Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Xu-Chao Zhang
Author of
-
+
JCSE01 - Perspectives for Lung Cancer Early Detection (ID 779)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Joint IASLC/CSCO/CAALC Session
- Track: Screening and Early Detection
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/23/2018, 07:30 - 11:15, Room 202 BD
-
+
JCSE01.09 - Cluster Trial: Ph2 Biomarker-Integrated Study of Single Agent Alpelisib, Capmatinib, Ceritinib and Binimetinib in advNSCLC (ID 11678)
10:15 - 10:25 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Several genetically altered signaling pathways have been profiled in NSCLC, enabling advanced management of NSCLC using targeted therapies. This study investigated the therapeutic spectrum of NSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations by allocating patients to treatment arms based on molecular aberrations; targeted therapies alpelisib (PI3Kαi), capmatinib (METi), ceritinib (ALKi), and binimetinib (MEKi) were evaluated.The study was based on the umbrella design. Key objectives: investigate feasibility of using one trial for different agents based on biomarker-integrated analysis, assess anti-tumor activity, characterize safety, tolerability and PK profiles of individual agents. Key eligibility criteria: age ≥18 years; ECOG PS ≤2; failed prior treatment/unsuitable for chemotherapy. Documentation of locally determined molecular alterations before treatment allocation was required (alpelisib, 350 mg QD: PIK3CA mutation/amplification; capmatinib, 400 mg BID (tablet): MET IHC overexpression/amplification; ceritinib, 750 mg QD: ALK or ROS1 rearrangement; binimetinib, 45 mg BID: KRAS, NRAS or BRAF mutation).Sixty-six patients with advNSCLC were enrolled (median age 58 years; 65.2% male: alpelisib, n=2; capmatinib, n=16; ceritinib, n=26; binimetinib, n=22). As of Feb 28, 2018, 10 patients in ceritinib and 2 in binimetinib arms were ongoing. Twenty-four patients had confirmed partial responses (36.4%): alpelisib, 0%; capmatinib, 18.8%; ceritinib, 73.1%; binimetinib, 9.1% (Figure). Longest mPFS (14.4 months) was in ceritinib arm. Among the most common treatment-related AEs: alpelisib: malaise, hyperglycemia, dysgeusia; capmatinib: nausea, anemia, peripheral edema, decreased appetite; ceritinib: diarrhea, vomiting, ALT/AST elevation; binimetinib: mouth ulceration, AST, blood CPK increased, rash. Most AEs were grade 1/2.
Objective responses/tumor shrinkage were observed in the study; highest ORR and mPFS were observed with ceritinib, although patient numbers differed between arms. All treatments were well tolerated; no new safety signals were observed. This study demonstrated the feasibility of an umbrella trial and importance of precision medicine in the management of advNSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA15 - Colliding Approaches - EGFR and Immunotherapy (ID 916)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Targeted Therapy
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 107
-
+
MA15.01 - Strong PD-L1 Expression Predicts Poor Response and de Novo Resistance to EGFR TKIs Among Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with EGFR Mutation (ID 12920)
13:30 - 13:35 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
This study evaluated whether tumor expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) predicted the response of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively evaluated patients who received EGFR-TKIs for advanced NSCLC between April 2016 and September 2017 at the Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute. None of them were enrolled in clinical studies, and their EGFR and PD-L1 statuses were simultaneously evaluated.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Among the 101 eligible patients, strong PD-L1 expression significantly decreased the objective response rate (ORR) compared with those with weak or negative PD-L1 expression (35.7% vs 63.2% vs 67.3%, P=0.002) as well as shortened progression-free survival (PFS, 3.8months vs 6.0months vs 9.5months, P<0.001), regardless of EGFR mutation types (19del or L858R). Furthermore, positive PD-L1 expression was predominantly observed among patients with de novo resistance rather than acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs (66.7% vs 30.2%, P=0.009). Notably, patients with de novo resistance had a high proportion of dual positive for PD-L1 and CD8 (46.7%, 7/15). Finally, one patient with de novo resistance to EGFR-TKIs and dual positivity for PD-L1 and CD8 experienced a favorable response to anti-PD-1 therapy.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This study uncovered the adverse impact of PD-L1 expression on the efficacy of EGFR- TKIs, especially in those with de novo resistance NSCLC, which inclined to reshape an inflamed immune phenotype of dual positive for PD-L1 and CD8 and showed potential therapeutic sensitivity to PD-1 blockade.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA15.06 - Circulating Tumor DNA Portrays the Resistance Landscape to a Novel Third Generation EGFR Inhibitor, AC0010 (ID 13641)
