Virtual Library
Start Your Search
Hai-Yan Tu
Author of
-
+
JCSE01 - Perspectives for Lung Cancer Early Detection (ID 779)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Joint IASLC/CSCO/CAALC Session
- Track: Screening and Early Detection
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/23/2018, 07:30 - 11:15, Room 202 BD
-
+
JCSE01.09 - Cluster Trial: Ph2 Biomarker-Integrated Study of Single Agent Alpelisib, Capmatinib, Ceritinib and Binimetinib in advNSCLC (ID 11678)
10:15 - 10:25 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Several genetically altered signaling pathways have been profiled in NSCLC, enabling advanced management of NSCLC using targeted therapies. This study investigated the therapeutic spectrum of NSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations by allocating patients to treatment arms based on molecular aberrations; targeted therapies alpelisib (PI3Kαi), capmatinib (METi), ceritinib (ALKi), and binimetinib (MEKi) were evaluated.The study was based on the umbrella design. Key objectives: investigate feasibility of using one trial for different agents based on biomarker-integrated analysis, assess anti-tumor activity, characterize safety, tolerability and PK profiles of individual agents. Key eligibility criteria: age ≥18 years; ECOG PS ≤2; failed prior treatment/unsuitable for chemotherapy. Documentation of locally determined molecular alterations before treatment allocation was required (alpelisib, 350 mg QD: PIK3CA mutation/amplification; capmatinib, 400 mg BID (tablet): MET IHC overexpression/amplification; ceritinib, 750 mg QD: ALK or ROS1 rearrangement; binimetinib, 45 mg BID: KRAS, NRAS or BRAF mutation).Sixty-six patients with advNSCLC were enrolled (median age 58 years; 65.2% male: alpelisib, n=2; capmatinib, n=16; ceritinib, n=26; binimetinib, n=22). As of Feb 28, 2018, 10 patients in ceritinib and 2 in binimetinib arms were ongoing. Twenty-four patients had confirmed partial responses (36.4%): alpelisib, 0%; capmatinib, 18.8%; ceritinib, 73.1%; binimetinib, 9.1% (Figure). Longest mPFS (14.4 months) was in ceritinib arm. Among the most common treatment-related AEs: alpelisib: malaise, hyperglycemia, dysgeusia; capmatinib: nausea, anemia, peripheral edema, decreased appetite; ceritinib: diarrhea, vomiting, ALT/AST elevation; binimetinib: mouth ulceration, AST, blood CPK increased, rash. Most AEs were grade 1/2.
Objective responses/tumor shrinkage were observed in the study; highest ORR and mPFS were observed with ceritinib, although patient numbers differed between arms. All treatments were well tolerated; no new safety signals were observed. This study demonstrated the feasibility of an umbrella trial and importance of precision medicine in the management of advNSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
MA16 - Novel Mechanisms for Molecular Profiling (ID 917)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Mini Oral Abstract Session
- Track: Advanced NSCLC
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 13:30 - 15:00, Room 203 BD
-
+
MA16.10 - Clinical Utility of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cell-Free DNA for Clarifying Genetic Features of Leptomeningeal Metastases in ALK Rearrangement NSCLC (ID 12142)
14:35 - 14:40 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
- Presentation
Background
Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) were associated with a poor prognosis in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). LM were much more frequent in EGFR mutant patients, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has shown unique genetic profiles of LM in patients harboring EGFR mutations in our previous studies. However, studies in ALK positive NSCLC patients with LM are scarce.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Lung cancer patients with ALK rearrangement were screened from Sept 2011 to Feb 2018 at our institute. Leptomeningeal metastases were diagnosed by MRI or CSF cytology or next-generation sequencing (NGS) of CSF cfDNAs. Paired plasma were also tested by NGS.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
LM were diagnosed in 22 (7.6%) of 288 ALK rearrangement patients with lung cancer. A total of 11 ALK positive patients with LM were enrolled with CSF cfDNA tested by NGS (one case used CSF precipitates instead of CSF cfDNA). Paired plasma were available in 11 patients. Driver genes were detected in 75.0% CSF samples and 45.5% plasma respectively (P=0.214). Max allele fractions were higher in CSF cfDNA than in plasma (40.8% versus 0%, P=0.021). ALK variant 1 (E13:A20) was detected in 3 cases of CSF and paired plasma, respectively. ALK variant 2 (E20:A20) was identified in 5 cases of CSF and 1 paired plasma. Multiple copy number variants (CNV) were mainly found in CSF cfDNA, including EGFR copy number gains. Resistance mutations including gatekeeper gene ALK G1202R was identified in CSF cfDNA with ALK variant 1 and ALK G1269A was detected in plasma. The detection rate of TP53 was 45.4% versus 27.3% in CSF cfDNA and plasma.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
CSF cfDNA was more sensitive than plasma to reveal genetic features of ALK-fusion LM, confirming its role as a liquid biopsy medium for LM in driver gene positive NSCLC.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53Only Members that have purchased this event or have registered via an access code will be able to view this content. To view this presentation, please login, select "Add to Cart" and proceed to checkout. If you would like to become a member of IASLC, please click here.
