of 10%, the cutoff value Pcutoff was 0.8588 and the logistic regression formula for differential diagnosis were shown as followed, of which the area under the ROC curve was 0.905.

Funding
The study was supported by the Presidential Foundation of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (2016B018).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
With more data collected, dielectric property test might become another rapid way of distinguishing lung malignancies from benign tumors.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 952)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.03-31 - LncRNA RGMB-AS1 Affects Lung Adenocarcinoma Prognosis by Regulating Microtube Associated Genes: A Genome-Wide Analysis in Silicon (ID 12669)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xiguang Liu
- Abstract
Background
To analyze the co-expression network of long non-coding RNA RGMB-AS1 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and to investigate its impact on prognosis by mining the molecular mechanisms and prognostic signature in silicon.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We performed a co-expression analysis of RGMB-AS1 by integrating sixty thousand public Affymetrix microarrays data to reveal its associated signal pathways. QPCR and Western blot were performed to validate the significant genes. Furthermore, survival analysis of data in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) was applied to seek the prognostic value of RGMB-AS1 and its co-expressed genes.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
The most enriched signal pathways of RGMB-AS1 co-expressed genes were pathogenic Escherichia coli infection, gap junction and ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. Among the 30 validated genes, we found that a sixteen microtube-associated genes signature is an independent prognostic marker of OS of LUAD patients and demonstrates good performance for predicting 5-year OS.