14:05 - 14:10 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
In a Phase I/II dose-escalation and expansion study conducted at Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, AC0010 demonstrated promising efficacy and good tolerability in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR T790M-mediated resistance to previous EGFR TKIs, (NCT02330367). As disease progression (PD) with EGFR T790M-directed therapy also emerges over time, we investigated the resistance mechanisms to AC0010 in this study.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Serial ctDNA samples obtained from patients who developed PD with AC0010 were analyzed using ultra-deep sequencing capturing 295 cancer-related genes. Alterations that were absent before treatment and acquired at PD or that increased in abundance during treatment were identified as putative resistance mechanisms.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Longitudinal plasma samples were obtained from 23 patients who progressed on AC0010 (data cut-off October 14, 2016; figure1). Putative resistance mechanisms to AC0010 were identified in 19/23 patients (>1 putative resistance mechanism was detected in some patients). EGFR amplification was the predominant resistance mechanism (21.1% [4/19 patients]), followed by TP53 loss of heterozygosity (15.8% [3/19]). EGFR C797S mutation, Met amplification and mutations in the PI3KCA pathway each occurred in 10.5% of patients (2/19). SCLC transformation, ERBB2 amplification, CD79A_A32G mutation, CDKN2A_R80 mutation, CRLF2 amplification, MLH1 amplification, Rb1 loss, and concurrent rise in the allelic fraction of tumor suppressor gene TP53 and Rb1 were each detected in 5.3% of patients (1/19). In a patient with PD following single-agent AC0010 and EGFR amplification as the putative resistance mechanism to AC0010, subsequent treatment with AC0010 plus nimotuzumab (EGFR monoclonal antibody) successfully overcame resistance, resulting in a response that lasted for 7.7 months.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The resistance landscape to AC0010 appears to differ from that described previously with osimertinib. In this cohort of patients in China, EGFR amplification was the predominant resistance mechanism to AC0010 and could be potentially overcome by EGFR dual inhibition.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA16 - Novel Mechanisms for Molecular Profiling (ID 917)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 203 BD
-
+
MA16.10 - Clinical Utility of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cell-Free DNA for Clarifying Genetic Features of Leptomeningeal Metastases in ALK Rearrangement NSCLC (ID 12142)
14:35 - 14:40 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) were associated with a poor prognosis in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). LM were much more frequent in EGFR mutant patients, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has shown unique genetic profiles of LM in patients harboring EGFR mutations in our previous studies. However, studies in ALK positive NSCLC patients with LM are scarce.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Lung cancer patients with ALK rearrangement were screened from Sept 2011 to Feb 2018 at our institute. Leptomeningeal metastases were diagnosed by MRI or CSF cytology or next-generation sequencing (NGS) of CSF cfDNAs. Paired plasma were also tested by NGS.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
LM were diagnosed in 22 (7.6%) of 288 ALK rearrangement patients with lung cancer. A total of 11 ALK positive patients with LM were enrolled with CSF cfDNA tested by NGS (one case used CSF precipitates instead of CSF cfDNA). Paired plasma were available in 11 patients. Driver genes were detected in 75.0% CSF samples and 45.5% plasma respectively (P=0.214). Max allele fractions were higher in CSF cfDNA than in plasma (40.8% versus 0%, P=0.021). ALK variant 1 (E13:A20) was detected in 3 cases of CSF and paired plasma, respectively. ALK variant 2 (E20:A20) was identified in 5 cases of CSF and 1 paired plasma. Multiple copy number variants (CNV) were mainly found in CSF cfDNA, including EGFR copy number gains. Resistance mutations including gatekeeper gene ALK G1202R was identified in CSF cfDNA with ALK variant 1 and ALK G1269A was detected in plasma. The detection rate of TP53 was 45.4% versus 27.3% in CSF cfDNA and plasma.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
