Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Caroline Caramella
Author of
-
+
MA08 - Clinical Trials in Brain Metastases (ID 906)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 15:15 - 16:45, Room 203 BD
-
+
MA08.09 - Impact of Brain Metastases in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients (ID 12575)
16:10 - 16:15 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Brain metastases (BM) are frequent in NSCLC. Unfortunately, patients with (untreated) BM are often excluded from ICI trials so that their outcome on ICI is largely unknown..
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Retrospective data collection of all consecutive advanced ICI treated NSCLC patients in 6 centers (5 French, 1 Dutch) (nov 2012 – march 2018). Active BM was defined as non-irradiated new and/or growing lesions on brain imaging < 6 weeks before ICI start. Progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and site of progression on ICI was collected.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
945 patients included: 63% male, 83% WHO PS 0-1, median age 64 years, 73% non-squamous, 4% targetable driver mutations, 33% known PD-L1 (65% ≥1% expression). ICI treatment was median 2nd line (range 1-12), 94% had monotherapy PD-(L)1 inhibition. 241 patients (26%) had BM, 68% had previous cranial irradiation, 40% had active BM. BM patients were significantly younger than others (61 vs 66 years), had more adenocarcinoma (78 vs 62%), more organs involved (median 3 vs 2), a poorer PS (0-1: 76 vs 85%) and more steroids at baseline (26 vs 9%). Median follow-up: 15 months. Median (95% CI) PFS and OS without and with BM were 2 (2-3) vs 2 (1-2) months and 13 (9-16) vs 9 (7-13) months, respectively. In multivariate analysis, > 2 metastatic sites, PS ≥2 and steroids use were associated with worse PFS and OS, BM were not (table 1). In univariate analysis of BM patients, active BM were not associated with worse outcome compared to stable BM (HR PFS 0.98 (p=0.66), HR OS 0.93 (p=0.92)). Progressing BM patients had more often brain PD and a dissociated response (not specifically brain dissociated) on ICI (40 vs 12% and 13 vs 7%, respectively).
Factor PFS HR (95% CI) p-value OS HR (95% CI) p-value Age > 65 vs ≤ 65 1.02 (0.87-1.20) 0.79 1.11 (0.92-1.34) 0.29 Smoking yes vs no 0.53 (0.41-0.69) <0.001 0.81 (0.59-1.12) 0.20 Histology squamous vs adeno 1.07 (0.89-1.28) 0.78 1.24 (0.99-1.55) 0.12 Nr of organs with metastases > 2 vs ≤ 2 1.28 (1.09-1.50) 0.003 1.48 (1.22-1.80) <0.001 Immuno line > 2 vs ≤ 2 1.11 (0.94-1.30) 0.22 1.10 (0.91-1.33) 0.34 WHO PS 0-1 vs ≥2 2.14 (1.75-2.62) <0.001 3.48 (2.78-4.36) <0.001 Use of corticosteroids yes vs no 1.36 (1.10-1.69) 0.005 1.31 (1.03-1.68) 0.03 BM yes vs no 1.05 (0.88-1.26) 0.58 0.96 (0.77-1.19) 0.70
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
BM, treated or active, do not negatively impact outcome on ICI although BM failure is more common in these patients.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA16 - Novel Mechanisms for Molecular Profiling (ID 917)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 203 BD
-
+
MA16.09 - Feasibility, Clinical Relevance of ALK/ROS1 Fusion Variant Detection by Liquid Biopsy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 13492)
14:30 - 14:35 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Liquid biopsy offers an alternative non-invasive approach to reflect the tumor genomic landscape of NSCLC patients; however, the potential of liquid biopsies for ALK/ROS1 fusion detection is poorly described. Herein, we evaluated an amplicon-based NGS assay for ctDNA detection of ALK and ROS1 fusions in a large cohort of ALK and ROS1 NSCLC patients and correlation of variants with clinical data.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
ALK- and ROS1-translocated advanced NSCLC patients, were prospectively enrolled from October 2015 to April 2018 in 9 French institutions. ALK or ROS1 positivity was as confirmed by immunochemistry and FISH or RNAseq. ALK (EML4 variants v1, v2, v3), ROS1 (CD74, SLC34A2, SDC4 and EZR) fusions, and mutations in a panel of 36 NSCLC-associated genes were investigated in ctDNA using InVisionFirst™ (Plagnol V PLoS ONE, 2018).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 120 patients were included: 96 ALK and 24 ROS1. 30 samples were collected from patients who were TKI-treatment-naive, 257 during follow-up and 73 at progressive disease (PD) under TKI. The median age was 55 years-old (range 23-75); most patients were female (57%) and had a non-smoking history (59%). At diagnosis, 20% of patients presented with brain metastasis. All patients received at least 1 ALK-TKI (median: 1.6; range:1-6).
