Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Yanwei Zhang
Author of
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 933)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-29 - Crizotinib in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with ALK or ROS-1 Rearrangement: Is it the Same? (ID 12929)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Crizotinib is an orally taken tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeting both ALK and ROS1 rearrangement, which have defined two different molecular subgroup patients. The aim of the study was to compare the therapeutic efficacy of crizotinib in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients diagnosed with ALK or ROS1 mutation.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Patients diagnosed with ALK (Group A) or ROS1 (Group B) mutation were identified from our standardized registration system. The effectiveness of crizotinib in eligible patients was retrospectively analyzed.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 5348 and 4695 patients were screened and 393 (7.3%, 95% CI, 6.6%-8.0%) and 105 (2.2%, 95% CI, 1.8%-2.7%) positive patients were identified among the two groups, respectively. There were 141 and 32 eligible patients were included for survival analysis. The ORR is 53.0% (95% CI, 43.0%-63.0%) in group A, without statistical significance compared with group B (71%, 95% CI, 51.2%-90.4%, P=0.11). Similar result was also observed in terms of DCR (86%, [95% CI, 79.1%-92.9%] vs. 92.0%, [95%, CI, 80.0%-100.0%], P=0.74). The median PFS in group A was 12.4 months (95% CI, 10.2 -14.7 months), which was statistically worse than patients in group B (18.2 months, 95% CI, 6.3 -29.0 months, P=0.02). The OS was too immature to analyze.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Patients harboring ROS1 rearrangement derived better prognosis compared with these who had ALK rearrangement when treated with crizotinib.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-30 - Crizotinib in Advanced Non-Adenocarcinoma, NSCLC (NA-NSCLC) Patients with ALK Rearrangement: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review (ID 12942)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
The aim of the study was to investigate the prevalence of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement in non-adenocarcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NA-NSCLC) patients and therapeutic efficacy of crizotinib in these patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
From January 2013 to January 2017, NA-NSCLC patients who were diagnosed with ALK rearrangement were screened. The effectiveness of crizotinib in positive patients was retrospectively analyzed. A literature review was performed and eligible cases were analyzed combined with our data.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 1212 NA-NSCLC patients were screened during the period with 25 positive patients identified (2.1%, 95% CI, 1.3%-2.9%). A statistically higher percentage of female patients (40.0% vs. 10.4%, P< 0.01), non-smoker (72.0% vs.43.2%, P< 0.01), containing adenocarcinoma component (36.0% vs. 7.1%, P< 0.01) and advanced stage (68.0% vs. 45.6%, P=0.03) were observed in ALK positive group. The median PFS of the 9 eligible patients in our institution was 7.0 months (95% CI, 0-15.6 months). We combined our data with the sporadic cases from 10 previous case reports (total n=19) and found that the median PFS was 7.0 months (95% CI, 5.6-8.4 months).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Our study suggested the opportunity to test ALK rearrangement in NA-NSCLC patients, especially in female, non-smoker and patients containing adenocarcinoma component. Crizotinib provides an option for the treatment of NA-NSCLC patients who diagnosed with ALK rearrangement.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 935)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 4
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.03-05 - Transcriptome Landscape of Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Revealed Distinct Trajectory Patterns (ID 12025)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
The hallmarks of cancer was proposed to elucidate the common trajectory of tumors of different tissues of origin and genetic makeups, which were expected to attributed to disruption of regulatory pathways conferring survival and growth advantages to tumor tissues. However, the specific biological processes involved in each milestones in the trajectory of development of lung adenocarcinoma, particularly regarding tumor stages, remain elusive. The datasets of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project lend potential for discovering the distinctive expressional patterns of differentiated subpopulations, and exploring the dynamic evolution of biological activities within tumor cells.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
