Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Wilbur A. Franklin
Author of
-
+
P1.04 - Immunooncology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 936)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.04-23 - Expression of Emerging Immunotherapy Targets in Early-Stage Squamous Lung Carcinoma (ID 13520)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Wilbur A. Franklin
- Abstract
Background
Anti-PD1/PD-L1 immunotherapy has demonstrated response in approximately 20% of unselected advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Strategies involving combination immunotherapies are under investigation to improve the overall response to immunotherapy. The objective of this study was to identify the expression of emerging immune targets in a cohort of early-stage squamous lung carcinoma (SqLC), which may be used to design combinatorial immunotherapy approaches.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
202 early stage (I-II) SqLC resected patient tumors and corresponding clinical data were collected from 6 cancer centers as part of the SPECS II program. Fourteen emerging immune targets or targeted axis were selected based on their advanced stage of development in preclinical/clinical studies. The mRNA expression level of these targets and PD-1/PD-L1 were determined by Affymetrix U133A gene expression profiling. The correlations among these targets and the overall survival were evaluated.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
The mRNA levels of the immune molecules which were grouped on PD-L1 protein expression in early stage SqLC are shown in Figure 1. No correlation was found between the mRNA level of PD-L1 and the other immune targets expressed on APC/tumor cells, except PD-L2 (r2= 0.41, p<0.00001). We found that the immune cell receptor, CD226, correlated with CD96 and CD112R respectively (r2= 0.514, p<0.00001; r2= 0.476, p<0.00001), and CD96 correlated with CD112R (r2= 0.644, p<0.00001) as well. In addition, higher expression of GAL-9, CD48 and ICOS were associated with better prognosis [p= 0.0358, HR=0.249 (0.068, 0.912); p= 0.0309, HR=1.61 (1.04, 2.49); p= 0.0429, HR=2.47 (1.03, 5.93)].
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion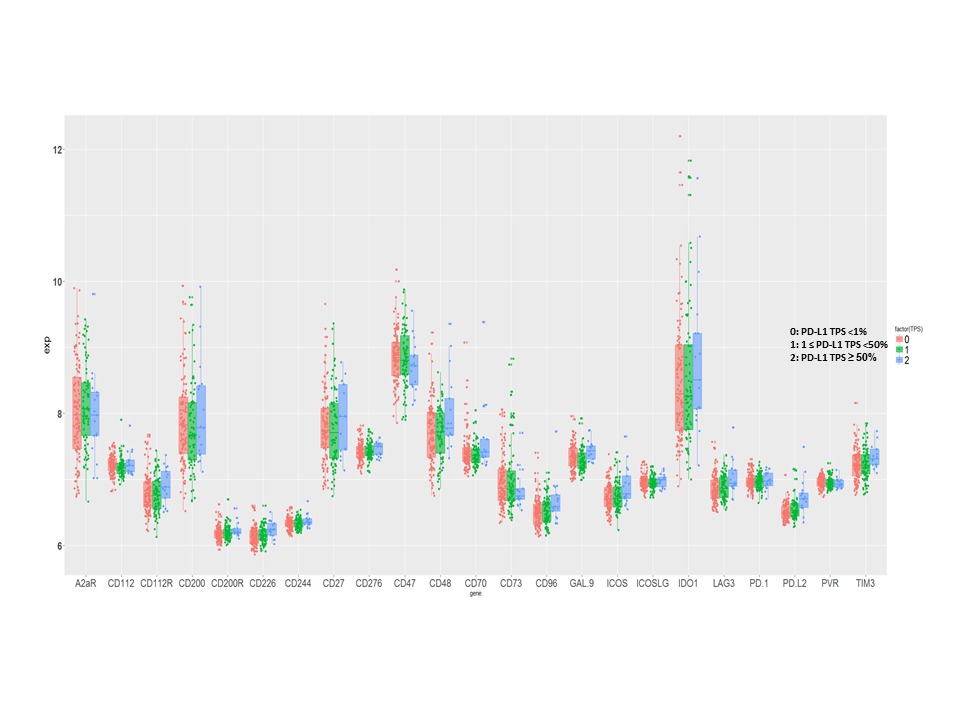
Several emerging immune targets were expressed at higher levels than PD-L1 in this early stage SqLC cohort. The mRNA levels of all immune targets evaluated were independent of PD-L1 expression, except PD-L2. The expression of GAL-9, CD48 and ICOS were identified as prognostic. These results may provide important information in the design of future combination immunotherapies for early-stage SqLC.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.09 - Pathology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 958)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.09-01 - Tumor-Associated Immune Cell Infiltration Patterns in Early Stage Squamous Lung Carcinoma (ID 13456)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Wilbur A. Franklin
- Abstract
Background
With the recent clinical success of immunotherapy in non-small cell lung carcinoma, the character of the inflammatory infiltrate associated with these tumors is now the subject of increasing interest. Molecular studies have suggested that tumors can be stratified by the character of their inflammatory infiltrate. We now describe the detailed histological appearances of a multi-institutional series of early stage squamous carcinomas and correlate them with mutation burden, PDL1 expression patterns and clinical outcome.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Histologic sections of from 250 tumors were evaluated by two pathologists independently for squamous subtype (WHO classification), percentage and character of intratumoral inflammatory cells, percentage and character of para-tumoral infiltrate and presence or absence of scalloping at tumor cell/stromal interface by inflammatory cells along the edges of tumor cell nests, a feature possibly related to existing immune reaction. The ratios of infiltrating inflammatory cells to tumor cells were estimated in 10% increments by microscopic inspection. Quantity and character of infiltrates was assessed by Kaplan-Meir testing for effect on survival and by Pearson bivariate testing for relationships among variables.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