Preliminary results are available for the first 54 patients: 21 at diagnosis and 33 at PD under TKI. ALK/ROS1 fusions were detected in 13/21 patients (62%) at diagnosis: 12/20 ALK-fusions (7 v1, 2 v2 and 3 v3) and in 1/1 ROS1-fusion (CD74-ROS1). No fusion was detected in 8 patients, which may be due to partner genes or variants not covered by this panel. However, 5 of these 8 patients had exclusive thoracic or brain PD.
Liquid biopsies collected at the radiographic evaluation under therapy revealed complete ctDNA clearance of the fusion when patients experienced PR (n=4). In samples at PD, fusion was detected in 44% of patients (24/55) with evidence of acquired resistance in patients both positive and negative for fusion.
Results for the remaining samples, correlation between fusion variant and survival, fusion variant and mechanism of resistance will be presented at the Congress.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Our results suggest that ctDNA profiling is a promising non-invasive tool for identification of ALK/ROS1 fusions and monitoring of response in advanced NSCLC patients. Systematic identification of the fusion partner may help to better understand the heterogeneity and evolution (sensitivity profile to targeted inhibitors and associated-mechanisms of resistance) of NSCLC driven by ALK and ROS1 rearrangement.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 933)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 4
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-07 - Immune-Related Pneumonitis in NSCLC Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI): Impact of Previous Thoracic Radiotherapy (ID 12805)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Pneumonitis is a potentially lethal side effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), occurring in 1–5% of patients enrolled in clinical trials. Little is known about the interactions between ICI and previous thoracic radiation. This is the aim of the present study.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Between December 2012 and November 2017, 318 consecutive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients received ICI in our Institution and their charts were retrospectively analyzed. Primary endpoint was to determine whether previous radiotherapy had an effect on pulmonary toxicity. Pulmonary toxicity was retrospectively assessed by Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Median follow-up was 32.8 months [95%CI: 5-190]. Median age at the start of ICI was 63 years. 205 patients (64,5%) were males, 103 (32,4%) smokers and 250 (78,6%) with PS ≤1; 206 (64,8%) had adenocarcinoma and 76 (23,9%) squamous; 79 (24,8%) were KRAS mutated, 18 (5,5%) EGFR mutated and 5 (1,6%) ALK positive. PDL1 was ≥ 1% by immunohistochemistry in 86 (27%), negative in 37 (11,6%) and unknown in 196 (61,3%) patients. ICI treatment was median 3rd line (range: 1-12), 89,4% monotherapy PD-(L)1 inhibition.
72 patients (22,6%) received a thoracic RT: 62 out of the 72 RT patients (87,5%) were irradiated with a curative intent. 53 patients (73,6% of the RT patients) received thoracic 3D-conformal RT or intensity modulated RT (normo- or mildly hypofractionated), whereas 9 received SBRT.
16,7% of the RT patients (12/72) showed a G1-4 immune-related pneumonitis (with a G=>3 of 11,1%), whereas for never-irradiated patients the G1-3 rate of immune-related pneumonitis was 2,4% (6/246), with only 1 G3 toxicity observed and no G>4 (t-test, p 0,001).