RNA sequencing level 3 data of 56 pairs of tissue and adjacent normal samples were obtained from TCGA. Differential expression analysis was conducted using ‘edgeR’ package across the each tumor stage. Differentially expressed genes were derived with fold change>=4 and FDR <= 0.01, followed by KEGG pathway analysis. Odd ratios (ORs) were extracted to indicate the degrees of dysregulation of each pathway.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
After removing non-cancer associated pathways from the 77 pathways identified as dysregulated in those samples, we arrived at 35 pathways. In “Cell cycle” and “Pathways in cancer”, ORs display positive correlation with tumor stages, and the Stage IV showed appreciably higher OR than other stages. Noteworthily, Stage IV has very high Ors in “PPAR signaling pathway”, “Renin-angiotensin system” and “p53 signaling pathway”, which represents canonical pathways implicated in cancer pathologies.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
We identified pathways that display correlation with tumor stages, although some deviations are expected to stem from differences in treatment, complicated disease, and health conditions, etc. These results display considerable linear correlation between the degree of dysregulation of cancer pathways, which promise applying RNA sequencing in characterizing the bona fide cell fate of tumor tissues.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.03-16 - Anlotinib Inhibits Angiogenesis of Refractory Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Blocking CCL2 Expression (ID 12406)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Anlotinib has been demonstrated to be effective in prolonging progression free survival (PFS; Anlotinib: 5.37 months vs Placebo: 1.40 months) and overall survival (OS; Anlotinib: 9.63 months vs Placebo: 6.30 months) of refractory advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) patients in clinical trials. Clinical evidences suggested that Anlotinib-induced anti-tumor efficacy could be attributed to anti-angiogenesis. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms and predictive biomarker of Anlotinib are still unclear.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
437 patients with advanced NSCLC enrolled in clinical study, and 294 patients received Anlotinib therapy. Retrospectively analysis of the Anlotinib-administrated 294 NSCLC patients was performed to screen out underlying biomarker for Anlotinib-responsive patients. Transcriptome and functional assays were performed to understand the anti-tumor molecular mechanism of Anlotinib in vitro. CCL2 levels and their roles in angiogenesis were evaluated by ELISA detection, RT-qPCR quantification, and immunofluorescence assay, in vivo. Changes in serum CCL2 levels were analyzed to reveal the correlation of Anlotinib response between responders and non-responders.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Anlotinib therapy is more beneficial to prolong OS for NSCLC patients harboring positive driver gene mutations, especially for patients harboring EGFRT790M mutation. Moreover, our data indicated that Anlotinib-induced cell viability downregulation, cell apoptosis induction, cell invasion inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and cell migration inhibition are associated with CCL2 levels in vitro. We demonstrated that Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis of NCI-H1975 derived xenografts model via inhibiting CCL2 in vivo. Lastly, we found that Anlotinib-induced serum CCL2 level decreases are associated with the benefits of PFS and OS, in refractory advanced NSCLC patients (n = 28).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Our study reports a novel anti-angiogenesis mechanism of Anlotinib via inhibiting CCL2 in NCI-H1975 derived xenografts model, and suggests the changes in serum CCL2 levels may be used to monitor and predict clinical outcome in Anlotinib-administered refractory advanced NSCLC patients. The biomarker of serum CCL2 alteration may guide precision therapy of Anlotinib for NSCLC patients at third-line or over third-line.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.03-22 - MiR-125b Plays a Tumor Suppressor Role in Inflammation-Related Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Repressing IGF-1 Signal Pathway (ID 11752)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Epidemiologic data have indicated that chronic inflammation was highly associated with the pathogenesis of lung cancer. However, the molecular relations between inflammation and lung cancer have not been well understood. MicroRNAs could connect the inflammatory response with tumorigenesis through regulating their cancer-related targets. The aim of the present study was to identify the core miRNA in inflammation-related lung cancer and its potential mechanisms.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
