Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Xueyan Zhang
Author of
-
+
P1.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 935)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 3
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.03-05 - Transcriptome Landscape of Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Revealed Distinct Trajectory Patterns (ID 12025)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xueyan Zhang
- Abstract
Background
The hallmarks of cancer was proposed to elucidate the common trajectory of tumors of different tissues of origin and genetic makeups, which were expected to attributed to disruption of regulatory pathways conferring survival and growth advantages to tumor tissues. However, the specific biological processes involved in each milestones in the trajectory of development of lung adenocarcinoma, particularly regarding tumor stages, remain elusive. The datasets of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project lend potential for discovering the distinctive expressional patterns of differentiated subpopulations, and exploring the dynamic evolution of biological activities within tumor cells.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
RNA sequencing level 3 data of 56 pairs of tissue and adjacent normal samples were obtained from TCGA. Differential expression analysis was conducted using ‘edgeR’ package across the each tumor stage. Differentially expressed genes were derived with fold change>=4 and FDR <= 0.01, followed by KEGG pathway analysis. Odd ratios (ORs) were extracted to indicate the degrees of dysregulation of each pathway.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
After removing non-cancer associated pathways from the 77 pathways identified as dysregulated in those samples, we arrived at 35 pathways. In “Cell cycle” and “Pathways in cancer”, ORs display positive correlation with tumor stages, and the Stage IV showed appreciably higher OR than other stages. Noteworthily, Stage IV has very high Ors in “PPAR signaling pathway”, “Renin-angiotensin system” and “p53 signaling pathway”, which represents canonical pathways implicated in cancer pathologies.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
We identified pathways that display correlation with tumor stages, although some deviations are expected to stem from differences in treatment, complicated disease, and health conditions, etc. These results display considerable linear correlation between the degree of dysregulation of cancer pathways, which promise applying RNA sequencing in characterizing the bona fide cell fate of tumor tissues.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.03-22 - MiR-125b Plays a Tumor Suppressor Role in Inflammation-Related Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Repressing IGF-1 Signal Pathway (ID 11752)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xueyan Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Epidemiologic data have indicated that chronic inflammation was highly associated with the pathogenesis of lung cancer. However, the molecular relations between inflammation and lung cancer have not been well understood. MicroRNAs could connect the inflammatory response with tumorigenesis through regulating their cancer-related targets. The aim of the present study was to identify the core miRNA in inflammation-related lung cancer and its potential mechanisms.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