Median interval between the onset of the immune-related pneumonitis and the end of the RT was 22,4 months.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
NSCLC patients treated with ICI may be at higher risk of developing immune-related pneumonitis when previously treated with curative-intent thoracic RT.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-18 - Immunosenescence Correlates with Progression upon PD-(L)-1 Blockade (IO) in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (aNSCLC) Patients. (ID 14074)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Immunosenescence is a progressive remodeling of immune functions with a multifactorial etiology (i.e. aging, chronic inflammation, cancer). Although a CD28-CD57+KLRG1+ phenotype on peripheral T-lymphocytes is a potential hallmark of immunosenescence, the characterization of such phenotype in IO-treated NSCLC patients and the correlation with clinical characteristics and benefit from immunotherapy are unknown.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
A senescent immune phenotype (SIP) defined as a percentage of circulating CD8+CD28-CD57+KLRG1+ T-lymphocytes was assessed by flow cytometry (FC) on fresh blood samples from IO-treated aNSCLC patients (03/2017–04/2018). A log-rank maximization method was used to identify a SIP cut-off level and dichotomize patients accordingly. The objective was to correlate SIP with clinical characteristics and RECIST response by univariate logistic regression analysis.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
39 aNSCLC patients were evaluable for SIP before IO: 38% ≥ 65 years, 87% non-squamous, 38% KRAS mutated, 54% with PD-L1 expression ≥1%, 13% chemotherapy naïve. Among 30 patients evaluable for IO response, 53% had progression (PD), 27% stability (SD), 20% partial response (PR). Median PFS was 1.9 months (95% CI 1.5; 2.5). OS was not calculated due to the short follow-up [6 months (95% CI 4-11)]. SIP (% CD28-CD57+KLRG1+) median value on circulating CD8+ lymphocytes was 15.26% (min 1.87%, max 56.28%). Overall, 13 (33%) of 39 patients had >22.25% CD8+ lymphocytes with a CD28-CD57+KLRG1+ phenotype, being classified as SIP+. SIP status did not correlate with age, IO-baseline patients’ characteristics or chemotherapy exposure. Among patients evaluable for IO response, only 1 (10%) of 10 SIP+ experienced disease control (PR/SD), compared to 13 (65%) of 20 SIP- patients; similarly, PD rate was significantly higher in SIP+ compared to SIP- patients (90% vs 35%, p=0.007) (Figure).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion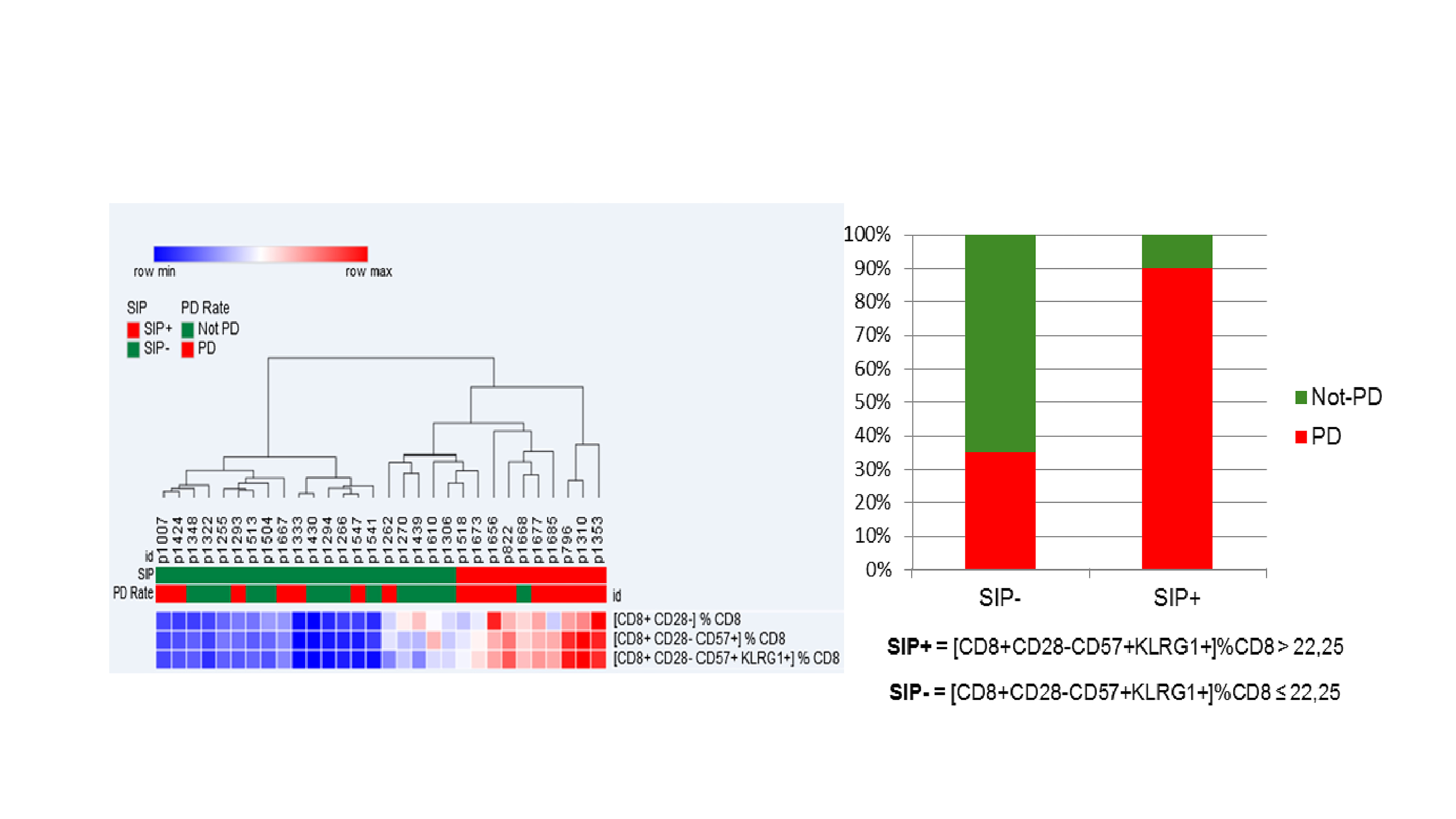
Immunosenescence, monitored by FC measurement of 3 surface molecules on circulating CD8 + lymphocytes, is observed in 33% of aNSCLC patients, is independent of age and correlates with lower IO disease control rate.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-19 - Efficacy of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Leptomeningeal Metastases. (ID 13820)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Leptomeningeal dissemination (LM) in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is usually associated with dismal prognosis. However, survival data and optimal management of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) in EGFR-mutated (EGFRm) patients (pts) are unknown.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Pts with EGFRm NSCLC with LM treated in 2 institutions were included. Clinical, pathological and radiological data were retrospectively collected. We performed overall survival (OS) analysis from LM diagnosis. We assessed survival, clinical response rate (CRR) and disease control rate (DCR; stable disease > 2 months or clinical response) in patients who received a subsequent TKI after experiencing LM progression with first-line TKI.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Seventy pts were included between Apr. 2003 and Feb. 2018. Median age was 54 [26-79], 60 (85%) were non-smokers, 51 (73%) female and median number of prior systemic treatments before LM diagnosis was 2 [1-7].
Median OS from LM diagnosis was 7 months (m) [95% CI 6-9], with a 1 year-OS of 29%. Pts received a median of 2 [1-6] lines of subsequent systemic therapy and 19 had additional intrathecal treatment.