CSF cfDNA was more sensitive than plasma to reveal genetic features of ALK-fusion LM, confirming its role as a liquid biopsy medium for LM in driver gene positive NSCLC.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA24 - Genomic Evolution, KEAP 3 and More Non-Coding RNA (ID 928)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Biology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 10:30 - 12:00, Room 205 BD
-
+
MA24.01 - Genomic Evolution Trajectory Depicts Invasiveness Acquisition from Pre-invasive to Invasive Adenocarcinoma (ID 11840)
10:30 - 10:35 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Accumulation of molecular abnormalities may depict evolution trajectories of tumor initiation and development. However, the genomic profile of early stage adenocarcinoma and molecular mechanism of invasiveness acquisition from pre-invasive to invasive adenocarcinoma remains barely explored.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We simultaneously collected 20 patients with adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) (n=5), minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) (n=5) and stage IA adenocarcinoma (lepidic/acinar predominant) (n=10). Whole exon sequencing (WES) was performed in pre-invasive adenocarcinoma with multi-region specimens and stage IA adenocarcinoma. Analysis of genomic alteration among different pathological status was performed and tumor mutation burden (TMB) was calculated as well as six mutation types individually. Enriched pathways of each pathology were measured through KEGG analysis.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Baseline characteristics was generated through heatmap with smokers (2/20, 10%) and EGFR mutation (13/20, 65%) among whole population. AIS/MIA indicated much lower number of mutations than invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC) while TMB revealed the same trend without statistical significance. Multi-region sequencing showed high heterogeneity of single nucleotide variation (SNV) in AIS and MIA. Unique SNV presented dominant proportion in initial status. Cluster analysis showed higher copy number variation in AIS/MIA than IAC with cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) enriched in AIS/MIA while variety pathway enrichment in IAC through KEGG analysis. C>A transversions held major proportion in early stage adenocarcinoma and a significant increase in the proportion of C>T and C>G mutation was exhibited when evolving into IAC.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Intratumor heterogeneity may occur in the very beginning of adenocarcinoma. High copy number variation was dominant event for AIS/MIA while higher tumor mutation burden was seen in IAC. Tobacco signature encompassing C>A transversions dominates the early development of adenocarcinoma and APOBEC signature may play a potential role in acquisition of cancer invasiveness.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 933)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-55 - Unique Genetic Profiles from Cerebrospinal Fluid Could Predict Survival of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC with Leptomeningeal Metastases (ID 12369)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) are more frequent in NSCLC with EGFR mutations;and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) could reveal the unique genetic profiles of LM in our previous studies, but whether they could predict the overall survival (OS) of LM remains unknown.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with LM were enrolled,and clinical data and genetic profiles detected by Next-generation sequencing were collected. We further drew nomogram with endpoint of OS after LM, then performed index of concordance (C-index) and survival analysis to evaluate predictive role.