The character and extent of inflammatory infiltrates were highly heterogeneous. The infiltrates could be divided into intratumoral and paratumoral patterns according to their location in relation to microscopic tumor cell nests. Intratumoral infiltrates could be further subdivided into two patterns: one consisted exclusively lymphocytes, usually few in number; a second polymorphous pattern contained many inflammatory cell types including polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). In paratumoral tissue, three patterns could be discerned: lymphocytic, plasmacytic and polymorphous. Inflammatory cell infiltrate quantity or character did not correlate with survival for either intratumoral or paratumoral infiltrates and there was no evident relationship to mutational burden or to PDL1 expression by IHC. Scalloping at the tumor cell stromal interface was also not prognostically significant.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The inflammatory infiltrates in early stage squamous lung carcinoma are highly heterogenous and are not associated with outcome. However, the complexity of tumor infiltrating inflammatory cells is worthy of further evaluation in future immunotherapeutic trials.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 969)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.03-25 - Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Associated Bronchial Dysplasias Demonstrate Altered T-helper Lymphocyte Differentiation (ID 13998)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Wilbur A. Franklin
- Abstract
Background
Persistent bronchial dysplasia (BD) is associated with an increased risk for development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma and demonstrates altered polarization of inflammatory cell subsets by gene expression analysis as compared to BD that regresses. We hypothesized that a decrease in the T-helper 1 (Th1) to T-helper 2 (Th2) lymphocyte ratio would be associated with progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
VECTRA 7-color multispectral staining was applied to formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) persistent (N=12) and regressive (N=10) BD that also included four biopsies from patients that subsequently developed SCC (3 persistent and 1 regressive, 2 from the actual site of progression). inForm (Perkin-Elmer) image analysis software was used to enumerate cells that showed double positivity for Tbet-CD4 (Th1) and GATA3-CD4 (Th2) and the ratios of the percentage of Th1 and Th2 cells amongst all CD4 positive cells were calculated from multiple lesional fields for each BD (dysplastic epithelium and underlying stroma). DNA extracted from the full remaining FFPE tissue of four of these cases were sequenced employing the Oncomine Comprehensive v3 NGS panel (ThermoFisher) and the number of somatic mutations and variant allele frequencies (VAF) were determined using a threshold of at least 200 total reads and 25 variant reads per variant identified.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A decreased Th1:Th2 ratio was seen in SCC-associated BD as compared to BD from patients that did not develop lung cancer (p=0.04; ratio = 0.04 vs. 0.68, respectively). No significant difference was seen in persistent versus regressive BD groups. There was an inverse correlation between Th1:Th2 ratios and mutational load (r2=0.21) and VAF (r2=0.28) although the small number of specimens precluded identification of a statistically significant relationship.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
A decreased Th1:Th2 ratio is associated with BD from subjects that progress to SCC suggesting that alterations in T-helper lymphocyte differentiation may contribute to progression. A potential inverse relationship between Th1:Th2 ratios and mutational load or mutant clonal expansion (increased VAF) will require further study.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


