Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Jack Lee
Author of
-
+
MA19 - Genomic Markers of IO Response (ID 922)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Immunooncology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 15:15 - 16:45, Room 201 BD
-
+
MA19.10 - Impact of STK11/LKB1 Genomic Alterations on Clinical Outcomes with Chemo-Immunotherapy in Non-Squamous NSCLC (ID 14295)
16:15 - 16:20 | Author(s): Jack Lee
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Chemo-immunotherapy with pemetrexed/carboplatin/pembrolizumab represents a standard of care for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC, irrespective of tumor cell PD-L1 expression. Genomic determinants of response to chemo-immunotherapy in NSCLC have not been reported thus far. We previously identified STK11/LKB1 alterations as a major genomic driver of de novo resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy in NSCLC (Skoulidis et al., Cancer Discovery, 2018). Here, we examine the impact of STK11/LKB1 mutations on clinical outcomes with chemo-immunotherapy with pemetrexed/carboplatin/pembrolizumab.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC that received at least 1 cycle of pemetrexed/carboplatin/pembrolizumab at MD Anderson Cancer Center, were alive for ≥14 days thereafter and had available next generation sequencing- based comprehensive tumor genomic profiling were eligible. Response assessment was based on RECIST1.1. PD-L1 expression on tumor cells was evaluated using the FDA-approved 22C3 pharmDx assay. All patients consented to collection of clinical and molecular data as part of the GEMINI protocol.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Among 49 eligible patients (median age 61 years, 51% female, 96% adenocarcinoma histology, 34.7% KRAS-mutant) the objective response rate to pemetrexed/carboplatin/pembrolizumab was 51% (25/49) for the overall population. The disease control rate (PR+SD≥ 6 months) differed significantly between STK11/LKB1-mutant and STK11/LKB1-wild-type tumors (31.3% vs 72.7%, P=0.011, two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). The objective response rate was 31.3% for STK11/LKB1-mutant and 60.6% for STK11/LKB1 wild-type tumors (P=0.07, two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). 37.5% (6/16) of STK11/LKB1-mutant tumors exhibited progressive disease as best overall response to chemo-immunotherapy compared with 6.1% (2/33) STK11/LKB1-wild-type tumors (P=0.01, two-tailed Fisher’s exact test). Patients bearing STK11/LKB1-mutant tumors exhibited shorter progression-free survival with chemo-immunotherapy (median PFS 4.4 months vs 11.0 months, P=0.039, log-rank test). STK11/LKB1-mutant tumors were less likely to be positive for PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 TPS ≥ 1%), although the difference did not reach statistical significance (43.8% vs 72%, P=0.1, two-tailed Fisher’s exact test).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
STK11/LKB1 genomic alterations are associated with inferior clinical outcomes with chemo-immunotherapy in non-squamous NSCLC, with response rates comparable to those previously reported for platinum doublet chemotherapy alone. Assessment of STK11/LKB1 status may help refine treatment approaches in non-squamous NSCLC.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
OA03 - Advances in Lung Cancer Pathology (ID 897)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Pathology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 10:30 - 12:00, Room 205 BD
-
+
OA03.05 - Characterization of the Immunologic Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity in Early Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Multiplex Immunofluorescence (ID 13334)
11:15 - 11:25 | Author(s): Jack Lee
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Recurrence of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is associated with genetic and epigenetic intra-tumor heterogeneity (ITH). The interaction between malignant cells, stromal cells, and tumor-associated immune-cells (TAICs), such as T-cell lymphocytes (TCLs) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), is important for progression of NSCLC and the characterization of the immunologic ITH might be relevant to predict recurrence in surgically treated patients at early stages of NSCLC. The aim of this study was to characterize the immunologic ITH of primary NSCLC tumors at early stages using image analysis and multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) approaches.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Eight cases of stage IA and 8 cases of stage IB surgically resected NSCLC (11 adenocarcinomas, ADCs; and 5 squamous-cell carcinomas, SCCs) with a history of early recurrence were selected for this preliminary analysis. FFPE blocks were obtained and consecutive sections were stained with two panels of mIF for immune profiling, panel 1: pan-cytokeratin (AE1/AE3), PD-L1, PD-1, CD3, CD8, and CD68; panel 2: AE1/AE3, CD3, CD8, granzyme-B (GB), CD45RO, and FOXP3. Three not adjacent, intra-tumor regions (3mm2 each) per case were randomly selected after gridding the whole tumor section. A total of 41 intra-tumor regions were scanned by Vectra multispectral-microscope and analyzed using InForm-software. TAICs were quantified in epithelial and stromal compartments from each intra-tumor region. G-Cross AUC (area under the curve) was computed for specific intervals of distances between TAICs and malignant cells. Median distance between TAICs and malignant cells within each region was calculated.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