RT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miRNAs and mRNAs. CKK8 and flow cytometry assays was performed for the function experiments. Microarray analysis and IPA analysis were used to predict the potential signal pathway.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Mir-125b was the most dramatically up-regulated miRNAs after treated with IFN-r, whereas after stimulated with IL-10, mir-125b was the most strikingly down-regulated ones. Restoration of mir-125b expression could completely overrode the impact of IL-10 on both cell proliferation and apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines(Figure1). And the level of mir-125b was significantly lower in 30 NSCLC tumor tissues compared with normal controls (P<0.0001). Microarray analysis found 69 up-regulated genes and 105 down-regulated genes after down-regulate mir-125b. And IPA analysis indicated that IGF-1 signaling pathway was dramatically activated. The results were validated by RT-PCR.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion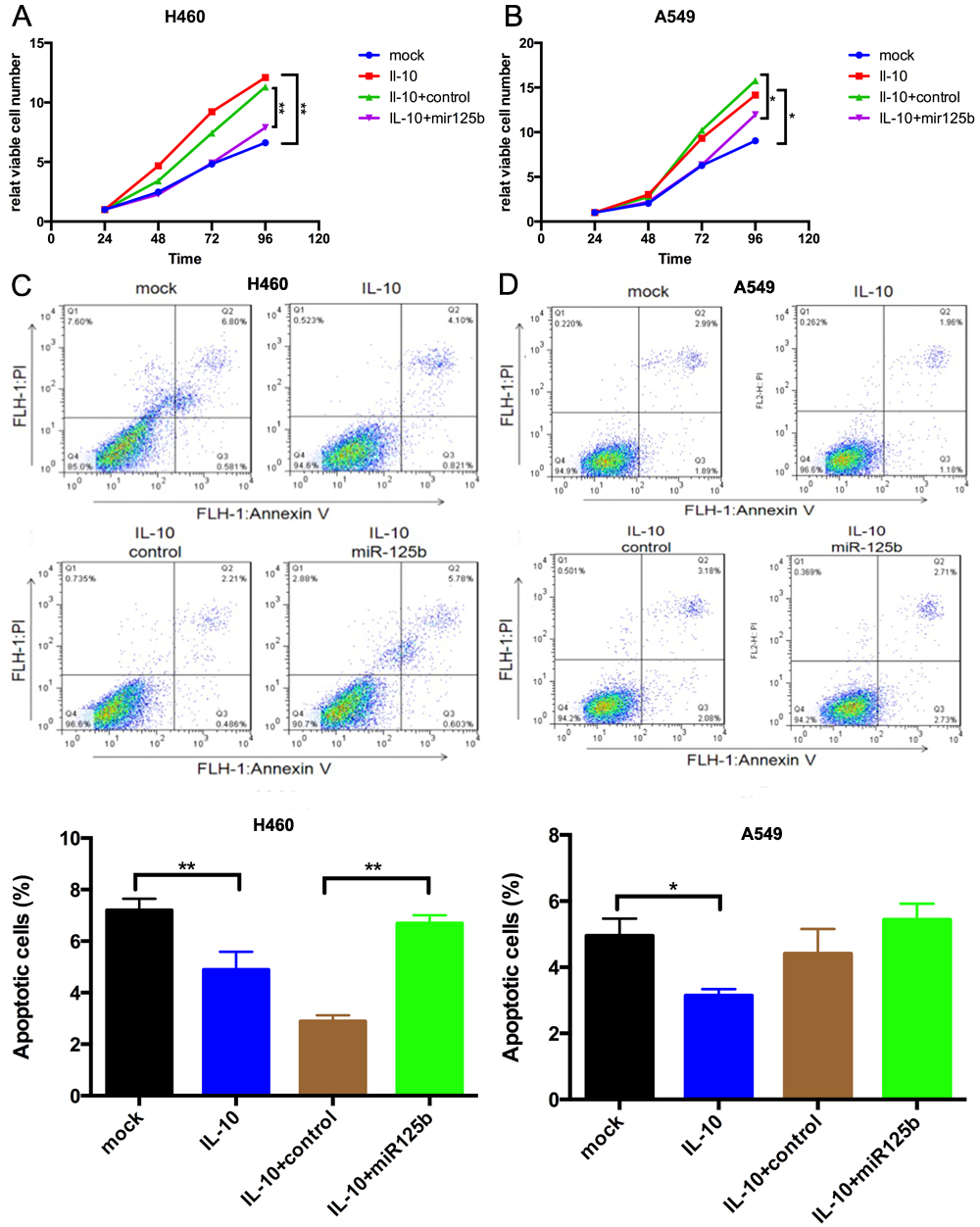
MiR-125b might play a tumor suppressor role via inhibiting IGF-1 signaling in inflammation-related lung cancer.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.03-30 - The Number of Mutated Repair Genes as Predictor for Tumor Mutation Burden of Lung Adenocarcinoma (ID 12027)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xueyan Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Disruption of repair gene products will result in higher risk of mutation events and genetic instability. Despite some repair genes such as BRCA1 and FANCA being intensively reported in breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and the predisposition to cancers, the effects of protein dysfunction of repair genes on mutation events have not been quantified. The established repair pathways are responsible for different mutation events and may account for respective mutation patterns. Therefore, we conducted an in-depth investigation of effect of individual repair pathways or individual repair genes on tumor mutation burden (TMB).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We obtained level 4 variant datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) which comprises of 568 samples. The TMB of each individual was calculated and the population was divided into subgroups as per the status of harboring mutations in repair genes as well as the specific repair pathways.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In the 568 lung adenocarcinoma patients, 434 patients have somatic mutations in any of the 112 DNA repair genes. The individuals harboring mutations in repair genes have significantly higher TMB (Mean=3.019, S.E.=0.206) than those do not (Mean=11.085, S.E.=0.493), and we derived a 3.81-fold increase in TMB for mutations occuring in an additional repair gene. Those that harbor mutations in TP53 account for 63% of the population, and ATM and PRKDC account for 11% and 10, respectively.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
We identified most highly mutated repair genes and quantified the increase in risk for each additional mutated repair gene. Although the TMB of individuals with mutations in specific repair gene or pathway show no significant difference, a larger dataset that comprises adequate number of samples within each explanatory variables such as incidence of cell division, tumor stages to be taken into model, can be expected to derive a more robust predictor.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