8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Our results suggest that RGMB-AS1 may serve as a novel prognosis indicator and therapeutic target for LUAD patients.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P2.03-32 - Genome-Wide Analysis of m6A-Modified RNA Binding Proteins Associated with Lung Cancer Survival (ID 12707)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xiguang Liu
- Abstract
Background
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) is a type of RNA modification involved in a variety of biological processes. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play a crucial role in post-transcriptional regulation in gene expression. However, no research reveals how m6A-modified RNA binding proteins affect lung cancer survival systematically.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
RNA-seq data were downloaded from NCBI GEO via accession number GSE62944 including both lung adenocarcinoma and squamous lung cancer. The differentiated analysis run by limma bioinformatic package and fold-change more than 1,5 with FDR<0.05 was considered as significant. The optimal cut-off value of low and high expression was defined by X-tile. Cox regression model and log-rank test was applied for survival analysis.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Eleven out of twenty-nine m6A-modified RNA binding proteins are differently expressed(FC>1.5,FDR<0.05,Figure 1). Furthermore, five RBPs are associated with lung cancer survival. Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that higher IGF2BP1 or IGF2BP3 expression is associated with poor survival of lung adenocarcinoma (P= 0.00058 and P=0.005171, respectively). Subgroup analysis show that high GNL3 expression is associated with poor prognosis of young and male patients, while its high expression is an indicator of good prognosis in female patients.
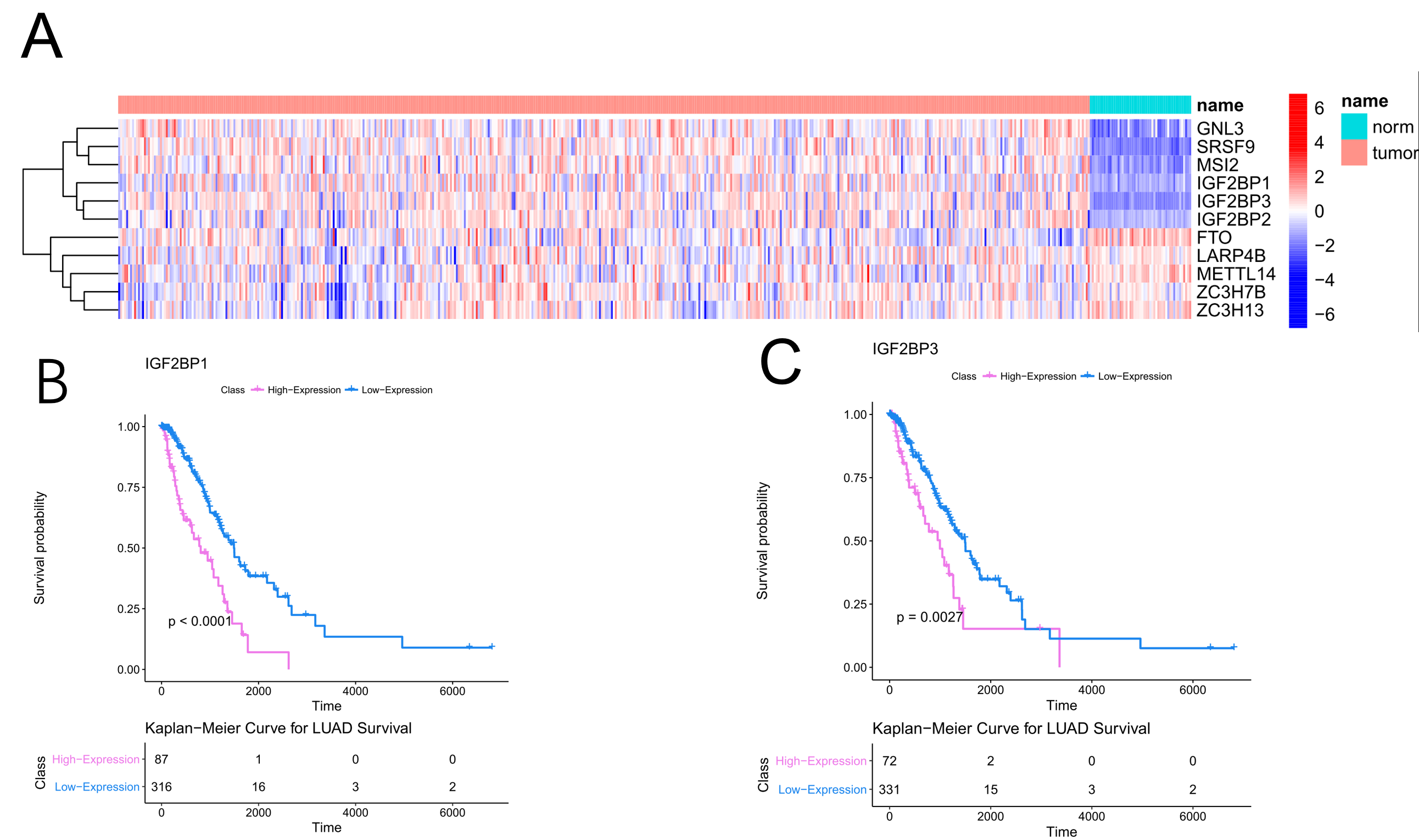
Figure1 Identification of lung cancer survival associated m6A-modified RNA binding proteins. (A) Heatmap shows the deferentially expreesed m6A-modified RNA binding proteins. (B) IGF2BP1 expression is associated with poor survival of lung adenocarcinoma (P= 0.00058). (C) IGF2BP3 expression is associated with poor survival of lung adenocarcinoma (P=0.005171).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In this analysis, we revealed that IGF2BP1 and IGF2BP3 are potential m6A targets which may affect lung adenocarcinoma survival. Further biomolecular experiments are warranted.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.12 - Small Cell Lung Cancer/NET (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 961)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.12-08 - Network Meta-Analysis of Angiogenesis Inhibitors on Survival of Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 12009)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xiguang Liu
- Abstract
Background
This network meta-analysis aimed at providing a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of angiogenic inhibitors on small cell lung cancer by using network meta-analysis.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
The relative efficacy of angiogenesis inhibitors vandetanib (Van), bevacizumab (Bev), Rh-endostatin (End), sunitinib (Sun) and thalidomide (Tha) was evaluated by conducting a network meta-analysis of progression-free survival and overall survival.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Nine phase II-III RCTs involving 1599 participants that investigated angiogenesis inhibitors on the treatment of SCLC were included. Sun and Bev achieved better PFS than Tha (Bev VS. Tha, HR=0.88, 95%CI: 0.79-0.98, Sun VS. Tha, HR=0.80, 95%CI: 0.65-1.00). Moreover, Sun and Bev were superior to placebo in terms of PFS (Bev VS. Placebo, HR=0.89, 95%CI: 0.81-0.97, Sun VS. Placebo, HR=0.81, 95% CI: 0.66-1.00). No significant difference of OS was found.

Figure 1 Networks of angiogenic inhibitors for the treatment of small-cell lung cancer.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In this network meta-analysis, the effect of sunitinib and bevacizumab may be superior to that of thalidomide for small cell lung cancer.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