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In total, 61 patients were enrolled and all with genetic profiles from CSF. Patents with high copy number variations (CNVs) or harboring CDK6, TP53 exon5 or FGF19 in CSF demonstrated significant poorer OS than those without (Fig. 1). Cox regression analysis indicated CNVs, CDK6,CDKN2A,TP53,MET and NTRK1 as prognostic factors and further selected for nomogram (Fig. 2). C-index of nomogram was 0.743, indicating the moderate predictive effect. In the calibration curves, we scored the patients based on the model, using bisection and trisection methods to divide into low and high points groups; and low, medium and high points groups (Fig. 3), and significant difference were found in both the survival analyses (NA versus 7.47months, P<0.01) and (NA, 10.33 versus 4.43 months, P<0.01) respectively. Patients who received Osimertinib after LM seemed to have longer OS than those who did not (14.5 months versus 7.7 months) but without significant difference(P=0.10); however interestingly, in those with EGFR T790M negative who took Osimertinib after LM by themselves obtained survival benefit than those who did not(NA versus 7.7 months, P=0.04), and the results needed to be validated.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Unique genetic profiles from CSF could well predict OS of LM. High CNVs, CDK6, TP53 exon5 or FGF19 in CSF in CSF may be related to poor prognosis of LM.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-97 - Cluster Trial: Ph2 Biomarker-Integrated Study of Single Agent Alpelisib, Capmatinib, Ceritinib and Binimetinib in advNSCLC (ID 12065)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Several genetically altered signaling pathways have been profiled in NSCLC, enabling advanced management of NSCLC using targeted therapies. This study investigated the therapeutic spectrum of NSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations by allocating patients to treatment arms based on molecular aberrations; targeted therapies alpelisib (PI3Kαi), capmatinib (METi), ceritinib (ALKi), and binimetinib (MEKi) were evaluated.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
The study was based on the umbrella design. Key objectives: investigate feasibility of using one trial for different agents based on biomarker-integrated analysis, assess anti-tumor activity, characterize safety, tolerability and PK profiles of individual agents. Key eligibility criteria: age ≥18 years; ECOG PS ≤2; failed prior treatment/unsuitable for chemotherapy. Documentation of locally determined molecular alterations before treatment allocation was required (alpelisib, 350 mg QD: PIK3CA mutation/amplification; capmatinib, 400 mg BID (tablet): MET IHC overexpression/amplification; ceritinib, 750 mg QD: ALK or ROS1 rearrangement; binimetinib, 45 mg BID: KRAS, NRAS or BRAF mutation).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Sixty-six patients with advNSCLC were enrolled (median age 58 years; 65.2% male: alpelisib, n=2; capmatinib, n=16; ceritinib, n=26; binimetinib, n=22). As of Feb 28, 2018, 10 patients in ceritinib and 2 in binimetinib arms were ongoing. Twenty-four patients had confirmed partial responses (36.4%): alpelisib, 0%; capmatinib, 18.8%; ceritinib, 73.1%; binimetinib, 9.1% (Figure). Longest mPFS (14.4 months) was in ceritinib arm. Among the most common treatment-related AEs: alpelisib: malaise, hyperglycemia, dysgeusia; capmatinib: nausea, anemia, peripheral edema, decreased appetite; ceritinib: diarrhea, vomiting, ALT/AST elevation; binimetinib: mouth ulceration, AST, blood CPK increased, rash. Most AEs were grade 1/2.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
Objective responses/tumor shrinkage were observed in the study; highest ORR and mPFS were observed with ceritinib, although patient numbers differed between arms. All treatments were well tolerated; no new safety signals were observed. This study demonstrated the feasibility of an umbrella trial and importance of precision medicine in the management of advNSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations.
-
+
P1.03 - Biology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 935)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.03-34 - Combined Molecular and Radiological Evaluation Unveils Three Subtypes of Disease Progression to a Third Generation EGFR TKI (ID 12055)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
The definition of disease progression (PD) to EGFR TKIs has evolved from RECIST to a combination of clinical and RECIST evaluation. Patients with dramatic, local or gradual progression to third generation EGFR TKIs have been tailored to different subsequent treatment strategies. However, little is known about progression to third generation EGFR TKIs from molecular perspective.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Longitudinal plasma samples were collected from T790M-positive patients who progressed on a third generation EGFR TKI AC0010 in a phase I/II study in Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute. A pre-defined and unified molecular and radiological evaluation of PD were performed. Ultra-deep sequencing capturing 295 cancer-related genes was performed to track the changes in ctDNA to depict molecular PD, which was defined by acquired SNV/SCNV, or ≥20% increase in allelic fraction/copy number of pre-existing SNV /SCNV or both. Radiological PD was defined by RECIST.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
