Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Paul K. Paik
Author of
-
+
OA12 - Novel Therapies in MET, RET and BRAF (ID 921)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Targeted Therapy
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 15:15 - 16:45, Room 106
-
+
OA12.01 - Phase II Data for the MET Inhibitor Tepotinib in Patients with Advanced NSCLC and MET Exon 14-Skipping Mutations (ID 12896)
15:15 - 15:25 | Author(s): Paul K. Paik
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
A subset (3%) of NSCLCs harbor mutations of the MET proto-oncogene that cause MET exon 14 skipping (METex14) and accumulation of active MET lacking a juxtamembrane domain. We report interim data from a single-arm phase II trial (NCT02864992) investigating the efficacy and safety of the potent, selective tyrosine-protein kinase MET inhibitor tepotinib in patients with METex14-skipping mutation-positive (METex14+) NSCLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Recruitment of ≤120 adult patients with advanced METex14+ NSCLC without EGFR-activating mutations or ALK rearrangements is ongoing. METex14+ mutations are identified in FPE tumor (T) material and/or plasma (L; 60 patients each, overlap anticipated) by a central laboratory. Patients receive tepotinib 500mg QD until disease progression, intolerable toxicity, or withdrawal. Primary endpoint: objective response rate (ORR). Secondary endpoints include safety.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Forty-one patients have been treated to date; data are available for 34 (median age 73.5 years; 23 male; 24/8 Caucasian/Asian; prior lines of therapy: 0, n=12; 1, n=11; 2, n=10; 3, n=1; stage IVA, n=4; stage IV, n=29; stage IIIB, n=1). Treatment is ongoing in 24 patients. Based on investigator assessment, 13/22 (59.1%) evaluable patients responded: 1 had a confirmed complete response; 12 had a confirmed partial response (PR); 3 (13.6%) had stable disease for ≥12 weeks (SD). Based on independent review, 9/22 (40.9%) had a confirmed PR; 5 (22.7%) had SD. Duration of response >12 months in 2 patients. Twenty (58.8%) patients have experienced tepotinib-related treatment-emergent adverse events (TRTEAEs), including serious TRTEAEs in 3 (8.8%): pneumonia =1, generalized oedema=1, interstitial lung disease=1, and grade ≥3 TRTEAEs in 6 (17.6%): generalized oedema=1, pneumonia=1, ALT increased=1, AST increased=1, amylase increased=2, gamma GT increased=1, lipase increased=1, hyperkalemia=1; no TRTEAEs were grade ≥4 or led to death. Five (14.7%) patients have died.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Tepotinib 500mg QD has promising activity in METex14+ NSCLC, with a favorable safety profile.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
OA12.02 - Updated Antitumor Activity of Crizotinib in Patients with MET Exon 14-Altered Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 13453)
15:25 - 15:35 | Author(s): Paul K. Paik
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
MET exon 14 alterations occur in ~3% of non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLCs) and 20–30% of sarcomatoid lung carcinomas. Here we present updated antitumor activity for crizotinib in patients with advanced NSCLC whose tumors are positive for MET exon 14 alterations (hereafter MET exon 14-positive NSCLC), including updated biomarker analyses in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Patients with MET exon 14-positive NSCLC by local molecular profiling were treated with 250 mg crizotinib BID in an expansion cohort of the ongoing PROFILE 1001 study (NCT00585195). Responses were based on derived investigator assessment per RECIST v1.0. Prospective plasma profiling for MET exon 14 alterations in plasma ctDNA was performed (PlasmaSELECT-R64; Personal Genome Diagnostics, Boston, MA).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
As of Jan 31, 2018, 69 patients (65 response-evaluable) with MET exon 14-positive NSCLC had been treated. Median age was 72 y (range: 34, 91). Tumor histology was: 84% adenocarcinoma, 9% sarcomatoid adenocarcinoma, 4% squamous cell carcinoma and 3% adenosquamous carcinoma. 61% were former-smokers, 38% never-smokers and 1% a current smoker. Median duration of treatment was 7.4 mo (95% CI: 5.5, 9.1), with 29% of patients ongoing. Confirmed responses were 3 CRs and 18 PRs (ORR, 32% [95% CI: 21, 45]); 29 patients had SD as their best overall response (Figure).