The median density of TCLs and TAMs were 1527 cells/mm2 and 635 cells/mm2, respectively, without significant differences between histologic subtypes. TCLs were predominantly concentered in stromal compartment (median, 2222 cells/mm2) compared with epithelial compartment (median, 332 cells/mm2). Percentage and density of TCLs and TAMs varied 4 and 8 times, respectively, between cases and regions. Non-cytotoxic T-cells and inactive cytotoxic T-cells were the most prevalent phenotypes. Higher density of TAMs and antigen-experienced TCLs were observed in stage IB than stage IA.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Characterization of immunologic ITH of NSCLC is able by mIF and image analysis with FFPE tumor tissue. There is variability of TAICs densities between regions from the same tumor and different subpopulations were observed. TAMs and exhausted T-cells were more prominent in stage IB (tumor >3cm) suggesting these cells may play an important role in recurrence. Ongoing studies with a larger cohort and comparison with non-recurrent surgically treated patients are warranted. Supported by CPRITRP160668 and UTLungSPORE grants
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-87 - Profiling the Symptom Burden of Patients with Metastatic NSCLC Receiving Either Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy: Real-World Data (ID 13348)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Jack Lee
- Abstract
Background
An understanding of the patient experience is lacking for newly developed cancer treatments, such as targeted therapies. We profiled the patient-reported outcome (PRO)-measured symptom burden experienced by patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) during 6 months of conventional chemotherapy or targeted therapy.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
During 2017, patients with mNSCLC at a single institution were recruited and completed the MD Anderson Symptom Inventory lung cancer module (MDASI-LC) at clinic visits. The MDASI-LC assesses the severity of 13 core and 3 lung-cancer-specific symptoms and 6 interference items on 0‒10 scales (0=no symptom or interference, 10=worst imaginable symptom or complete interference). Descriptive statistics for MDASI-LC scores over 6 months of treatment were summarized. Symptom trajectories for the chemotherapy patients versus the targeted-therapy patients were compared via linear mixed-effects models.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Of 65 patients receiving chemotherapy and 27 receiving targeted therapy, the targeted-therapy group had more women (74% vs. 49%, P=0.029) and younger patients (57.6±12.2 vs. 64.2±9.9 years, P=0.012). Before treatment, both groups reported similar symptom burden, although sadness was worse in the targeted-therapy group (2.4±1.6 vs. 0.8±1.5, P=0.021). During the first 60 days of treatment, patients receiving chemotherapy reported significant increase in pain (estimate (est)=0.03, P=0.037) and interference with walking (est=0.04, P=0.025). Compared with those receiving chemotherapy, patients receiving targeted therapy experienced significantly less severe pain (est=‒1.17, P=0.024), fatigue (est=‒1.16, P=0.019), and shortness of breath (est=‒1.23, P=0.028) and less interference with walking (est=‒1.23, P=0.042) (figure 1). More severe dry mouth was reported by patients undergoing targeted therapy (est=1.17, P=0.027).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
This real-world data demonstrates that, compared with conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapy correlates with less impairment of physiological condition and functioning in patients with mNSCLC. Additional follow up will confirm and expand these findings about the patient experience relative to treatment response.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 967)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.01-109 - Real-World Patient-Reported Outcome Assessment of Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ID 12213)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Jack Lee
- Abstract
Background
Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs) provide information on patient treatment experience. We have established a real-world Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Holistic Registry (ANCHoR) to understand how the advent of immunotherapy impacts treatment choice, clinical outcomes, and PROs of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC). The aim of this analysis is to report early results of baseline symptom status and quality of life among mNSCLC patients using the MD Anderson Symptom Inventory lung cancer module (MDASI-LC) and EuroQol-5D 5-level version (EQ-5D-5L).