As of October 2016, 102 serial plasma samples from 23 patients with clinical PD were included. Three subtypes of PD to AC0010 were revealed (Fig1). Molecular PD occurred prior to radiological PD in 43.5% of patients (10/23), with an average lead time of 3.0 months. Molecular PD occurred concurrently with radiological PD in 39.1% of patients (9/23). Interestingly, 17.4% of patients (4/23) experienced radiological PD prior to molecular PD, with molecular PD occurred during AC0010 continuation beyond progression (CBPD) in 3 patients. Of patients experienced clinical stable PD in extracranial lesions, radiological PD occurring prior to molecular PD group (n=2) demonstrated longer duration of AC0010 CBPD than molecular PD occurring prior to (n=3) or concurrently with radiological PD groups (n=4) (Median, 5.6 months vs. 1.9 months vs. 1.8 months).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion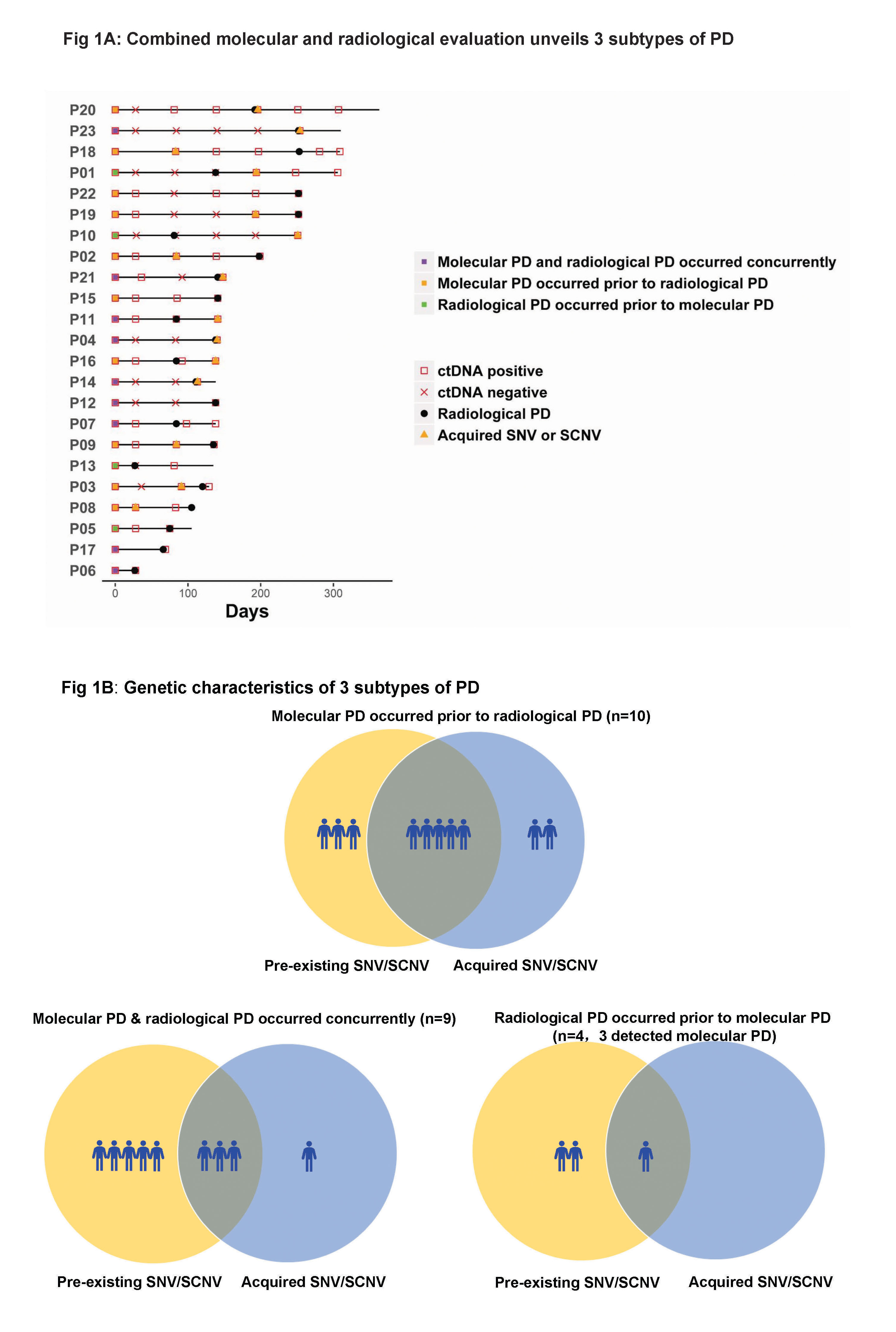
Our study revealed 3 distinct subtypes of PD to AC0010, providing insights into PD by combining molecular and radiological evaluation and might guide the optimal time for treatment switch and personalized subsequent treatments.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-52 - Identification of Leptomeningeal Metastasis-Specific Exosomal miRNA Signatures in Cerebrospinal Fluids of NSCLC Patients (ID 13074)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) is a devastating complication with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. The confirmed diagnosis of LM usually involves neurological evaluation, MRI imaging, and cytopathology analysis of limited tumor cells from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Exosomes are extracellular vesicles in body fluids enriched with microRNAs (miRNAs), which have been implicated to participate in brain metastasis. Here, we aimed to identify LM-specific exosomal miRNA signatures in NSCLC patients to elucidate their potential role in LM mechanism and to predict LM via liquid biopsy.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Exosomes prepared from CSF and plasma samples of 39 advanced NSCLC patients with (LM+) or without (LM-) LM as well as 12 non-cancer individuals (NC) were underwent small RNA next-generation sequencing. For patients in the LM+ group, paired plasma samples were taken before (PLM+pre) and upon (PLM+post) LM diagnosis. Exosomal miRNA profiles were subjected for differential expression analysis, pathway enrichment analysis, and signature discovery.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the miRNA expression profiles clearly separated CSF samples into LM+ and LM free groups (LM- and NC). Interestingly, these samples were stratified based on their LM status only, regardless of their intraparenchymal metastasis status. In total, 247 (185 up and 62 down-regulated) miRNAs were identified differentially presented in the LM+ CSF exosome samples compared to the LM- and NC groups. Top altered miRNAs include dramatically up-regulated miR-200 family and down-regulated miR-144/451 cluster. Predicted gene targets of these top-regulated miRNAs were significantly enriched in Ras/MAPK/PI3K-AKT signaling, endocytosis pathways, and so on. Promisingly, a signature of five CSF exosomal miRNAs (let-7e-5p, miR-28-3p, miR-375, miR-200a-3p, and miR-486-5p) was identified for classification of LM+ patients with 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Due to the higher background complexity, we only identified one miRNA (miR-24-3p) was significantly up-regulated and one miRNA (miR-92b-5p) was significantly down-regulated in LM+ patients’ plasma-derived exosomes (PLM+pre and PLM+post) compared with the LM free group (PLM- and PNC). However, a combined signature of seven miRNAs (miR-24-3p, miR-223-3p, miR-340-5p, miR-27a-3p, miR-423-5p, miR-2110 and miR-342-5p) from PLM+pre samples was identified for the prediction of future LM with 81% sensitivity and 76% specificity.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
