Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Jia-Tao Zhang
Author of
-
+
MA25 - Oligometastasis: Defining, Treating, and Evaluating (ID 929)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Oligometastatic NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 203 BD
-
+
MA25.06 - RPA Analysis for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Smoking Combine T3/4 Patients May Not Be Benefit from Local Consolidative Treatment (ID 11994)
14:05 - 14:10 | Presenting Author(s): Jia-Tao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
In the literature on oligometastasis, the relative importance of local consolidative treatment (LCT) has been gradually accepted. This study set out to investigate the prognosis heterogeneity and the effect of LCT for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We identified 436 patients in Guangdong General Hospital (GGH) from 2009 to 2016 with oligometastatic disease, and the factors predictive of overall survival (OS) were evaluated using Cox regression. Risk stratifications were defined using recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) on training set (2009~2014), which were further confirmed on validation set (2015-2016). And the effect of LCT for different risk groups was further examined by Kaplan-Meier method.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Factors predictive of OS were: T stage (p=0.001), N stage (p=0.008), metastatic sites (p=0.031) and EGFR status (p=0.043). Prognostic risk RPA model was established, 4 risk groups were identified: Group I, never smokers and N0 disease (3-year OS: 55.6%, median survival time (MST)=42.8m); Group II, never smokers and N+ disease (3-year OS: 32.8%, MST=26.5m); Group III, smokers and T1/T2 disease (3-year OS: 23.3%, MST=19.4m); and Group IV, smokers and T3/T4 disease (3-year OS: 12.5%, MST=11.1m). Among four groups, OS significant differences were observed according to LCT except group IV (p=0.45).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This retrospective study identified the poor prognostic population (smoking combine T3/4 disease) of oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients, and this population may not be benefit from local consolidative therapy.

6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.11 - Screening and Early Detection (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 943)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
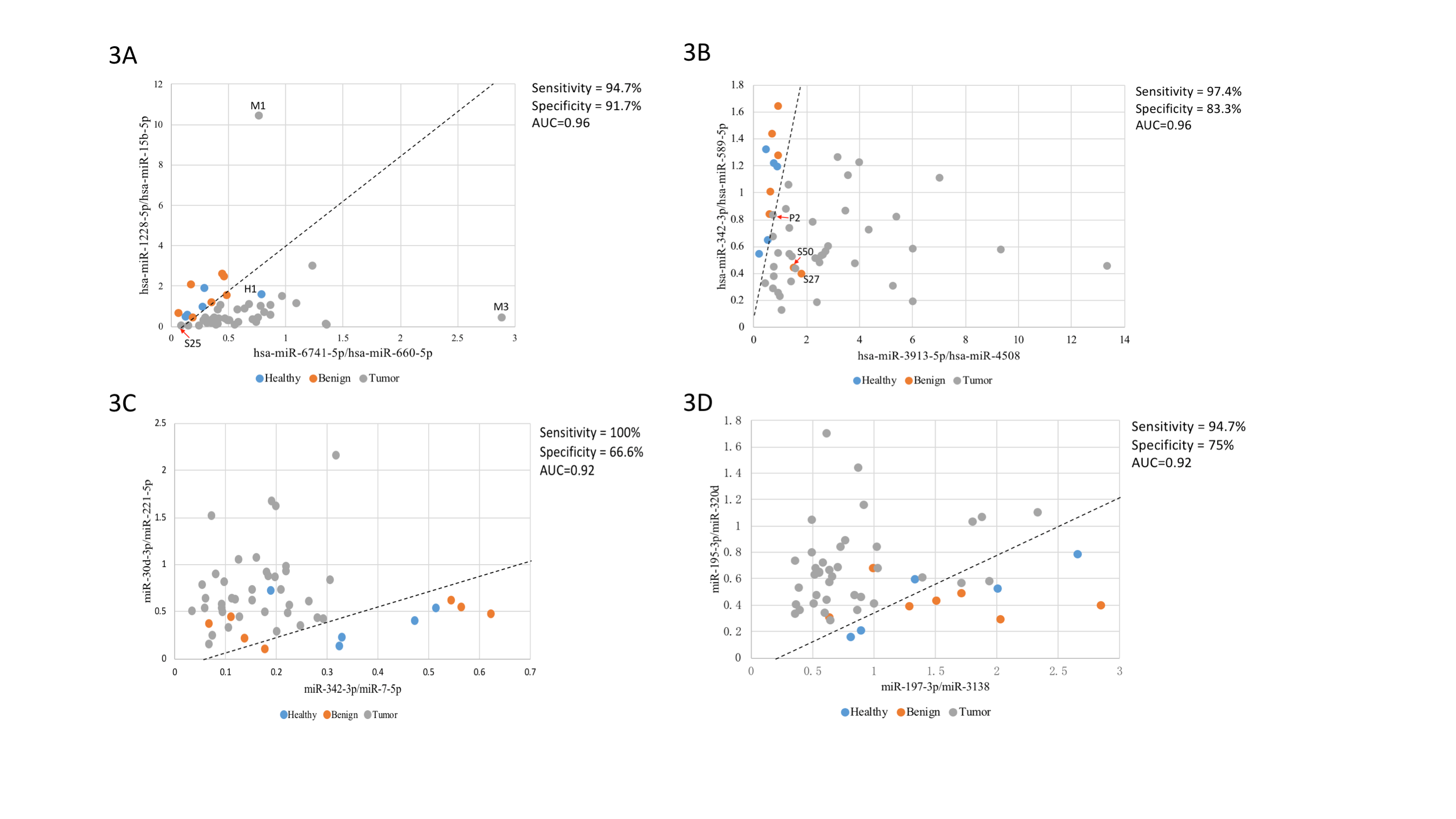
P1.11-18 - A Classification-Based Machine Learning Method Reveals Exosomal miRNA Biomarkers for Patients with Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodule (ID 12462)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Jia-Tao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Non-invasive detection of lung cancer is of critical importance but has proven challenging due to the rate of false-negative diagnosis with current tests. Plasma exosomes have been implicated as a non-invasive diagnostic source. However, little high throughput screening has been done in the early-stage lung cancer and problems such as bias of enrollment, less rigorous identification exists. This study aimed to reveal the plasma exosome-derived miRNA biomarkers for early-stage lung cancer patients, especially those with ground glass nodule (GGN).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Pre-operative and paired post-operative plasma samples from patients with solitary pulmonary nodule and healthy volunteers were prospectively collected. Finally 38 malignant nodules, 7 benign nodules and 5 healthy volunteers were enrolled. The malignant nodules included 9 pure GGNs, 11 mixed GGNs and 18 solid nodules. Exosomes were collected from 1mL plasma and were isolated with 3D Medicine EV isolation kit. Exosomal miRNA profiling was performed using miRNA-seq. And an exosomal miRNA diagnostic model for patients with malignant nodules was constructed by using support vector machine (SVM).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In general, malignant nodules, benign nodules and healthy volunteers were indistinguishable based on overall clustering. Regarding to malignant nodules, pure GGNs and solid nodules could be separated under principal component analysis (PCA), and the mixed GGNs presented a transitional state between the pure GGNs and the solid nodules. Ultimately, a two-dimensional SVM diagnostic model for discriminating malignant and benign nodules was established. The optimal miRNA combination could reach an area under curve (AUC) of 0.96, with sensitivity and specificity of 94.7% and 91.7%, respectively.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This preliminary analysis highlights the potential of exosomal miRNA based liquid biopsy for non-invasive detection of early-stage lung cancer. The SVM model seems could effectively distinguish pulmonary nodules, but needs further verified.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53