At first LM progression, 40 pts received subsequent TKI treatment with a median PFS of 3m [95% CI 2-not reached]. DCR and CRR were 73% and 38%, respectively. In patients without T790M mutation (N=36), median OS was 7 months [95% CI 4-7] with 2nd-line erlotinib (N=21) and 3 months [2-17] with 2nd-line afatinib or gefitinib (N=5). Eight patients received high-dose erlotinib as 2nd-line treatment after prior erlotinib with a median OS of 3 months [1-3] and a DCR of 75%. Four patients with T790M mutation received 2nd-line osimertinib with a median OS of 10 months [6-10] and a DCR of 100%.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Pts with LM from EGFRm NSCLC have prolonged survival with 1st generation TKI. Second-line erlotinib after LM progression is an efficient approach in T790M-negative pts. Erlotinib dose increase is a suitable strategy in erlotinib-refractory T790M-negative pts.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-67 - Clinical Relevance of ALK/ROS1 Resistance Mutations and Other Acquired Mutations Detected by Liquid Biopsy in Advanced NSCLC Patients (ID 14279)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Liquid biopsies (LB) for circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can be a tool for somatic mutation detectionin NSCLC patients. However, the applicability and clinical relevance of ALK/ROS1 and other acquired mutation detected by LB is poorly described. We evaluated ALK/ROS1 and other acquired mutations detected by ctDNA in a large cohort of ALK/ROS1+ NSCLC patients described to date.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Advanced ALK/ROS1+ NSCLC patients were prospectively enrolled from October 15 to April 2018 in 9 French institutions. ctDNA anlaysis was performed using ctDNA using InVisionFirst™ (36-gene panel) for ALK (EML4 variants v1, v2, v3), ROS1 (CD74, SLC34A2, SDC4 and EZR) fusions, and other somatic mutations.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
120 patients were included: 96 ALK, 24 ROS1. The median prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) received was 2 (0-4). Blood samples (n=402) were collected: tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI)-naive (n=30), during (n=257) or at progression (PD) under TKI (n=73. Prior treated patients received at least 1 TKI (1-6). Preliminary results are available for the first 54 patients; ALK/ROS1 status was confirmed by ALK IHC (39), FISH (56) and RNAseq (2).
ALK mutations were detected in 36% of blood samples at PD to TKI (12/33): 8% (1/13) post-crizotinib and 55% (11/20) post next-generation TKI (F1174/F1174V/D1203N/R1192P/G1202R (6)/F1174L+G1202/G1202R+F1174L+C1156Y). Complex ALK mutations were observed in 2/12 samples (17%) post next-generation TKI (G1202R+F1174L+C1156Y/F1174L+G1202R). Other acquired mutations were found in 36% (12/33) of samples at PD: TP53 (10), NFE2L2 (4), PTEN (2), PI3KCA (1), CDKN2A (1). Complex ALK mut.+ non-ALK mut. were found in 6/33 (18%) samples, 1 post crizotinib (G1269A+R1264K+L1196Q+F1164L+C1156Y+NFE2L2(4)), and 5 samples post next-gen TKI (G1202R+PTEN/G1202R+TP53/F1174L+G1202R+TP53/TP53(2)+D1203N/TP53+R1192P). Non-ALK mut. were exclusive and could explain TKI resistance in 6/33 (18%) samples.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Routine liquid biopsies can assess the heterogeneity of the TKI resistance, detecting ALK resistance and other acquired mutations in pretreated advanced ALK & ROS1 NSCLC patients. This could have an impact on clinical outcomes. The association of ALK mut. and complex ALK mut. +/- other acquired mut. with clinical outcomes will be presented at the congress.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.13 - Targeted Therapy (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 962)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.13-24 - Prospective Efficacy of Osimertinib in Circulating Tumour DNA (ctDNA) T790M-Mutant NSCLC Patients (ID 14031)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Liquid biopsy circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis in advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients is an approved tool for molecular profiling and disease surveillance when tissue is not available. Long-term efficacy of osimertinib in patients with the T790M resistance mutation positive detected only by ctDNA (without tissue information) has not been fully validated.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