-
+
P1.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 933)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 2
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/24/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P1.01-55 - Unique Genetic Profiles from Cerebrospinal Fluid Could Predict Survival of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC with Leptomeningeal Metastases (ID 12369)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
Background
Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) are more frequent in NSCLC with EGFR mutations;and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) could reveal the unique genetic profiles of LM in our previous studies, but whether they could predict the overall survival (OS) of LM remains unknown.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with LM were enrolled,and clinical data and genetic profiles detected by Next-generation sequencing were collected. We further drew nomogram with endpoint of OS after LM, then performed index of concordance (C-index) and survival analysis to evaluate predictive role.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
In total, 61 patients were enrolled and all with genetic profiles from CSF. Patents with high copy number variations (CNVs) or harboring CDK6, TP53 exon5 or FGF19 in CSF demonstrated significant poorer OS than those without (Fig. 1). Cox regression analysis indicated CNVs, CDK6,CDKN2A,TP53,MET and NTRK1 as prognostic factors and further selected for nomogram (Fig. 2). C-index of nomogram was 0.743, indicating the moderate predictive effect. In the calibration curves, we scored the patients based on the model, using bisection and trisection methods to divide into low and high points groups; and low, medium and high points groups (Fig. 3), and significant difference were found in both the survival analyses (NA versus 7.47months, P<0.01) and (NA, 10.33 versus 4.43 months, P<0.01) respectively. Patients who received Osimertinib after LM seemed to have longer OS than those who did not (14.5 months versus 7.7 months) but without significant difference(P=0.10); however interestingly, in those with EGFR T790M negative who took Osimertinib after LM by themselves obtained survival benefit than those who did not(NA versus 7.7 months, P=0.04), and the results needed to be validated.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
Unique genetic profiles from CSF could well predict OS of LM. High CNVs, CDK6, TP53 exon5 or FGF19 in CSF in CSF may be related to poor prognosis of LM.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53 -
+
P1.01-97 - Cluster Trial: Ph2 Biomarker-Integrated Study of Single Agent Alpelisib, Capmatinib, Ceritinib and Binimetinib in advNSCLC (ID 12065)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
Background
Several genetically altered signaling pathways have been profiled in NSCLC, enabling advanced management of NSCLC using targeted therapies. This study investigated the therapeutic spectrum of NSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations by allocating patients to treatment arms based on molecular aberrations; targeted therapies alpelisib (PI3Kαi), capmatinib (METi), ceritinib (ALKi), and binimetinib (MEKi) were evaluated.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
The study was based on the umbrella design. Key objectives: investigate feasibility of using one trial for different agents based on biomarker-integrated analysis, assess anti-tumor activity, characterize safety, tolerability and PK profiles of individual agents. Key eligibility criteria: age ≥18 years; ECOG PS ≤2; failed prior treatment/unsuitable for chemotherapy. Documentation of locally determined molecular alterations before treatment allocation was required (alpelisib, 350 mg QD: PIK3CA mutation/amplification; capmatinib, 400 mg BID (tablet): MET IHC overexpression/amplification; ceritinib, 750 mg QD: ALK or ROS1 rearrangement; binimetinib, 45 mg BID: KRAS, NRAS or BRAF mutation).
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Sixty-six patients with advNSCLC were enrolled (median age 58 years; 65.2% male: alpelisib, n=2; capmatinib, n=16; ceritinib, n=26; binimetinib, n=22). As of Feb 28, 2018, 10 patients in ceritinib and 2 in binimetinib arms were ongoing. Twenty-four patients had confirmed partial responses (36.4%): alpelisib, 0%; capmatinib, 18.8%; ceritinib, 73.1%; binimetinib, 9.1% (Figure). Longest mPFS (14.4 months) was in ceritinib arm. Among the most common treatment-related AEs: alpelisib: malaise, hyperglycemia, dysgeusia; capmatinib: nausea, anemia, peripheral edema, decreased appetite; ceritinib: diarrhea, vomiting, ALT/AST elevation; binimetinib: mouth ulceration, AST, blood CPK increased, rash. Most AEs were grade 1/2.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
Objective responses/tumor shrinkage were observed in the study; highest ORR and mPFS were observed with ceritinib, although patient numbers differed between arms. All treatments were well tolerated; no new safety signals were observed. This study demonstrated the feasibility of an umbrella trial and importance of precision medicine in the management of advNSCLC with uncommon molecular alterations.