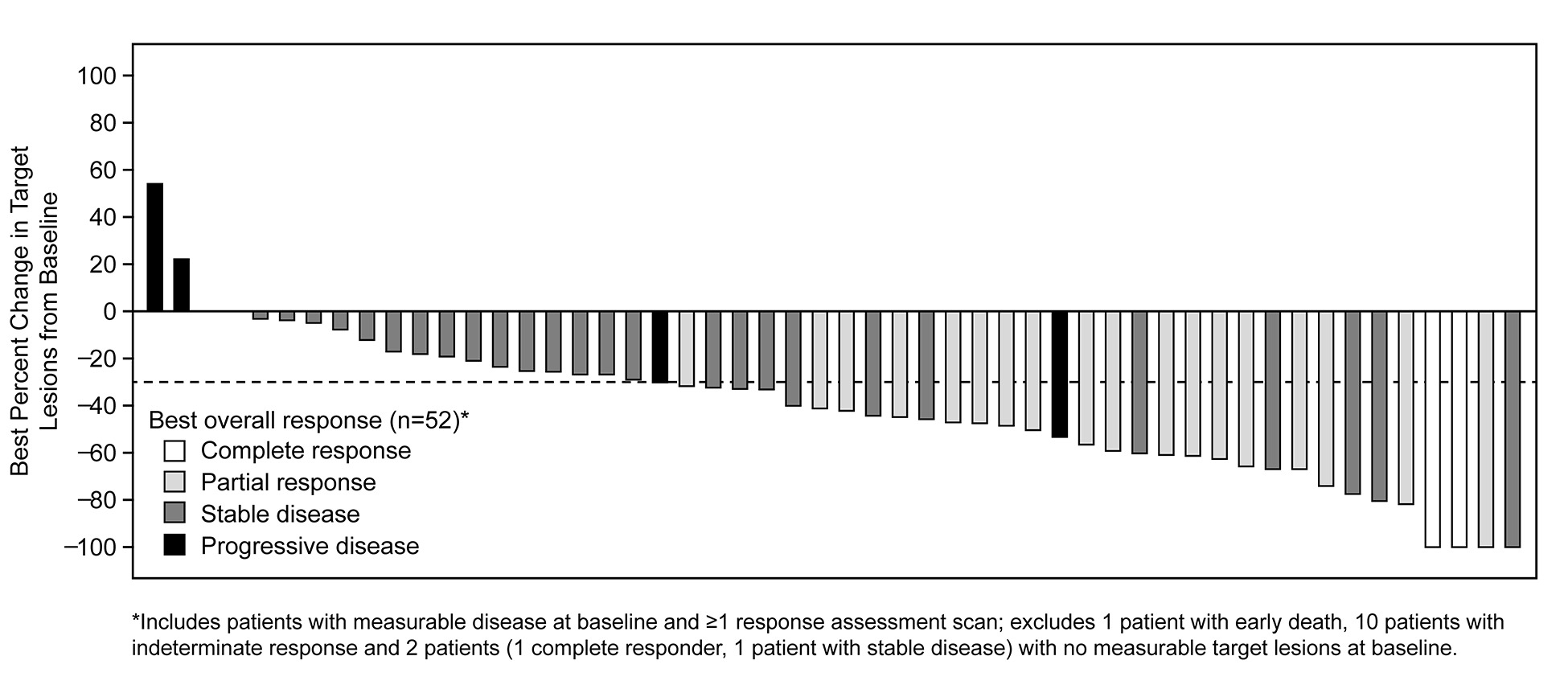
Median time to response was 7.6 weeks (range: 3.7, 16.3). Median DOR was 9.1 mo (95% CI: 6.4, 12.7). Median PFS was 7.3 mo (95% CI: 5.4, 9.1). MET exon 14 alterations were detected in ctDNA from 18/37 (49%) patients with analyzable samples.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In patients with MET exon 14-positive advanced NSCLC, crizotinib treatment led to objective responses that were rapid and durable, with CRs in some cases. Plasma ctDNA profiling detected MET exon 14 alterations in a subset of patients who harbor MET exon 14 alterations by tumor testing.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 933)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-76 - A Phase II Trial of Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel and Gemcitabine in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancers (ID 13324)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Paul K. Paik
- Abstract
Background
Therapeutic options for SQCLC patients are limited. The efficacy of platinum-based doublets, long the standard first-line treatments, has plateaued, with ORR=30%. Anti-tumor synergy between gemcitabine and albumin-bound paclitaxel (ABP) was demonstrated by Frese et al. who showed that ABP downregulates cytidine deaminase, leading to increased intratumoral gemcitabine (Cancer Disc 2012). Based on these data, we sought to assess the efficacy of ABP + gemcitabine in patients with SQCLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
This was a Simon two-stage phase 2 study of ABP + gemcitabine in chemotherapy-naïve, PD-L1 low/unknown advanced SQCLC patients (NCT02525653). Primary endpoint: best ORR. H0=25% (≥6/17 responses) and HA=45% (≥16/41 responses). ABP (100mg/m2) + gemcitabine (1000mg/m2) was initially given on D1, D8, D15 of an every 4 week cycle for up to 6 cycles (A1). After clearing H0, the study was amended to a 3 week cycle (D1, D8 treatment) and to allow maintenance ABP after C4 (A2). All patients underwent NGS by MSK-IMPACT.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
N=27 patients were evaluable for the primary endpoint. Median age=70, age ≥70=60%, female=30%, median KPS=80%, smokers=93%. 46% of patients had PD-L1 IHC <50% (0-20%). 54% were PD-L1 unknown. Grade ≥3 related AEs included: fatigue-13%, neuropathy-4%; diarrhea-4%; lung infection-4%, anemia-9%; decreased platelet count-4%, and decreased neutrophils (4%). Four patients (17%) experienced related SAEs including, separately, G3 febrile neutropenia, G3 WBC decrease, G3 thrombocytopenia, and G3 anemia.
ORR for the entire cohort was 63% (Figure 1). ORR in A2= 71% (10/14). 8 patients in A1 had dose modifications resulting in equivalency to the A2 schedule. ORR in the A2+A1 dose modified cohort=73% (16/22), meeting the primary endpoint early. Median PFS=8mo; OS not yet mature.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