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
During 2017, patients with mNSCLC at a single institution were enrolled in ANCHoR and completed the PRO questionnaires at clinic visits. MDASI-LC consists of thirteen core and three lung cancer-specific symptom severity questions, and six interference items rated on 0-10 scales (0 = no symptom or interference, 10 = worst imaginable symptom or complete interference). EQ-5D-5L captures five health state dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression rated on a five-level scale (1= no problems, 5= extreme problems). A single visual analogue scale (VAS) on EQ-5D-5L records patient self-rated health between ”best imaginable” (100) and “worst imaginable” (0) health state. Descriptive statistics for PRO scores at baseline are summarized.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Forty-two patients completed baseline PROs before the start of therapy. Mean patient age was 63 years and 45% were males. For MDASI-LC, the mean scores for the core symptom, lung cancer-specific symptom, and interference subscales at baseline were 2.2 (standard deviation [SD] = 2.80), 2.1 (SD = 2.80), and 2.8 (SD = 3.10), respectively. Fatigue was the most severe symptom reported at baseline (mean = 4.1, SD = 3.01), followed by shortness of breath (mean = 3.2, SD = 2.81) and pain (mean = 3.19, SD = 3.00). The highest percentages of patients reporting moderate to severe symptom levels (score of ≥5) were 38% for fatigue, 33% for pain, 31% for drowsiness, 29% for shortness of breath and disturbed sleep, and 26% coughing. For EQ-5D-5L, 91% of patient reported problems with self-care, 81% with mobility, 48% with usual activity and anxiety, and 33% with pain. Mean EQ-5D VAS was 73.9 (SD = 18.2).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Prior to the start of treatment, fatigue, pain, drowsiness, disturbed sleep, and coughing were the most common symptoms with fatigue, shortness of breath, and pain being the most severe. Additional follow up will confirm and expand these findings and will also allow us to examine change in PROs after first-line treatment is administered.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P3.01-91 - Computing the Impact of Immunotherapy on the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Therapeutic Landscape (ID 12209)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Jack Lee
- Abstract
Background
The Advanced Non-Small Lung Holistic Registry (ANCHoR) is established to examine the real-world impact of immunotherapy on choice of treatment, clinical outcomes, and patient reported outcomes of patients with Stage IV NSCLC.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Stage IV NSCLC patients diagnosed or initiating treatment at MD Anderson from January 1, 2017 are enrolled in the ongoing ANCHoR study. Their demographic, clinicopathological, molecular, and treatment data were populated in a prospective database. Treatment patterns by line and PD-L1 status were summarized in this interim analysis.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
At the time of data cut off (Dec 31, 2017) 182 patients were enrolled in the registry, of which 150 were tested for PD-L1. Number of patients initiating first-, second-, and third-line treatment were 163, 42 and 7, respectively. Of the 30 patients not tested for PD-L1, 10 did not have enough tissue and 8 had actionable mutations.