-
+
P2.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 950)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/25/2018, 16:45 - 18:00, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P2.01-52 - Identification of Leptomeningeal Metastasis-Specific Exosomal miRNA Signatures in Cerebrospinal Fluids of NSCLC Patients (ID 13074)
16:45 - 18:00 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
Background
Leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) is a devastating complication with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. The confirmed diagnosis of LM usually involves neurological evaluation, MRI imaging, and cytopathology analysis of limited tumor cells from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Exosomes are extracellular vesicles in body fluids enriched with microRNAs (miRNAs), which have been implicated to participate in brain metastasis. Here, we aimed to identify LM-specific exosomal miRNA signatures in NSCLC patients to elucidate their potential role in LM mechanism and to predict LM via liquid biopsy.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
Exosomes prepared from CSF and plasma samples of 39 advanced NSCLC patients with (LM+) or without (LM-) LM as well as 12 non-cancer individuals (NC) were underwent small RNA next-generation sequencing. For patients in the LM+ group, paired plasma samples were taken before (PLM+pre) and upon (PLM+post) LM diagnosis. Exosomal miRNA profiles were subjected for differential expression analysis, pathway enrichment analysis, and signature discovery.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the miRNA expression profiles clearly separated CSF samples into LM+ and LM free groups (LM- and NC). Interestingly, these samples were stratified based on their LM status only, regardless of their intraparenchymal metastasis status. In total, 247 (185 up and 62 down-regulated) miRNAs were identified differentially presented in the LM+ CSF exosome samples compared to the LM- and NC groups. Top altered miRNAs include dramatically up-regulated miR-200 family and down-regulated miR-144/451 cluster. Predicted gene targets of these top-regulated miRNAs were significantly enriched in Ras/MAPK/PI3K-AKT signaling, endocytosis pathways, and so on. Promisingly, a signature of five CSF exosomal miRNAs (let-7e-5p, miR-28-3p, miR-375, miR-200a-3p, and miR-486-5p) was identified for classification of LM+ patients with 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Due to the higher background complexity, we only identified one miRNA (miR-24-3p) was significantly up-regulated and one miRNA (miR-92b-5p) was significantly down-regulated in LM+ patients’ plasma-derived exosomes (PLM+pre and PLM+post) compared with the LM free group (PLM- and PNC). However, a combined signature of seven miRNAs (miR-24-3p, miR-223-3p, miR-340-5p, miR-27a-3p, miR-423-5p, miR-2110 and miR-342-5p) from PLM+pre samples was identified for the prediction of future LM with 81% sensitivity and 76% specificity.
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion
NSCLC patients with LM present a remarkably distinct CSF exosomal miRNA signature, which may involve in the progression of LM, and can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for LM. Furthermore, the identification miRNA signature in the pre-LM plasma samples suggests the potential use of liquid biopsy to predict LM for better patient care.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53
-
+
P3.01 - Advanced NSCLC (Not CME Accredited Session) (ID 967)
- Event: WCLC 2018
- Type: Poster Viewing in the Exhibit Hall
- Track:
- Presentations: 1
- Moderators:
- Coordinates: 9/26/2018, 12:00 - 13:30, Exhibit Hall
-
+
P3.01-64 - Preliminary Data of Diverse Therapies in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harbouring RET-Rearrangement (ID 13677)
12:00 - 13:30 | Author(s): Hai-Yan Tu
- Abstract
Background
Activating RET-rearrangement has been discovered to play a crucial role in NSCLC tumorigenesis. However, the lack of specificity narrowed efficacy of multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs) and the optimal treatment remains unknown. In this study, we compared chemotherapy, immunotherapy and MKIs in this group of patients.
a9ded1e5ce5d75814730bb4caaf49419 Method
We retrospectively evaluated the efficacy of these three treatments in advanced, RET-rearranged NSCLC patients between January 2013 and April 2018 at our institution. RET-rearrangements were assessed by Next-generation sequencing (NGS) or any of FISH, IHC, RT-PCR. Treatment data were collected after the patients had been diagnosed with RET-rearranged advanced NSCLC. Progression-free survival (PFS) was measured from treatment start to disease progression, all-cause mortality or last follow up. Median follow-up time was 5.1months. NGS was performed to assess somatic mutation of available samples.
