Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Chao Zhang
Author of
-
+
JCSE01 - Perspectives for Lung Cancer Early Detection (ID 779)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Joint IASLC/CSCO/CAALC Session
- Track: Screening and Early Detection
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/23/2018, 07:30 - 11:15, Room 202 BD
-
+
JCSE01.22 - Differential Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Dramatic and Gradual Progression in NSCLC Patients with Intrathoracic Dissemination (ID 14713)
11:15 - 11:15 | Author(s): Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Lung cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease with diverse clinical outcomes. The pleural cavity is a frequent metastasis site of proximal lung cancer. Better understanding of its underlining molecular mechanisms associated with dramatic and gradual progression of pleural metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is essential for prognosis, intervention and new therapy development.We performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) of matched primary lung adenocarcinoma and pleural metastatic tumors from 26 lung cancer patients with dramatic progression (DP, n=13) or gradual progression (GP, n=13). Somatic alterations at both genome-wide level and gene level were detected. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and multivariate Cox regression models were applied to analyze the association between different somatic alterations and clinical parameters.We first analyzed the differences in somatic alterations between AP and RP group in the primary tumors, and identified higher somatic copy number alteration (SCNA) level in DP group compared to GP group, which is significantly (p=0.016) associated with poorer progression-free survival (PFS). More specifically, patients with chromosome 18q loss in the primary tumor showed a trend (p=0.107) towards poorer PFS. PTEN (p=0.002) and GNAS (p=0.002) mutations are enriched in the primary tumors of DP group, and are associated with poorer PFS. Furthermore, pleural metastatic tumors harbor a relatively higher level of mutation burden (p=0.105) and significantly increased SCNA (p=0.035) compared to the primary tumors.NSCLC patients in the attenuated progression group have more stable genomes. High level of genomic instability, GNAS and PTENmutations, as well as chromosome 18q loss are associated with rapid progression. a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419
-
+
MA24 - Genomic Evolution, KEAP 3 and More Non-Coding RNA (ID 928)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Biology
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 10:30 - 12:00, Room 205 BD
-
+
MA24.01 - Genomic Evolution Trajectory Depicts Invasiveness Acquisition from Pre-invasive to Invasive Adenocarcinoma (ID 11840)
10:30 - 10:35 | Presenting Author(s): Chao Zhang
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Accumulation of molecular abnormalities may depict evolution trajectories of tumor initiation and development. However, the genomic profile of early stage adenocarcinoma and molecular mechanism of invasiveness acquisition from pre-invasive to invasive adenocarcinoma remains barely explored.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We simultaneously collected 20 patients with adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) (n=5), minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) (n=5) and stage IA adenocarcinoma (lepidic/acinar predominant) (n=10). Whole exon sequencing (WES) was performed in pre-invasive adenocarcinoma with multi-region specimens and stage IA adenocarcinoma. Analysis of genomic alteration among different pathological status was performed and tumor mutation burden (TMB) was calculated as well as six mutation types individually. Enriched pathways of each pathology were measured through KEGG analysis.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Baseline characteristics was generated through heatmap with smokers (2/20, 10%) and EGFR mutation (13/20, 65%) among whole population. AIS/MIA indicated much lower number of mutations than invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC) while TMB revealed the same trend without statistical significance. Multi-region sequencing showed high heterogeneity of single nucleotide variation (SNV) in AIS and MIA. Unique SNV presented dominant proportion in initial status. Cluster analysis showed higher copy number variation in AIS/MIA than IAC with cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) enriched in AIS/MIA while variety pathway enrichment in IAC through KEGG analysis. C>A transversions held major proportion in early stage adenocarcinoma and a significant increase in the proportion of C>T and C>G mutation was exhibited when evolving into IAC.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Intratumor heterogeneity may occur in the very beginning of adenocarcinoma. High copy number variation was dominant event for AIS/MIA while higher tumor mutation burden was seen in IAC. Tobacco signature encompassing C>A transversions dominates the early development of adenocarcinoma and APOBEC signature may play a potential role in acquisition of cancer invasiveness.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P2.12 - Small Cell Lung Cancer/NET (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 961)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.12-11 - A Prognostic Model Integrating Immunohistochemistry Markers for Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ID 11828)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC) is a subtype of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma (HGNEC) with poor prognosis. We tend to build a prognostic nomogram and illustrate the failure pattern of first line etoposide/Irinotecan with paclitaxel (EP/IP) treatment.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
250 ED-SCLC patients received first line EP/IP treatment were enrolled. Cox regression analysis was used to identify the prognostic factors to establish nomogram. The predictive accuracy of nomogram was evaluated by concordance index (C-index). Further stratification based on Ki67 and brain metastasis was performed through X-tile plot and Kaplan Meier.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Cox regression analysis indicated brain metastasis as the prognostic factor and we further selected NSE, gender, TTF-1, Syn, tumor size and smoking status under clinical consideration for nomogram. C-index of nomogram suggested 0.65 with moderate predictive effect. Subgroup analysis showed patients with Ki67 lower than 85% had poorer prognosis than those over 90% (HR 0.59, 95%CI 0.39-0.92, p=0.02). Those without brain metastasis at baseline achieving partial response (PR)/complete response (CR) suggested no prognostic significance in brain progression compared to other progression group.