NSCLC patients with LM present a remarkably distinct CSF exosomal miRNA signature, which may involve in the progression of LM, and can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for LM. Furthermore, the identification miRNA signature in the pre-LM plasma samples suggests the potential use of liquid biopsy to predict LM for better patient care.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.04 - Immunooncology (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 953)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.04-30 - PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibition Might be an Option for the Treatment of Advanced Primary Pulmonary Lymphoepithelioma-Like Carcinoma (ID 12698)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Primary pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma (LELC) is a rare subtype of non-small-cell lung cancer mostly reported in Asian countries, which is frequently associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. There is no consensus on the choice for the treatment of advanced primary pulmonary LELC. The utility of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor to this cancer type remains poorly understood.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
From January 2008 to April 2017, a total of 53 patients receiving surgical removal and diagnosed as primary pulmonary LELC in Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute (GLCI) were enrolled in this study. Sections formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor samples were stained with PD-L1 antibody (clone E1L3N, Cell Signaling Technology) by immunohistochemistry (IHC). PD-L1 expression more than 1% in tumor cells was considered as PD-L1 positive. Moreover, we reviewed the medical records of 13 primary pulmonary LELC patients who received the treatment of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in GLCI. Their clinicopathological characteristics and relevant prognostic data were analyzed.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Among the 53 patients with operable disease, the median age was 56 (36-78), there were 26 males and 27 females, 15 smokers and 38 nonsmokers. Positive rates of PD-L1 in the early pulmonary LELC were 78.8% (41/52,one specimen can't evaluate) and 73.1% (38/52) and 23.1% (12/52) respectively at the cutoff values of 1% and 5% and 50% positivity in tumor cells. ORR of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition in the evaluable 12 patients with advanced LELC was 16.7% (2/12), and DCR was 75.0% (9/12). In the 6 patients with positive PD-L1 expression, ORR was 33.3% (2/6), DCR was 100.0% (6/6). The two responder patients got 55% and 64% shrinkage of the tumors respectively. All patients had no EGFR mutations.

8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This preliminary study showed that pulmonary LELCs have remarkably high incidence of PD-L1 expression. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors might be an option for the treatment of advanced primary pulmonary LELC, which needs further investigation.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.17 - Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 966)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.17-32 - Dynamic Monitoring Before and After Neo-Adjuvant Crizotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Brief Report (ID 11829)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Neo-adjuvant therapy has been considered as an optional approach for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. While targeted therapy has been widely applied in advanced NSCLC, neo-adjuvant targeted therapy remains poorly explored.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We describe four ALK-positive patients with pathological confirmed locally advanced NSCLC receiving neo-adjuvant Crizotinib. All patients received Crizotinib at a starting dose of 250mg twice daily for 1-3 months before surgical resection. One patients provided dynamic monitoring before and after neo-adjuvant therapy through next generation sequencing of plasma and tissue.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Three patients were partial response without apparent adverse event before surgery while one received pathological complete response to neo-adjuvant Crizotinib but suffering from grade 4 hepatic damage. One of them had disease recurrence but achieved long duration of response (PFS=15m) through first-line Crizotinib. Dynamic monitoring with both plasma and tissue indicated simultaneously decrease of sensitive ALK-signaling in a patient with partial response (-51%) and no ALK-dependent resistant variants were captured.