RT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miRNAs and mRNAs. CKK8 and flow cytometry assays was performed for the function experiments. Microarray analysis and IPA analysis were used to predict the potential signal pathway.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Mir-125b was the most dramatically up-regulated miRNAs after treated with IFN-r, whereas after stimulated with IL-10, mir-125b was the most strikingly down-regulated ones. Restoration of mir-125b expression could completely overrode the impact of IL-10 on both cell proliferation and apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines(Figure1). And the level of mir-125b was significantly lower in 30 NSCLC tumor tissues compared with normal controls (P<0.0001). Microarray analysis found 69 up-regulated genes and 105 down-regulated genes after down-regulate mir-125b. And IPA analysis indicated that IGF-1 signaling pathway was dramatically activated. The results were validated by RT-PCR.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion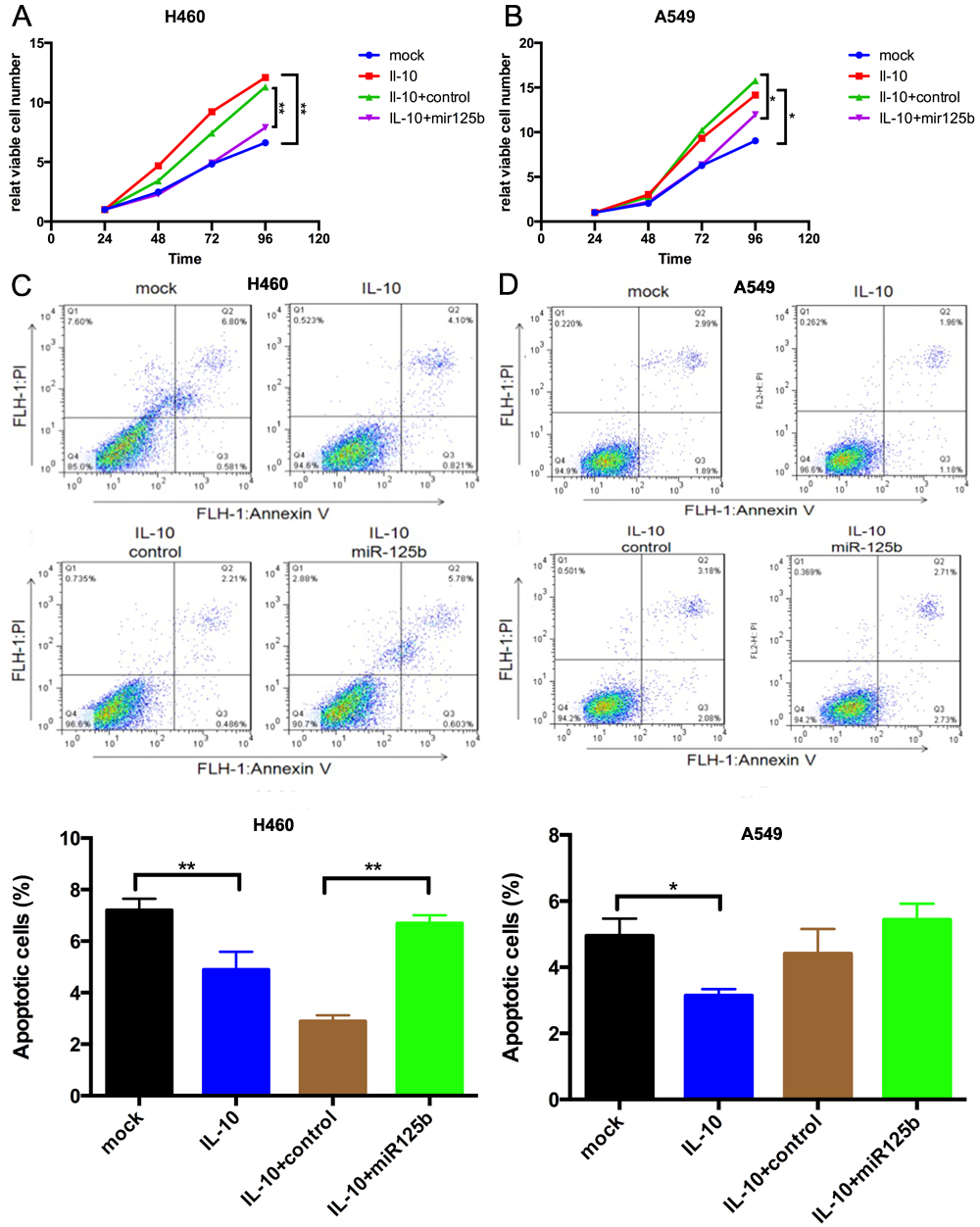
MiR-125b might play a tumor suppressor role via inhibiting IGF-1 signaling in inflammation-related lung cancer.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.03-30 - The Number of Mutated Repair Genes as Predictor for Tumor Mutation Burden of Lung Adenocarcinoma (ID 12027)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Disruption of repair gene products will result in higher risk of mutation events and genetic instability. Despite some repair genes such as BRCA1 and FANCA being intensively reported in breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and the predisposition to cancers, the effects of protein dysfunction of repair genes on mutation events have not been quantified. The established repair pathways are responsible for different mutation events and may account for respective mutation patterns. Therefore, we conducted an in-depth investigation of effect of individual repair pathways or individual repair genes on tumor mutation burden (TMB).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We obtained level 4 variant datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) which comprises of 568 samples. The TMB of each individual was calculated and the population was divided into subgroups as per the status of harboring mutations in repair genes as well as the specific repair pathways.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In the 568 lung adenocarcinoma patients, 434 patients have somatic mutations in any of the 112 DNA repair genes. The individuals harboring mutations in repair genes have significantly higher TMB (Mean=3.019, S.E.=0.206) than those do not (Mean=11.085, S.E.=0.493), and we derived a 3.81-fold increase in TMB for mutations occuring in an additional repair gene. Those that harbor mutations in TP53 account for 63% of the population, and ATM and PRKDC account for 11% and 10, respectively.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
We identified most highly mutated repair genes and quantified the increase in risk for each additional mutated repair gene. Although the TMB of individuals with mutations in specific repair gene or pathway show no significant difference, a larger dataset that comprises adequate number of samples within each explanatory variables such as incidence of cell division, tumor stages to be taken into model, can be expected to derive a more robust predictor.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.11 - Screening and Early Detection (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 943)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.11-19 - Expression of TNFRII in Serum is Correlated with the Significant Risk of Subcentimeter Lung Adenocarcinoma (ID 12954)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