ABP + gemcitabine is an effective and well-tolerated regimen in patients with untreated advanced SQCLC with a response rate exceeding that associated with platinum regimens and first-line immunotherapy.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P1.17 - Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 949)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.17-08 - Genetic Predictors of Response to Chemoradiation in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ID 12804)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Paul K. Paik
- Abstract
Background
Radiation with platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the standard of care for patients with unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite aggressive treatment, progression-free survival and overall survival remain poor. It is unclear whether any tumor genetic alterations are associated with response to therapy.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively reviewed clinical outcomes of patients with stage III NSCLC treated with definitive radiation, who had undergone tumor molecular profiling through an institutional next-generation sequencing platform. This platform is an FDA-approved, targeted-DNA-sequencing panel that contains 341 (now expanded to 468) somatic mutations and other genetic alterations. Basic patient and tumor characteristics, clinical outcomes including loco-regional recurrence, distant recurrence, and overall survival, were collected. Overall and recurrence-free survivals were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional hazards model was used to investigate association between clinical outcome and genetic alterations.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
We identified 110 patients with stage III NSCLC who were treated with definitive radiation between 2013 and 2017 and underwent tumor molecular profiling. Fifty-one patients (46%) had stage IIIA disease and 59 patients (54%) had stage IIIB disease. Median radiation dose delivered was 60Gy in 30 fractions (range 48.6Gy to 74Gy). Either concurrent or sequential chemotherapy was given in 104 patients (95%) with 83 patients (75%) receiving concurrently. One patient received induction crizotinib and one patient died before start of chemotherapy. With a median follow-up time of 15.3 months, the median overall survival was 31.2 months. Several genetic mutations were significantly associated with worse overall survival after therapy, including AKT2 any mutation (Hazard ratio 13.71, p<0.001), KMT2C truncating mutations (HR 13.42, p<0.001), KMT2D truncating mutations (HR 6.97, p<0.001), ARID1A frameshift mutations (HR 8.54, p<0.001), and FLT1 any mutation (HR 6.62, p<0.001). These genes were also associated with increased loco-regional recurrence. Mutation in the PIK3C2G gene was significantly associated with improved overall survival. Association of other common genetic alterations such as EGFR mutation with response to therapy was not observed.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This study coupled multiplex targeted sequencing with clinical outcome information to identify several potential genetic predictors of response to chemotherapy and radiation in locally advanced NSCLC. KMT2C and KMT2D encode two subunits of a histone methyltransferase, and mutations of KMD2 have been shown to correlate with worse survival in locally advanced and advanced NSCLC patients. Further studies including in vitro validations are necessary to confirm the findings.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.13 - Targeted Therapy (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 962)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.13-44 - Targeting NFE2L2 Mutations in Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancers with the TORC1/2 Inhibitor TAK-228 (ID 12591)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Paul K. Paik