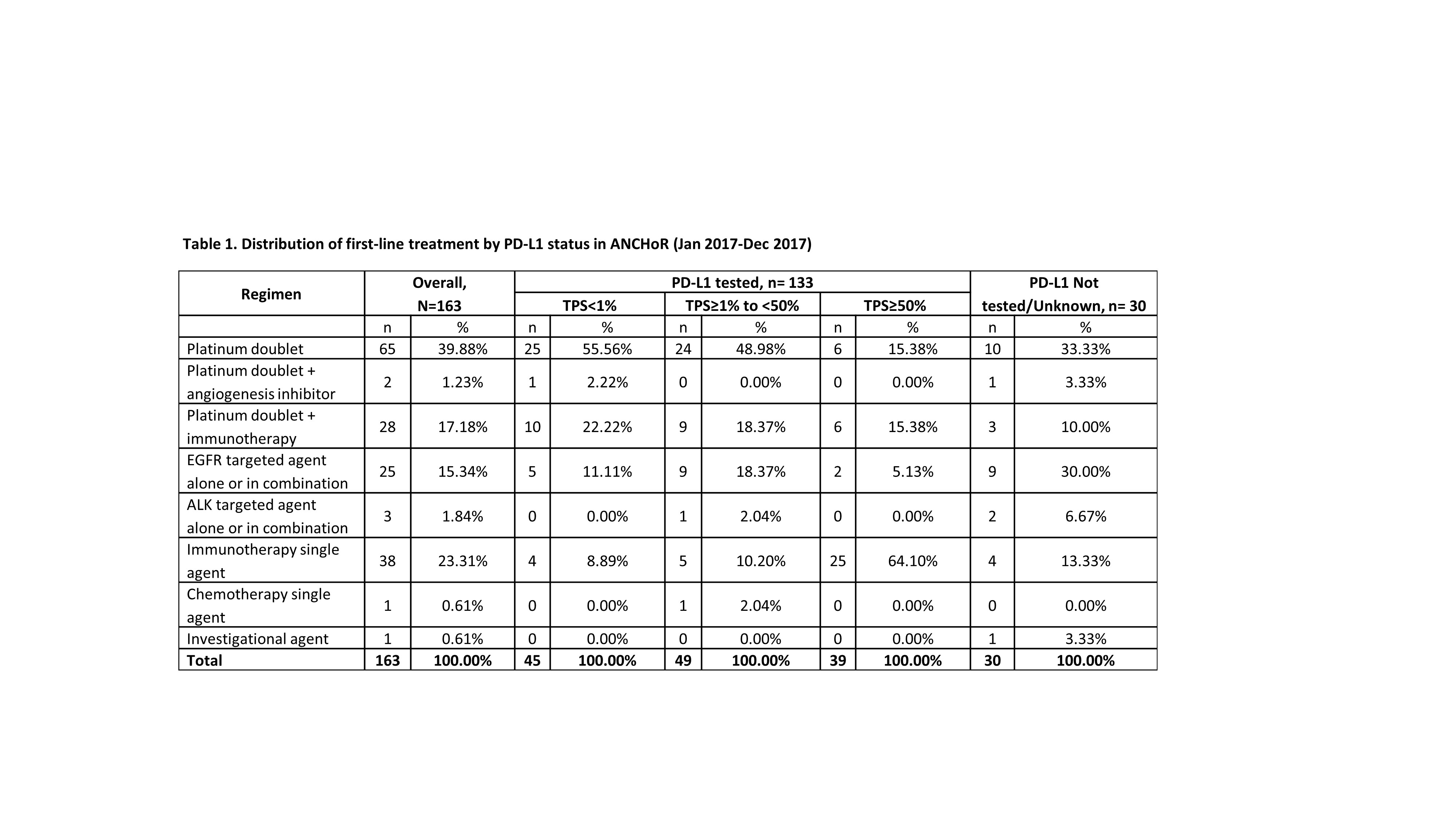
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
The emergence of immunotherapy has had a dramatic impact on the first-line treatment of patient with advanced NSCLC. As of December, 2017 up to 41% of patient received immunotherapy either singly (23%) or in combination with chemotherapy. Only 40% of the patients now receive chemotherapy alone. There has been dramatic decrease in the use of chemotherapy with an anti-angiogenesis agent (1.23%). In our dataset 16% of the patients were eligible for targeted therapy as initial treatment.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