With the rapid advances of low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening for lung cancer, the opportunity to detect subcentimeter non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is gradually increasing. The results of many previous studies have shown that even subcentimeter NSCLCs are not always in the early stage. Thus, it is quite important for us to judge the possibility of malignancy for these patients, even the tumor size is less than 10mm. However, subcentimeter lung cancer is hard to diagnose only via biopsy and imaging features because of its tinny size. Chronic inflammation is well established as a hallmark in lung carcinogenesis. In our previous study, B lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC), is found to be slightly associated with the risk of subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the correlation between TNF receptor type II (TNFRII) and the risk for subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma, and the efficacy of diagnosing subcentimeter lung cancer after combining TNFRII and BLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Inflammatory biomarkers were measured in 71 subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma patients and 71 age-, sex- and smoking-matched healthy controls by using the Luminex bead-based assay.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
The mean (standard deviation or SD) age of patients was 56.01 (8.91) years, and 73.20% of them were female patients (n=52). Never smokers accounted for 85.96% of patients (n=57). The expression level of TNFRII is significantly down-regulated in subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma patients compared with the healthy controls (P<0.001). And the results were validated by oncomine data mining analysis.
Elevated levels of TNFRII were associated with an 89% reduced risk for subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma. (OR=0.11, 95% CI: 0.04-0.30, P=2.4*10-5). BLC was associated with a 2.70-fold (95% CI: 1.31-5.58, P=7.0*10-3) increased risk of subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma for the comparison of patients in the higher-level group with the lower-level group. To yield more information, the BLC/TNFRII ratio was created to examine their prediction for the risk of subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma, and as expected there was a 35- fold increased risk for patients in the higher-level group relative to patients in the lower-level group. Further ROC curve analysis revealed that TNFRII was a significant diagnostic biomarker for subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma, with the area under the curve of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.65-0.82, P=2.0*10-6). The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were 0.75, 0.72 and 0.73, respectively.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Our findings demonstrated that TNFRII was associated with the significant risk of subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma, and could be a promising biomarker for accessorily diagnosing subcentimeter lung adenocarcinoma.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 952)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.03-22 - OCT4&SOX2 Specific CTLs Plus PD-1 Inhibitor Had Synergistic Effect on Killing CSC And Treating Drug-Resistant Lung Cancer Mice (ID 12402)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
This study aimed to investigate the synergistic effect of OCT4&SOX2 specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and PD-1 inhibitor on killing lung cancer stem-like cells (LCSCs) and their efficacy in treating drug-resistant lung cancer (DRLC) mice.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
OCT4&SOX2 specific CTLs and PD-1 inhibitor with differed doses were applied to treat PC9 cells and PC9 LCSCs. CCK8 assay and flow cytometry (FCM) assay with CFSE staining target cells before treatment and PE staining died cells after treatment were conducted to detect the cytotoxic activity. DRLC mice were constructed by injection of PC9 LCSCs suspension and Matrigel into left lung of SD mice. DRLC mice was randomly divided into 5 group: Control group, CMV pp65 CTLs group, OCT4&SOX2 CTLs group, PD-1 inhibitor group and OCT4&SOX2 CTLs+PD-1 inhibitor group.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In vitro, Both CCK8 assay and FCM assay disclosed that OCT4&SOX2 specific CTLs plus PD-1 inhibitor presented with elevated cytotoxic activity on PC9 cells and PC9 LCSCs. In vivo, tumor volume and tumor weight were decreased, while tumor necrosis and tumor apoptosis were increased in OCT4&SOX2 CTLs group than CMV pp65 CTLs group and control group, and in OCT4&SOX2 CTLs+PD-1 inhibitor group than OCT4&SOX2 CTLs group and PD-1 inhibitor group. In addition, CD8 expression was increased while OCT4 and SOX2 expressions were decreased in OCT4&SOX2 CTLs+PD-1 inhibitor group than OCT4&SOX2 CTLs group and PD-1 inhibitor group.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In conclusion, OCT4&SOX2 specific CTLs and PD-1 inhibitor presented with synergistic effect on killing LCSCs in vitro and treating DRLC mice in vivo.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P2.03-37 - The Efficiency of Octamer-4 Specific Cytotoxic T Cells Induce By CD40-B Cells in Killing Lung Cancer Stem-Like Cells (ID 12399)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