- Abstract
Background
Despite research efforts over the past decade, no targeted therapy options exist for patients with SQCLC. Analyses by TCGA and others (Paik Cancer Disc 2015) have identified a heretofore untargeted, frequently mutated oncogene (NFE2L2)/tumor suppressor (KEAP1) pair, each mutated in ~20% of patients with SQCLC. NFE2L2 encodes Nrf2, a transcription factor involved in the oxidative stress response which is targeted for degradation by Keap1. NFE2L2 mutations occur exclusively in an exon 2 hotspot that encodes the Neh2 domain (~aa.1-86), which is the binding site for Keap1. Mutations in this region disrupt Keap1 binding, leading to Nrf2 nuclear translocation and increased mTOR signaling through regulation of RagD (Shibata Cancer Res 2010). We now report translational studies and preliminary results from a phase 2 trial of the oral TORC1/2 inhibitor TAK-228 in SQCLC patients with these mutations.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Cytotoxicity, signaling, and xenograft experiments were performed using LK-2 SQCLC cells harboring an NFE2L2 E79K mutation treated with TAK-228, everolimus, rapamycin, or deforolimus with requisite vehicle controls. Patients with stage IV SQCLC harboring NFE2L2 mutations were treated on an NCI CTEP- single-institution phase 2 study of TAK228 3mg po qd (continuous, 28 day cycles; NCT02417701). Primary endpoint: ORR. Secondary endpoints: PFS/OS. The study utilizes a Simon 2-stage design with H0=5% (N≥1/5 responses), HA=40% (N≥2/10 responses).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
TAK-228 exhibited significantly increased anti-tumor activity over TORC1 rapalogs in LK-2 cells. TAK-228 alone was cytotoxic at sub-[μM] (IC50 68nM); all other rapalogs exhibited IC50s >10μM. This was associated with an 80% decrease in downstream S6 phosphorylation. Tumor response (-55% shrinkage) was also seen in an LK-2 xenograft treated with TAK228. No anti-tumor/growth inhibitory response was seen with any other rapalog tested.
N=4 patients have been treated on study (exon 2 del, D29H, F37V, W24C). 3 are evaluable for response. 2 related-SAEs (G3 hyperglycemia, G3 confusion) were seen; no other G3 AEs reported. ORR=67% (2 PR, 1 SD, 0 PD). Prolonged disease response is present, with DOR= 12mo, 10mo (ongoing), 8mo (ongoing).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
TAK228 is tolerable with evidence of pre-clinical and clinical activity in this biomarker-selected population. The trial has met its first-stage endpoint and has expanded to N=10 patients. The trial has also expanded to included patients with KRAS mutant lung cancers harboring co-alterations in NFE2L2 or KEAP1.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