8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Neo-adjuvant Crizotinib may be feasible and well-tolerated in locally advanced disease for complete resection. Crizotinib prior to surgery may provide thorough elimination of circulating molecular residual disease and it did not influence the response of reusing Crizotinib in first-line setting.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 967)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.01-64 - Preliminary Data of Diverse Therapies in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harbouring RET-Rearrangement (ID 13677)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Activating RET-rearrangement has been discovered to play a crucial role in NSCLC tumorigenesis. However, the lack of specificity narrowed efficacy of multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs) and the optimal treatment remains unknown. In this study, we compared chemotherapy, immunotherapy and MKIs in this group of patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively evaluated the efficacy of these three treatments in advanced, RET-rearranged NSCLC patients between January 2013 and April 2018 at our institution. RET-rearrangements were assessed by Next-generation sequencing (NGS) or any of FISH, IHC, RT-PCR. Treatment data were collected after the patients had been diagnosed with RET-rearranged advanced NSCLC. Progression-free survival (PFS) was measured from treatment start to disease progression, all-cause mortality or last follow up. Median follow-up time was 5.1months. NGS was performed to assess somatic mutation of available samples.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 30 patients with RET-rearrangement were investigated in this study. After the diagnosis, 15 patients, genetic profiles confirmed by NGS, received chemotherapy (n=10), checkpoint-inhibitors (n=7) and RET targeted MKI (n=6) with evaluable response. Several patients take any two of these three treatments as different line therapies. The disease control rate of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, MKI group was 70.0%, 71.43% and 50%, respectively. While the median PFS of three groups was 2.50 months, 2.70 months, 0.30 months, respectively, which of no significance. The NGS data of 10 patients showed that RET-rearrangement co-occurred with several other genes, including TP53, NTRK, CDK4, ERBB4. A low mutation burden (mean 4.5 mutations) was observed (Figure 1).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion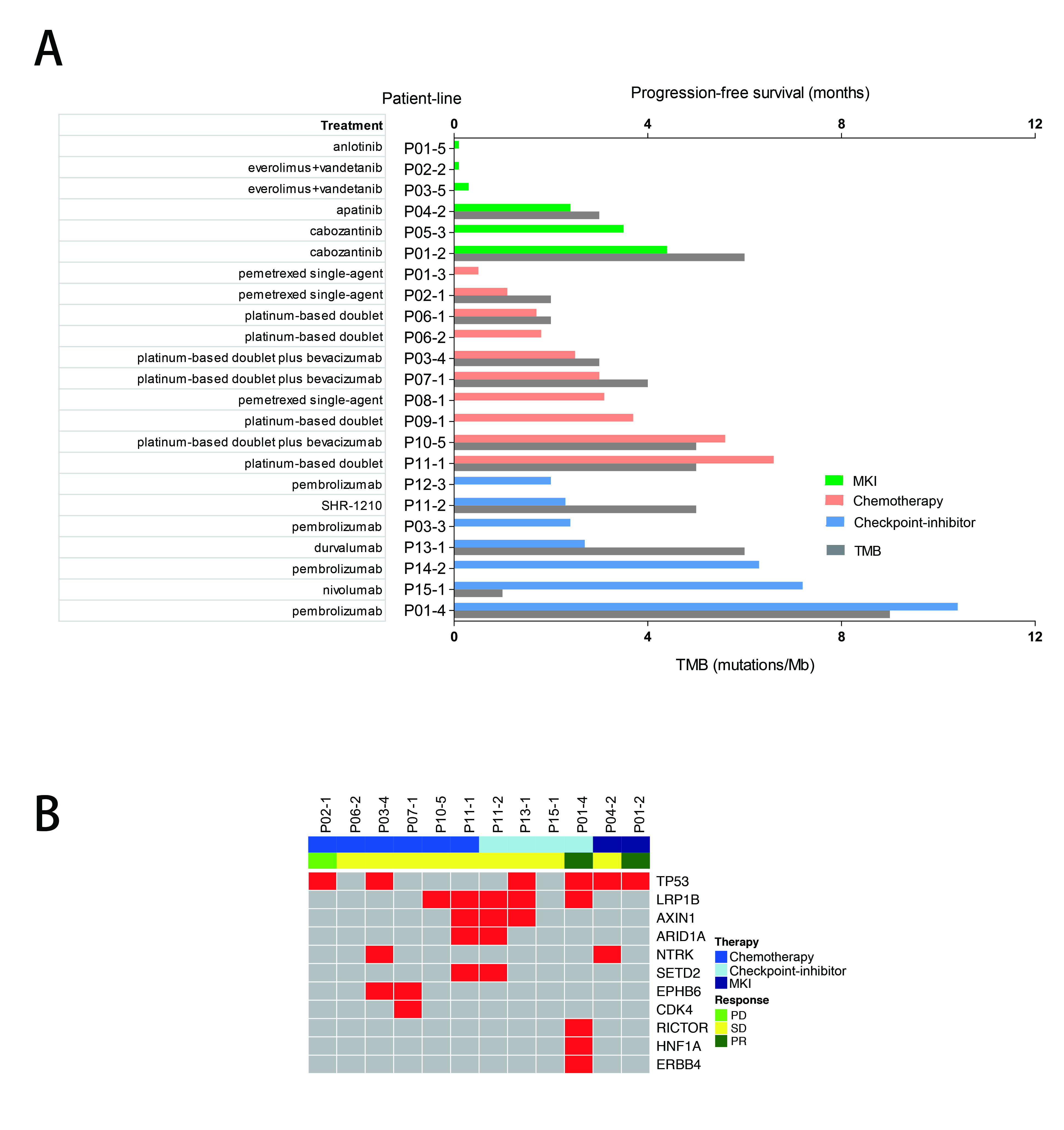
We confirmed relatively low PFS in advanced RET-rearranged NSCLC with MKIs reported in previous studies. But further investigation is warranted. Treatment with checkpoint-inhibitors seemed to encouragingly prolong PFS but a larger group of patients is needed to draw a definite conclusion.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.12 - Small Cell Lung Cancer/NET (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 978)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.12-10 - Immunogenomic Characteristics of SCLC and LCNEC Redefined Molecular Subgroups (ID 12577)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Xu-Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