In a prospective study, EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC patients with acquired resistance to EGFR TKI, in whom a repeat tissue biopsy was not feasible, were assessed for ctDNA T790M mutational status using InVisionSeqTM. T790M-positive NSCLC patients received osimertinib (80 mg daily; extended access program or approval) at RECIST progression. The objectives were to assess: proportion of patients with acquired ctDNA-T790M positive; overall survival (OS) of the overall EGFR-mutant population as well as OS comparison for T790M +ve/-ve. Also, for those T790M-positive NSCLC patients who received osimertinib in a real world data we assessed: response rate (RR) according to RECIST 1.1 by investigator and progression free survival (PFS), calculated from the date of osimertinib initiation until the date of progression or death (whichever came first), or the date of last follow-up are also reported.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
We recruited 82 patients (71% female, median age 64 years, 72% Del19 EGFR mutation, 71% never-smokers). The ctDNA T790M mutation was detected in 55% (N=45) of NSCLC patients. Median OS of EGFR-mutant population was 38.2 months (mo.). According to T790M status, median OS was 41.2 months and 30.4 mo. for T790M-positive and T790M-negative NSCLC patients, respectively. Both cohorts had already received a median of 3 previous treatment lines. In 40 T790M-positive NSCLC patients who receive osimertinib, RR was 55% (PR: 55%, SD 27.5% and PD: 12.5%) and median PFS of 8.5 mo. Median OS on osimertinib among 10 patients with brain and/or leptomeningeal metastases at baseline was of 13.4 months.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
In patients with acquired resistance to first- or second-generation EGFR TKIs, ctDNA T790M detection by InVisionSeq™ is equivalent to what has been reported in tissue biopsy. Osimertinib has clinical benefit in patients for which the T790M resistance mutation is detected only through a liquid biopsy procedure.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.12 - Small Cell Lung Cancer/NET (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 978)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.12-11 - Association of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index (LIPI) with Outcomes for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Diffuse SCLC Patients (ID 14200)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Caroline Caramella
- Abstract
Background
Pretreatment LIPI (Lung Immune Prognostic Index), based on derived NLR (neutrophils/[leucocytes-neutrophils] ratio) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) has been associated with outcomes for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in advanced NSCLC patients. We tested whether LIPI has the same role in diffuse small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Baseline dNLR and LDH and clinical data were retrospectively collected in SCLC patients, treated with ICI (PD1 inhibitor, PDL1 inhibitors +/- CTLA4 inhibitor) from April 2014 to Jan. 2018 (N=66) from 6 European centers. LIPI was calculated combining dNLR and LDH, stratifying 3 risk groups: good (dNLR<3+LDH<upper limit of normal (ULN), intermediate (dNLR>3 or LDH>ULN), poor (dNLR>3+LDH>ULN). The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), and secondary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Fifty-three patients (80%) were males, 58 (88%) smokers and all patients had PS ≤1, with median age 63 years (41-82). PDL1 was ≥ 1% by immunohistochemistry in 6 patients, and unknown in 60 patients. The median of prior lines was 1 (0-6). Platinum-based therapy was the prior line in 63 (95%) patients, with ORR of 88%. The median PFS and OS with ICI were 2.7 months (m) [95% CI 1.87-4.43] and 10.3 m [95% CI 5.8-12.6]. dNLR was greater than 3 in 16 (25%) and LDH> Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) in 33 (50%) patients. Based on both, LIPI stratified the population in 3 groups: 26 patients as good (40%), 29 (45%) as intermediate and 10 (15%) as poor LIPI risk groups. LIPI was an independent factor for OS (HR 2.77, 95% CI 1.07-7.14, P=0.03) and PFS (HR 3.13, 1.37-7.16, P=0.01). Median OS for good, intermediate, and poor risk groups were 11.4 m [95% CI 5.5-27.3], 11 m [95% CI 6.8-not-reached (NR)] and 2.3 m [95% CI 0.7-NR], respectively (P=0.004). Median PFS for good, intermediate, and poor risk groups were 3 m [95% CI 1.9-12.6], 2.8 m [95% CI 1.6-6.0 and 1.2 m [95% CI 0.47-NR], respectively (P=0.004).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Baseline LIPI poor risk group is associated with poor outcomes for ICI in diffuse SCLC patients. LIPI effect in a validation cohort is currently evaluated.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