4c3880bb027f159e801041b1021e88e8 Result
A total of 30 patients with RET-rearrangement were investigated in this study. After the diagnosis, 15 patients, genetic profiles confirmed by NGS, received chemotherapy (n=10), checkpoint-inhibitors (n=7) and RET targeted MKI (n=6) with evaluable response. Several patients take any two of these three treatments as different line therapies. The disease control rate of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, MKI group was 70.0%, 71.43% and 50%, respectively. While the median PFS of three groups was 2.50 months, 2.70 months, 0.30 months, respectively, which of no significance. The NGS data of 10 patients showed that RET-rearrangement co-occurred with several other genes, including TP53, NTRK, CDK4, ERBB4. A low mutation burden (mean 4.5 mutations) was observed (Figure 1).
8eea62084ca7e541d918e823422bd82e Conclusion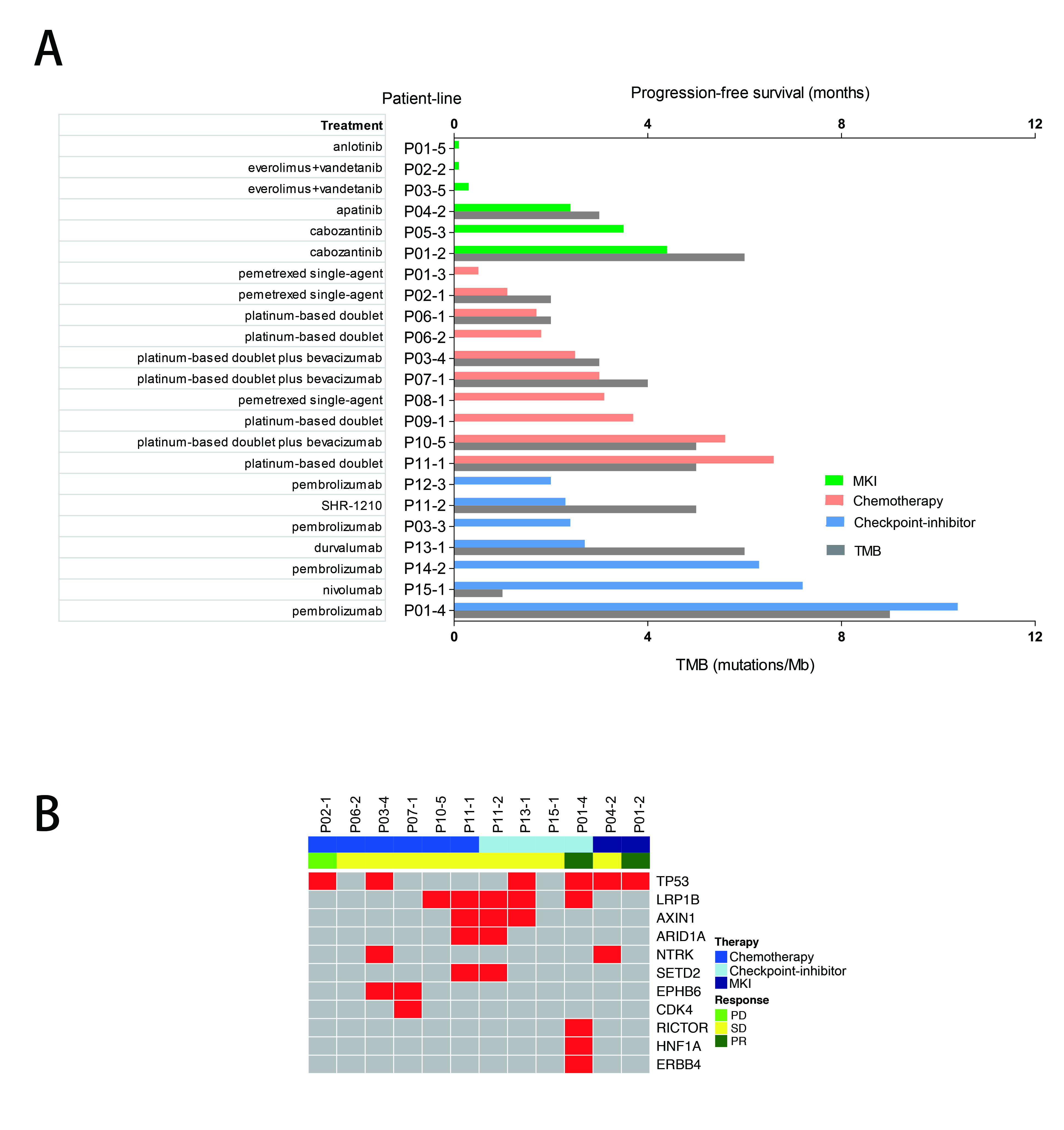
We confirmed relatively low PFS in advanced RET-rearranged NSCLC with MKIs reported in previous studies. But further investigation is warranted. Treatment with checkpoint-inhibitors seemed to encouragingly prolong PFS but a larger group of patients is needed to draw a definite conclusion.
6f8b794f3246b0c1e1780bb4d4d5dc53