While small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) are distinct classes of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas, the differential diagnosis between SCLC and LCNEC remains challenging. In fact SCLC and LCNEC overlap in clinical, histopathologic, cytologic, morphologic and genetic characteristics. Molecular profiling with microarray or next-generation sequencing has provided growing evidence suggesting that both SCLC and LCNEC are biologically heterogeneous and a great part of them are borderline neuroendocrine carcinomas falling between typical SCLC and LCNEC. On account of accumulated knowledge, we speculated that immunogenomically characterizing SCLC and LCNEC collectively as one group, or rather morphologically or cytologically separating SCLC from LCNEC has superior clinical value.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We analyzed gene expression profiles of 44 SCLCs, 56 LCNECs and 25 normal lung samples obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus. Unsupervised and supervised analyses were performed to understand molecular characteristics of samples. Pathway and CIBERSORT analyses were employed to obtain immune landscape of SCLC and LCNEC.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Unsupervised clustering with 1189 differentially expressed genes revealed 2 distinct molecular subgroups (G1 and G2) of SCLC and LCNEC, which is not associated with histopathology. Targeted pathway analysis found that G1 was marked by activated IL-17, MAPK and Hippo signaling pathways. In contrast, transcriptional factors, such as ASCL1, INSM1, SOX2, and NKX2-1 were significantly up-regulated in G2, but not in G1. Moreover, in silico analysis of cellular composition and expression of immune genes disclosed unique immunoprofiles for G1 and G2. G1 was characterized by enriched CD4 memory cells, M1 macrophages and activated dendritic cells. While G2 was composed of high fractions of memory B cells and naïve CD4 cells. Strikingly, expression of both immunoinhibitors (IL10, PDL1, IDO1) and immunomodulators (OX40L, BAFF, GITR, IL6), as well as MHC class I and II molecules was higher in G1 compared to that in G2.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
We identified the common intrinsic features and molecular subgroups of SCLC and LCNEC, which are beyond conventional histopathology and better associated with immunogenomics of tumors. Further research is warranted to identify potential clinical implication of SCLC and LCNEC molecular subgroups.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