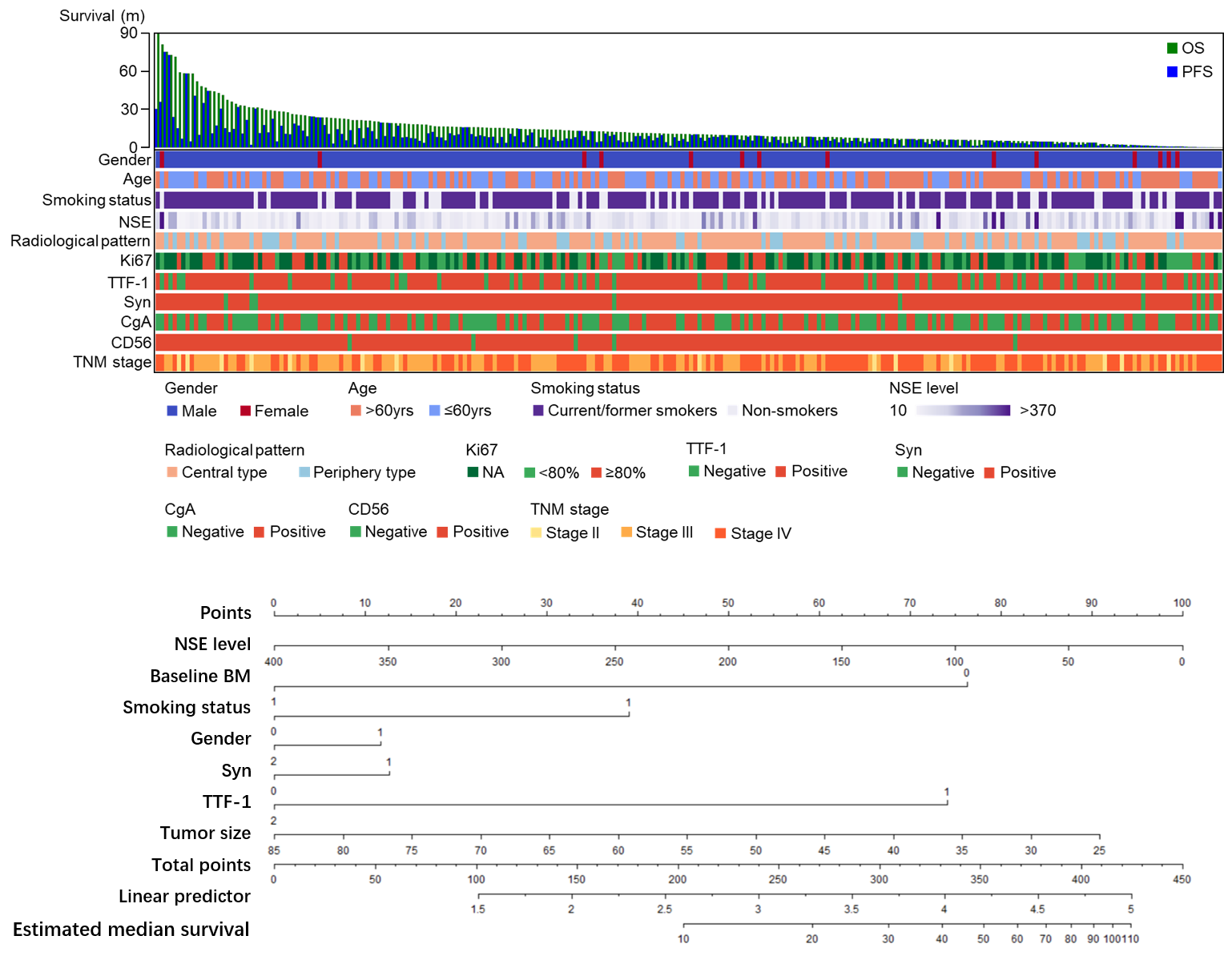
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Established nomogram could well predict prognosis in ED-SCLC. Ki67 might play a potential role in prognosis of SCLC. Application of preventive cranial irradiation might be challenged in ED-SCLC patients without brain metastasis.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P2.17 - Treatment of Locoregional Disease - NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 966)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.17-32 - Dynamic Monitoring Before and After Neo-Adjuvant Crizotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Brief Report (ID 11829)
16:45 - 18:00 | Presenting Author(s): Chao Zhang
- Abstract
Background
Neo-adjuvant therapy has been considered as an optional approach for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. While targeted therapy has been widely applied in advanced NSCLC, neo-adjuvant targeted therapy remains poorly explored.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We describe four ALK-positive patients with pathological confirmed locally advanced NSCLC receiving neo-adjuvant Crizotinib. All patients received Crizotinib at a starting dose of 250mg twice daily for 1-3 months before surgical resection. One patients provided dynamic monitoring before and after neo-adjuvant therapy through next generation sequencing of plasma and tissue.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Three patients were partial response without apparent adverse event before surgery while one received pathological complete response to neo-adjuvant Crizotinib but suffering from grade 4 hepatic damage. One of them had disease recurrence but achieved long duration of response (PFS=15m) through first-line Crizotinib. Dynamic monitoring with both plasma and tissue indicated simultaneously decrease of sensitive ALK-signaling in a patient with partial response (-51%) and no ALK-dependent resistant variants were captured.


8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Neo-adjuvant Crizotinib may be feasible and well-tolerated in locally advanced disease for complete resection. Crizotinib prior to surgery may provide thorough elimination of circulating molecular residual disease and it did not influence the response of reusing Crizotinib in first-line setting.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