This study aimed to investigate the correlation of Octamer-4 (OCT4) expression with clinicopathological features and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients, and to further explore the killing effect of OCT4 specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) on lung cancer stem cells (LCSCs).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
257 lung adenocarcinoma patients underwent thoracic surgery were enrolled in this study and tissue samples were obtained during the operation. OCT4 expression was detected by immunofluorescence staining assay. CD154+ feeder cells were constructed to transfect CD40-B cells, and then mixed with OCT4 antigen peptides and CD8+ T lymphocytes extracted from peripheral blood of lung adenocarcinoma patients, subsequently the OCT4 specific CTLs were co-cultured with PC9 LCSCs to detect the killing efficacy. OCT4+ phenotype was illuminated to be associated with poor differentiation, worse disease free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). And Cox’s analysis revealed OCT4+ was an independent predictive factor for shorter DFS and OS.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
CD40-B-cells with antigen presenting capacity was successfully constructed indicated by elevated CD86+, human leukocyte antigens (HLA)-A+ and CD80+ cells percentage, and OCT4 specific CTLs was successfully activated suggested by increased CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ cells percentage as well as elevated interleukin (IL-2) and interferon (IFN)-γ expressions. OCT4 specific CTLs presented an elevated cytotoxic activity on LCSCs at percentage 75.5% ± 8.2% compared with CMV pp65 CTLs (25.6% ± 5.1%) and blank control CTLs (20% ± 4.7%).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In conclusion, OCT4 expression could be served as a convincing risk biomarker for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients and potential target of CTLs as immuntherapy in killing LCSCs.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.12 - Small Cell Lung Cancer/NET (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 961)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.12-17 - Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Can Not Provide Survival Benefits for Resected Small Cell Lung Cancer Without Lymph Node Involvement (ID 13996)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Yanwei Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Currently, prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) was recommended for all patients after resection small-cell lung cancers, even those without lymph node metastasis. However, there is no directly evidence supporting this recommendation. The purpose of the present study is to assess the role of PCI for this subset of patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively identified completely resected SCLC without lymph node involvement (N0M0) at the Shanghai Chest Hospital between January 2006 and May 2017.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 146 patients (44 patients received PCI, 102 patients did not) were identified in the study. During the observation period, 8.8 % (9/102) patients in the non-PCI-treated cohort and 11.4 % (5/44) patients in the PCI-treated cohort developed brain metastases. There was no significant difference in the risk of cerebral recurrence between the two cohorts with regard to the time to recurrence (P = 0.677). What is more, neither overall survival benefit (HR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.47–1.65, P = 0.700) nor disease-free survival (HR = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.55–1.62, P = 0.835) was significant between the PCI-treated and non-PCI-treated cohorts.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The present study did not support using PCI in surgically resected small cell lung cancer without lymph node involvement. A relatively lower risk of brain metastasis in this particular subset might explain the inferior efficacy of PCI.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


